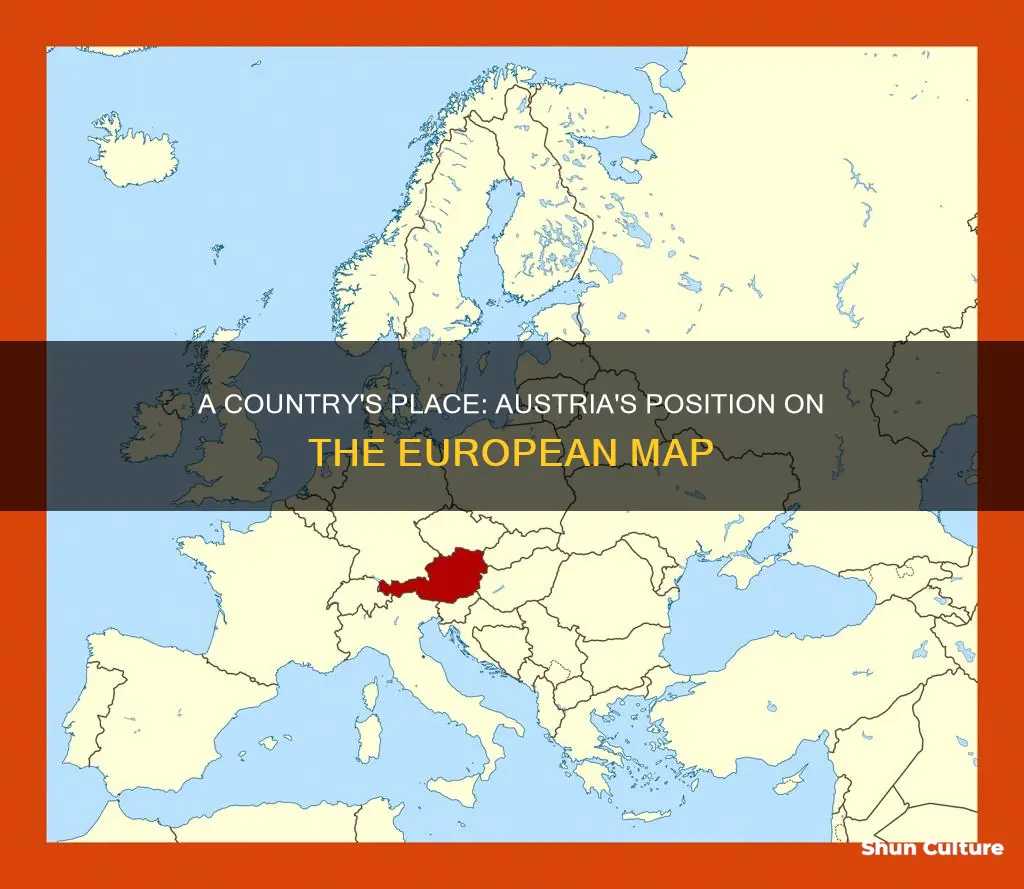
Austria, a landlocked country in Central Europe, holds a unique position on the continent's map. Its geographical location is defined by its borders with Germany to the north, the Czech Republic to the northwest, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland to the west. Austria's precise location on the map is often determined by its ranking among European countries, typically placing it in the middle to upper-middle range in terms of size and population. This introduction sets the stage for a discussion on Austria's specific number or ranking in various geographical contexts.
What You'll Learn
- Geographical Location: Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, bordered by Germany, Switzerland, and Italy
- Political Boundaries: It is a member of the European Union and shares borders with several EU countries
- Map Coordinates: Coordinates: 47.0000° N, 13.5000° E. It is located in the heart of the continent
- European Context: Austria is one of the 27 member states of the European Union, contributing to its political and economic integration
- Cultural Diversity: The country is known for its rich cultural heritage, blending German, Slavic, and Alpine influences

Geographical Location: Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, bordered by Germany, Switzerland, and Italy
Austria is a landlocked country located in the heart of Central Europe, and its geographical position is quite unique. It is one of the few countries in Europe that does not have a coastline, making it a fascinating destination for those interested in the continent's geography. Austria is nestled between some of Europe's most prominent countries, sharing borders with Germany to the north, Switzerland to the west, and Italy to the south. This strategic location has historically made it a significant crossroads for trade and cultural exchange.
The country's borders with Germany and Switzerland are defined by the Danube River, a major European waterway. The Danube flows through Austria, providing a natural boundary and a vital transportation route. In the west, the Swiss Alps form a picturesque and challenging border, while the Italian Alps, including the famous Dolomites, are found in the south, offering stunning landscapes and a diverse range of outdoor activities.
Austria's landlocked status has had a profound impact on its history and culture. Over the centuries, the country has been a coveted prize for various empires, including the Romans, Bavarians, and, most notably, the Hapsburgs, who ruled much of Central Europe. This rich historical context has contributed to Austria's cultural diversity and architectural grandeur, with many cities boasting well-preserved medieval and Baroque architecture.
In terms of its position on the map, Austria is typically associated with the number 8 on a European map, placing it in the upper-middle region of the continent. This number reflects its central location and the fact that it is one of the few countries that does not have a direct coastline, making it a unique and intriguing geographical feature.
The country's geography is characterized by a diverse range of landscapes, from the snow-capped peaks of the Alps to the rolling hills and vineyards of the Austrian countryside. The northern regions are dominated by the Danube Valley, while the south features the picturesque Lake Worthersee and the Salzkammergut region, known for its salt mines and crystal-clear lakes. Austria's geographical diversity makes it a popular tourist destination, offering something for every type of traveler.
Visa Requirements for Malaysians Traveling to Austria
You may want to see also

Political Boundaries: It is a member of the European Union and shares borders with several EU countries
Austria, officially the Republic of Austria, is a country located in Central Europe. It is a member of the European Union (EU) and shares borders with several other EU countries, making it a significant player in the European political landscape. This unique geographical position has had a profound impact on Austria's history, culture, and economy.
Politically, Austria's membership in the EU has brought numerous benefits. As an EU member, Austria has access to the single market, allowing for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people. This has facilitated trade and economic integration, making Austria an attractive destination for businesses and investors within the EU. The country's participation in EU policies and institutions also enables it to have a say in shaping European legislation and regulations, ensuring its interests are represented on a continental level.
In terms of its borders, Austria is surrounded by several EU countries, which has both advantages and challenges. To the west, it shares a border with Germany, a powerful and influential EU member. This border provides Austria with access to Germany's extensive infrastructure and market, fostering economic cooperation. However, it also means that Austria is directly connected to one of the largest and most dynamic economies in Europe, which can be both a boon and a potential challenge in terms of competition and regulation.
To the south, Austria borders Italy, another EU member with a rich cultural heritage. This border offers opportunities for cultural exchange and tourism, as Austria's scenic landscapes and historical sites are popular among Italian visitors. Additionally, Austria's proximity to Italy allows for cooperation in various sectors, including transportation and energy.
To the east, Austria shares a border with the Czech Republic and Slovakia, both EU members. These borders facilitate trade and transportation links, contributing to Austria's economic growth. The eastern borders also provide a gateway to Central and Eastern European markets, allowing Austria to expand its business reach within the EU.
In summary, Austria's political boundaries as an EU member state and its proximity to several other EU countries have significant implications. It enables Austria to benefit from the EU's single market, fostering economic growth and integration. The shared borders with Germany, Italy, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia provide opportunities for trade, cultural exchange, and regional cooperation. These political and geographical factors collectively shape Austria's role and influence within the European Union.
Hetalia: Prussia, Austria, and Their Historical Relationship
You may want to see also

Map Coordinates: Coordinates: 47.0000° N, 13.5000° E. It is located in the heart of the continent
The coordinates 47.0000° N, 13.5000° E pinpoint the location of Austria, a country nestled in the central region of Europe. This geographical positioning places Austria in the heart of the continent, surrounded by neighboring countries that share its borders. The country's latitude, 47 degrees north, indicates its northern location, while its longitude, 13.5 degrees east, places it in the eastern part of Europe.
These coordinates provide a precise reference point for locating Austria on a map. The country's position at this latitude and longitude makes it easily identifiable, as it is situated in the central core of Europe, often referred to as the 'heart' of the continent. This heartland location has historically been a significant cultural and political center, influencing the region's development and trade throughout history.
The specific numbers in the coordinates, 47 and 13.5, are essential for navigation and mapping purposes. They allow cartographers and travelers to pinpoint the exact location of Austria, ensuring accurate directions and facilitating efficient travel and trade. These coordinates are a fundamental part of the country's geographical identity, providing a unique and distinct position on the European map.
In the context of Europe, Austria's location is particularly notable. It is surrounded by countries such as Germany to the west, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, and Italy and Slovenia to the south. This central European position has contributed to Austria's rich cultural heritage, as it has been influenced by its neighboring nations throughout history.
Understanding the map coordinates of a country like Austria is crucial for various reasons. It aids in geographical education, enabling students and enthusiasts to visualize and comprehend the country's location. Additionally, these coordinates are valuable for travel planning, allowing tourists and adventurers to navigate towards their desired destinations with precision. The 47.0000° N, 13.5000° E coordinates, therefore, serve as a vital tool for both geographical knowledge and practical navigation.
Austria's Economic Growth: A Country's Success Story
You may want to see also

European Context: Austria is one of the 27 member states of the European Union, contributing to its political and economic integration
In the context of Europe, Austria holds a significant position as one of the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). This membership is a cornerstone of the country's political and economic landscape, shaping its relationships and contributions to the broader European community. As a member, Austria actively participates in the decision-making processes that influence the EU's policies and regulations, which cover a wide range of areas, including trade, agriculture, environmental protection, and social policies.
The EU's structure is designed to foster cooperation and integration among its member states, allowing Austria to benefit from collective strength and shared resources. This integration has led to the establishment of the Eurozone, a monetary union where Austria, along with 19 other member states, uses the Euro as its official currency. This economic integration has facilitated trade and financial transactions within the EU, enhancing Austria's economic stability and growth.
Politically, Austria's membership in the EU has resulted in the adoption of the EU's legal framework, which includes the Treaty on European Union and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. These treaties provide a foundation for the EU's democratic principles, fundamental rights, and the rule of law, ensuring that Austria, like all member states, upholds these standards. The EU's political institutions, such as the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, provide avenues for Austria to have its voice heard and contribute to the EU's legislative process.
Furthermore, Austria's participation in the EU has facilitated its integration into the European single market, enabling the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people. This integration has opened up new opportunities for Austrian businesses to expand across Europe and for citizens to live, work, and study in other EU countries. The EU's policies and programs also support cultural exchange, education, and research, fostering a sense of European identity and cooperation.
In summary, Austria's position as a member of the European Union is integral to its role in the European context. It actively contributes to the political and economic integration of the EU, benefiting from the collective strength and shared resources of the union. This membership allows Austria to shape European policies, participate in decision-making, and enjoy the advantages of the European single market, ultimately enhancing its global standing and influence.
Central Europe: Russian, Prussian, and Austrian Influence
You may want to see also

Cultural Diversity: The country is known for its rich cultural heritage, blending German, Slavic, and Alpine influences
Austria, a country nestled in the heart of Europe, boasts a unique cultural tapestry that reflects its diverse history and geographical location. Its cultural identity is a fascinating blend of three primary influences: German, Slavic, and Alpine. This cultural diversity is a result of Austria's strategic position, which has been a crossroads of various civilizations throughout history.
The German influence is prominent in Austria's language and legal system. The majority of the population speaks German, and the country's legal framework is heavily based on the German model. This influence is particularly evident in the country's administrative structure and the widespread use of the German language in official contexts. Vienna, the capital, showcases this German heritage through its elegant architecture and sophisticated cultural institutions.
In contrast, the Slavic influence is more pronounced in the country's eastern regions, particularly in the former Yugoslavian territories that were once part of Austria-Hungary. The Slavic minority in Austria, including those of Croatian, Slovenian, and Serbian descent, has contributed to the country's cultural mosaic. Their traditions, cuisine, and language have left an indelible mark on Austrian culture, especially in the regions of Styria and Carinthia.
The Alpine culture is an integral part of Austria's identity, shaped by its mountainous terrain. The Alps have played a significant role in shaping the country's economy, lifestyle, and even its cuisine. The Alpine region is known for its picturesque villages, vibrant festivals, and a strong tradition of outdoor activities. The unique architecture, with its wooden houses and distinctive roofing styles, is a testament to the region's cultural heritage.
This cultural diversity is celebrated through various festivals and events throughout the year. The country's calendar is filled with traditional festivals like the Vienna Festival, a celebration of music and arts, and the Salzburg Festival, renowned for its opera and classical music performances. Additionally, the Alpine regions host numerous winter sports festivals and summer hiking festivals, attracting visitors from around the world.
Austria's cultural heritage is a testament to its ability to embrace and integrate diverse influences. This unique blend of German, Slavic, and Alpine cultures has contributed to the country's vibrant and dynamic society, making it a fascinating destination for cultural exploration in Europe.
Exploring Switzerland and Austria: Similarities and Differences
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Austria is a landlocked country located in Central Europe. It is bordered by Germany to the west, the Czech Republic to the northwest, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland to the west.
The geographical center of Austria is approximately at 47.8167° N, 14.0000° E. This point is often considered the central location within the country.
Austria shares borders with six countries. In the west, it borders Germany; in the north, the Czech Republic; in the east, Slovakia and Hungary; and in the south, Italy and Switzerland.
Vienna, the capital city of Austria, is a prominent cultural and political center in Central Europe. It is often used as a reference point for understanding Austria's geographical position within the continent.







