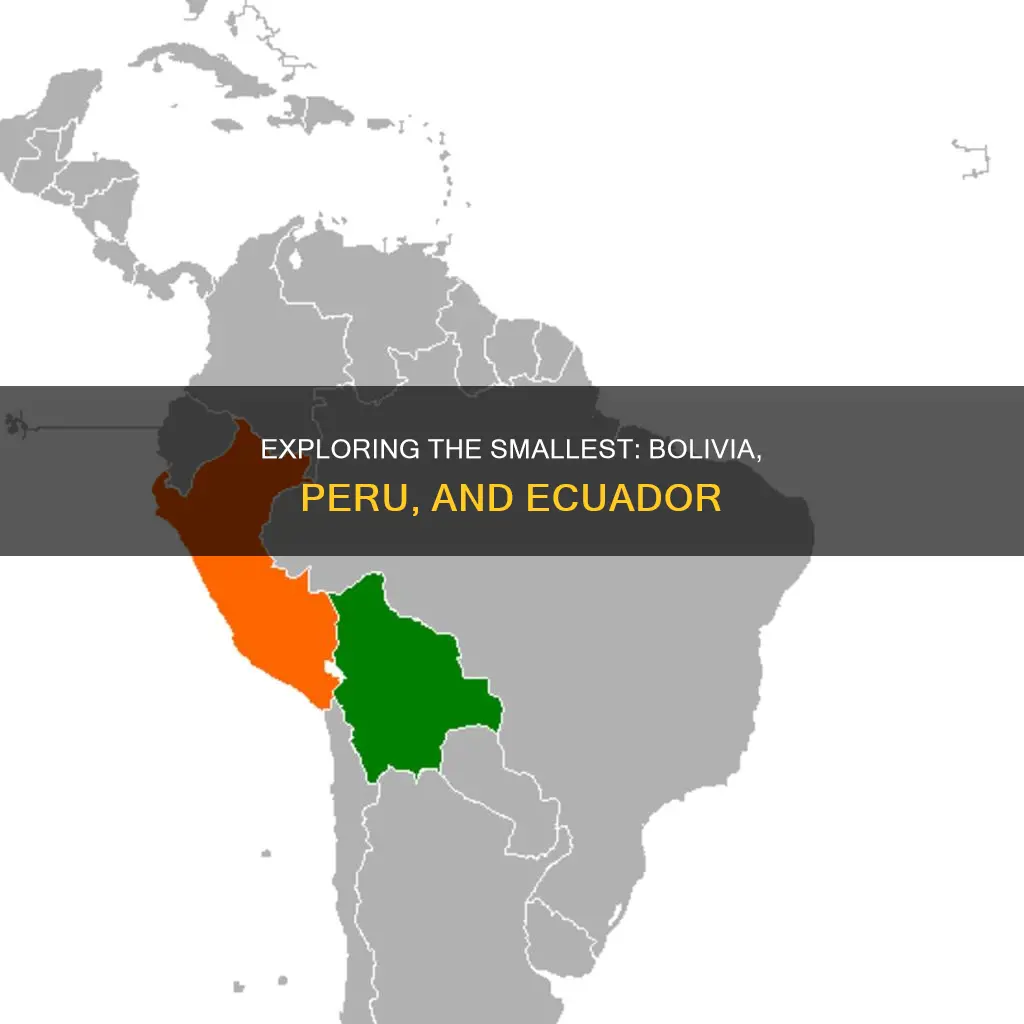
Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador are three countries in South America that share a border and a history of Incan rule. All three countries are part of the Andean region, a geopolitical area that encompasses the states through which the Andes mountain range runs. Bolivia is the largest of the three countries, with an area of 1,098,581 square kilometres (424,164 sq mi), making it the fifth-largest country in South America. Peru is the second-largest, with an area of 1,285,216 square kilometres (496,225 sq mi). Ecuador is the smallest of the three countries, with an area of 256,370 square kilometres (98,985 sq mi).
| Characteristics | Bolivia | Peru | Ecuador |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | 1,098,581 km2 | 1,285,216 km2 | 283,571 km2 |
| Population | 12 million | 33.396 million | 17.797 million |
| Capital | Sucre | Lima | Quito |
| Largest City | Santa Cruz de la Sierra | Lima | Guayaquil |
| Government Type | Presidential Representative Republic | Presidential Republic | Presidential Republic |
| GDP per Capita | $3,552 | $6,977 | $6,183 |
| Official Language(s) | Spanish, several dozen indigenous languages | Spanish, Aymara, Quechua | Spanish, 13 native languages |
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | Roman Catholicism | Roman Catholicism |
| Global Freedom Score | 66 | 71 | 67 |
What You'll Learn
- Bolivia is landlocked, while Peru and Ecuador are not
- Bolivia is the fifth-largest country in South America
- Peru has the highest mountain in the northern and central Andes
- Bolivia has the largest geographic extension of Amazonian plains and lowlands
- Ecuador is home to the most prominent peak in the northern and central Andes

Bolivia is landlocked, while Peru and Ecuador are not
Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador are three South American countries that share cultural characteristics initially spread by the Incan Empire in pre-colonial times. The three countries are also part of the Andean region, a geopolitical area that encompasses the states through which the Andes mountain range runs.
Bolivia is the only landlocked country among the three. Bolivia lost its coastline to Chile during the War of the Pacific in 1879 and became landlocked. Chile annexed the coastal territory, and this was ratified by the Treaty of Ancón in 1883 and the Treaty of Peace and Friendship in 1904. Bolivia still claims a corridor to the Pacific Ocean.
Being landlocked has negatively impacted Bolivia's economic growth. The country has higher transport costs compared to those of Peru and Ecuador due to the higher cost of land transport. Bolivia's GDP is less than 15% the size of Chile's, and the country has faced challenges in developing its economy due to its landlocked status.
On the other hand, Peru and Ecuador have coastlines and are not landlocked. Peru has a coastline on the Pacific Coast region, and Ecuador has a coastline on the Ecuadorian coastal region. Both countries have access to ports, which facilitates trade and contributes to their economic growth.
In summary, while Bolivia is landlocked, Peru and Ecuador enjoy the benefits of having coastlines and access to ports, which has positively impacted their economic development. Bolivia's landlocked status has hindered its economic growth and development, and the country continues to aspire for sovereign access to the sea.
Exploring Bolivia's Salt Flats: Travel Guide
You may want to see also

Bolivia is the fifth-largest country in South America
Bolivia's elevation varies significantly, from the western snow-capped peaks of the Andes to the eastern lowlands of the Amazon Basin. One-third of the country lies within the Andean mountain range, with peaks such as Nevado Sajama and Illimani rising above 6,000 metres. The country also boasts the world's largest geographic extension of Amazonian lowlands, as well as tropical valleys, high plateau areas, and Chaco regions. Bolivia's climate varies drastically across these diverse ecoregions, from tropical climates in the Llanos to polar climates in the Andean highlands.
Bolivia's biodiversity is considered one of the greatest in the world, with a wide array of organisms and ecosystems. The country is home to numerous ecoregions, ecological sub-units, and over 199 ecosystems. It has a high level of biodiversity, with four types of biomes and 32 ecological regions. Bolivia's variable altitudes, ranging from 90 to 6,542 metres above sea level, contribute to its vast biological diversity. The country has over 17,000 species of seed plants, including ferns, marchantiophyta, moss, and fungi, as well as more than 3,000 species of medicinal plants.
Bolivia's population is estimated at 12 million and is multiethnic, including Amerindians, Mestizos, Europeans, Asians, Africans, Arabs, and Jews. Spanish is the official and predominant language, although 36 indigenous languages also have official status, with Guaraní, Aymara, and Quechua being the most commonly spoken. The country's seat of government is La Paz, while Sucre is the constitutional capital. Bolivia is named after Simón Bolívar, the Venezuelan leader in the Spanish American wars of independence, and its people are known as Bolivians.
The Joyous Alasitas Festival: A Unique Bolivian Tradition
You may want to see also

Peru has the highest mountain in the northern and central Andes
Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador are three South American countries located in the Andean region. The Andean region is a geopolitical area that includes the states through which the Andes mountain range runs. The Andes are the world's longest mountain range, stretching some 7,000 km from the northern edge of South America to the continent's southern tip.
Of these three countries, Ecuador is the smallest in terms of area. Now, focusing on Peru, this country is located in the Central group of the Andes, which also includes Bolivia, and is situated between the Northern group (Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador) and the Southern group (Argentina and Chile).
The Andes in Peru offer a combination of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and opportunities for physical challenges. The mountains in Peru have attracted visitors from all over the world, eager to explore the numerous wonders the Peruvian Andes present. The Peruvian Andes are characterized by their ubiquity and complexity, with dozens of smaller named ranges contributing to the vastness of this mountain system.
The Inca Empire, which once ruled over a large part of the Andes region, including Peru, has left a significant mark on the country's mountain ranges. Machu Picchu, one of the New Seven Wonders of the World, stands as a testament to the Inca's architectural prowess. The dry-fit stone architecture at Machu Picchu features blocks with up to 12 angles and weighing up to 50 tons each. The Inca Trail, the Lares Trek, and the Salkantay Trek offer adventurous routes to reach this ancient citadel, providing trekkers with incredible scenery and a sense of connection to the Inca's past.
In addition to Machu Picchu, there are several other notable mountain ranges and peaks in Peru. The Huaguruncho, Raura, Huanzo, and Vilcabamba ranges contribute to the complexity of the Peruvian Andes. The Salkantay Peak, at 6,271 meters, is the highest in the Vilcabamba Range and offers awe-inspiring views for those who dare to venture there. The Cordillera Huayhuash, Cordillera Occidental, and Cordillera Vilcanota are other notable ranges in Peru, each presenting its own unique challenges and attractions.
Peru is also home to a diverse range of wildlife, with some species found exclusively in the Andean region. The puma, the big cat found throughout North and South America, roams the high altitudes of the Peruvian Andes. The Andean bear, also known as the spectacled bear, can be spotted hunting at the edges of alpine forests. Other mammals, such as vizcachas and Andean deer, also inhabit these highlands.
The Andean condor, the world's largest flying bird, is a subject of much Andean mythology. With a massive ten-foot wingspan, this scavenger bird is considered by the Incas to be related to the sun deity as a ruler of the upper world. Peru is also home to four distant relatives of the camel: vicuñas, guanacos, alpacas, and llamas, with the latter two being domesticated.
In conclusion, Peru, nestled in the Central group of the Andes, boasts the highest mountain in the northern and central regions of this majestic mountain system. Huascarán Sur, towering at 6,768 meters, is a testament to the grandeur and allure of the Peruvian Andes. The country's mountain ranges offer a plethora of natural and cultural experiences, from the ancient Inca sites to the diverse wildlife that calls these mountains home.
Bolivia's Revolutionary History: A Count of Uprisings
You may want to see also

Bolivia has the largest geographic extension of Amazonian plains and lowlands
Bolivia is a landlocked country in the west-central area of South America. It is bordered by Brazil to the north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the south, Chile to the southwest, and Peru to the northwest. Bolivia has the largest geographic extension of Amazonian plains and lowlands, mountains, and Chaco with a tropical climate. It is also part of the Andes of South America and its high plateau areas with cold climates, hills, and snow-capped mountains.
The geography of Bolivia is characterised by the imposing Andes Mountains, which bisect the country from north to south. This gives rise to three distinct geographic zones: the Andean region in the west, the Sub-Andean region in the centre, and the Llanos (plains) region in the northeast. Bolivia's western and southern borders with Chile, Argentina, and Peru are dominated by the Andean mountain range, while its borders with Brazil and Paraguay lie in the lowlands of the Amazon Basin.
The Andean region spans 28% of Bolivia's territory and includes the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Oriental mountain ranges. The Cordillera Occidental is a chain of dormant volcanoes and volcanic vents, with the country's highest peak, Nevado Sajama, located in this range. The Altiplano, a highland plateau between the two cordilleras, makes up the rest of the Andean region. The Altiplano includes Lake Titicaca, the highest commercially navigable lake in the world, which is shared with Peru.
The Sub-Andean region, constituting 13% of Bolivia's territory, is an intermediate area between the Altiplano and the eastern lowlands. This region is characterised by farming activities and a temperate climate.
The Llanos region, covering 59% of Bolivia's territory, is located north of the Cordillera Central and extends from the Andean foothills to the Paraguay River. This region is mostly flat, with extensive rainforests and enormous biodiversity.
Bolivia's geographic diversity is further reflected in its four types of biomes, 32 ecological regions, and 199 ecosystems. The country boasts a rich biodiversity, recognised as the 18th most biodiverse country globally by the Global Biodiversity Index. Bolivia is committed to sustainability and conservation, with robust legal frameworks and collaborations in place to protect its natural heritage.
Bolivia's Landlocked Geography: A Unique Challenge
You may want to see also

Ecuador is home to the most prominent peak in the northern and central Andes
Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia are three South American countries that are part of the Andean region. This region is characterised by the cultural influence of the Incan Empire, which spread across the area before the arrival of the Spanish in the 15th century.
Ecuador is the smallest of the three countries by land area, and it is also one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries. It is home to the most prominent peak in the northern and central Andes, Chimborazo, which rises to 6,268m (20,564 ft) above sea level. The summit of Chimborazo is the furthest point on the planet's surface from the Earth's centre due to the equatorial bulge.
Ecuador's Andes form a barrier between the coastal region to the west and the Amazon rainforest to the east. The country's capital, Quito, is located in the heart of the "Sierra" region, which includes the Andes. There are several national parks and reserves in this region, such as Cotopaxi National Park, El Cajas National Park, and Sangay National Park.
The Andes in Ecuador are also home to a number of protective forests that showcase the country's exceptional biodiversity. These forests include the Jatumpamba-Jorupe Protective Forest and the Rio Arenillas Presa Tahuin Protective Forest.
Ecuador's diverse landscapes, which include coastal regions, high mountains, and tropical rainforests, along with its location along the Equator, contribute to its rich biodiversity. The country is home to a wide array of animal species, including tapirs, mountain lions, ocelots, jaguars, and culpeo.
The Andes Mountains, which extend through Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina, are the longest continental mountain range in the world, stretching approximately 8,900 km (5,530 mi). The range is characterised by jagged peaks, stunning glaciers, and beautiful landscapes.
Bolivia's Most Celebrated Holiday: Traditions and Importance
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Bolivia is the smallest in area, with 1,098,581 square kilometers (424,164 sq mi).
The seat of government in Bolivia is La Paz, while Sucre is the constitutional capital.
Bolivia's population is estimated to be 12 million.
Spanish is the official and predominant language in Bolivia, although 36 indigenous languages also have official status.
The currency of Bolivia is the Bolivian boliviano (BOB).