Belarus is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe with a population of around 9.4 million people. It has a predominantly flat terrain intersected by hills, flatlands, and lowlands with marshes and lakes. The country has a hemiboreal climate and is divided into six administrative regions. Minsk, the capital and largest city, is located in the central region and administered separately as a city with special status.
Belarus has a mixed economy, with important agricultural and industrial sectors. Agricultural products include potatoes, sugar beets, flax, and beef and milk. The industrial sector includes metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, motorcycles, chemical fibres, fertilisers, textiles, and refrigerators. Belarus also has a growing IT business, with several companies based in the Minsk Hi-Tech Park.
The country has a rich cultural heritage, with a strong tradition of folk and religious music, as well as literature and art. Belarusian literature dates back to the 11th-13th centuries, with notable figures including Yanka Kupala and Vasil Bykaŭ. Marc Chagall, one of the country's most distinguished artists, was born in Liozna near Vitebsk in 1887.
What You'll Learn
- Belarus's agricultural products: grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax, beef and milk
- Belarus's industrial products: metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, chemical fibres, fertiliser, textiles, radios, refrigerators
- Belarus's exports: machinery, equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, foodstuffs
- Belarus's imports: imports from Russia, China and Germany
- Belarus's economic system: market socialism, with a planned economy

Belarus's agricultural products: grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax, beef and milk
Belarus's agricultural sector is divided into two segments: livestock production and crop production. The latter accounts for around 55% of gross agricultural output and includes potatoes, flax, rapeseed, sugar beets, barley, rye, oats, and wheat. Belarus produced 5.8 million tons of potatoes in 2018, making it the 11th largest producer in the world. The country also produced 4.8 million tons of sugar beet, which is used to make sugar and ethanol.
In terms of livestock production, Belarus has about 1.5 million cows, and its main products of animal origin are pork, beef, and poultry. However, milk yields are relatively low, at less than 3,000 kg per cow per year.
Putin's Belarus Visit: What Does It Mean?
You may want to see also

Belarus's industrial products: metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, chemical fibres, fertiliser, textiles, radios, refrigerators
Belarus is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe with a population of 9.1 million people. It has a diverse industrial economy, manufacturing a range of products, including metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, chemical fibres, fertiliser, textiles, radios, and refrigerators.
Belarus's industrial products are varied and wide-ranging. Metal-cutting machine tools are a key output, used in the metalworking industry for shaping and cutting metal. The country also produces tractors, which have been a significant export since the early days of its independence. In addition, Belarus manufactures trucks and earthmovers, catering to the construction and transportation industries. Furthermore, the country produces motorcycles, catering to those seeking a more personalised mode of transport.
Belarus also has a well-established electronics industry, manufacturing televisions and radios, ensuring that its citizens stay informed and entertained. The country's chemical industry is also notable, with the production of chemical fibres and fertilisers, which are essential for the agricultural sector. Additionally, Belarus has a strong textiles industry, producing a range of fabric-based products.
Belarus's industrial capabilities extend to refrigeration, with the production of refrigerators, ensuring food preservation and storage for its citizens. Overall, the country's industrial sector plays a crucial role in its economy and provides a diverse range of products, both for domestic consumption and export to international markets.
Belarus' Western Territory: Poland's New Acquisition
You may want to see also

Belarus's exports: machinery, equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, foodstuffs
Belarus's exports are varied and include machinery and equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, and foodstuffs. The country has a predominantly flat terrain intersected by hills, flatlands, and lowlands with marshes and lakes. It is landlocked and bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus has a population of around 9.4 million people, with the urban population accounting for 78.4% of the total. Minsk, the capital and largest city, is home to nearly 2 million residents.
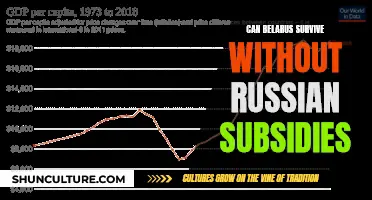
Belarus has a cool continental climate moderated by maritime influences from the Atlantic Ocean. The country has a relatively well-developed industrial base but it is now outdated and inefficient, dependent on subsidized Russian energy and preferential access to Russian markets. The economy is based on industry, agriculture, and a growing IT business, with the main industrial center in Minsk. Belarus's agricultural products include grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax, beef, and milk. The country's industries include metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, chemical fibers, fertilizer, textiles, and radios.
Belarus's exports partners include Russia, Ukraine, and the United Kingdom, while its import partners are Russia, China, and Germany. The country's economy is highly dependent on Russia, with close to half of its exports going to Russia and over half of its imports coming from there. Belarus has maintained closer political and economic ties to Russia than any other former Soviet republic.
Sanctions on Belarus: Understanding the Impact and Implications
You may want to see also

Belarus's imports: imports from Russia, China and Germany
Belarus has trade relations with more than 170 countries worldwide. In 2019, Russia was Belarus's primary trade partner, accounting for 40.3% of its total exports and 55.6% of its imports. The European Union was the second-largest trade partner, accounting for 27.1% of exports and one-fifth of imports.
In 2022, Belarus imported goods worth $12.5 billion. The top imports were cars ($1.87 billion), packaged medicaments ($422 million), light rubberized knitted fabric ($318 million), video displays ($292 million), and motor vehicles, parts, and accessories ($282 million).
Belarus's main import sources were China ($3.23 billion), Poland ($1.83 billion), Germany ($1.53 billion), Lithuania ($1.5 billion), and Turkey ($1.13 billion). From China, Belarus imported cars, video displays, and combustion engines.
Germany, as the third-largest source of imports for Belarus, exported machinery (31.2% of total exports), chemicals (15.4%), and transport equipment (12.3%) to Belarus.
Russia's Nuclear Weapon Move: Belarus in Danger?
You may want to see also

Belarus's economic system: market socialism, with a planned economy
Belarus's economic system is a form of market socialism with a planned economy. The country has retained close economic ties with Russia, its most dominant neighbour, since gaining independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. In 1999, Belarus and Russia signed the Union State Foundation Treaty, which aimed to create a politically integrated confederation with a common currency. However, the precise nature of this partnership remains unclear.
Following the break-up of the Soviet Union, Russia liberalized most prices, which forced the other former Soviet republics to follow suit to avoid an accelerated drainage of their goods supply to Russia. This move caused a generalized cash scarcity in Belarus and the other republics, as they were dependent on Russia for the issuance of the rouble currency. The Russian Gosbank initially set a ceiling on the non-cash roubles issued by the other republics, before disowning them outright. As a result, the republics were forced to establish their own central banks and issue their own currencies.
The economic disintegration within the former Soviet Union disrupted traditional trade flows between the republics and exposed state enterprises to market forces. Belarus has since maintained government control over key industries and avoided the large-scale privatizations seen in other former Soviet republics. About 39.3% of Belarusians were employed by state-controlled companies in 2015, and the government has continued several Soviet-era policies, such as state ownership of large sections of the economy.
The country has a cool continental climate, with a range of natural resources, including peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite, dolomite, marl, chalk, sand, gravel, and clay. The service sector contributes the most to Belarus's GDP, followed by the industrial and agricultural sectors. Important agricultural products include potatoes and cattle by-products, while manufacturing industries produce heavy machinery (especially tractors), agricultural products, and energy products.
Belarus' Flag: A Colorful History and Meaning
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Belarus has a predominantly industrial economy, with about 39.3% of its population employed by state-controlled companies. The country manufactures machinery and equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, and foodstuffs.
Belarus produces grain, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets, flax, beef, and milk.
Belarus manufactures metal-cutting machine tools, tractors, trucks, earthmovers, motorcycles, televisions, chemical fibres, fertilisers, textiles, radios, and refrigerators.
Belarus has forests, peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas, granite, dolomite, marl, chalk, sand, gravel, and clay.
Belarus exports machinery and equipment, mineral products, chemicals, metals, textiles, and foodstuffs.