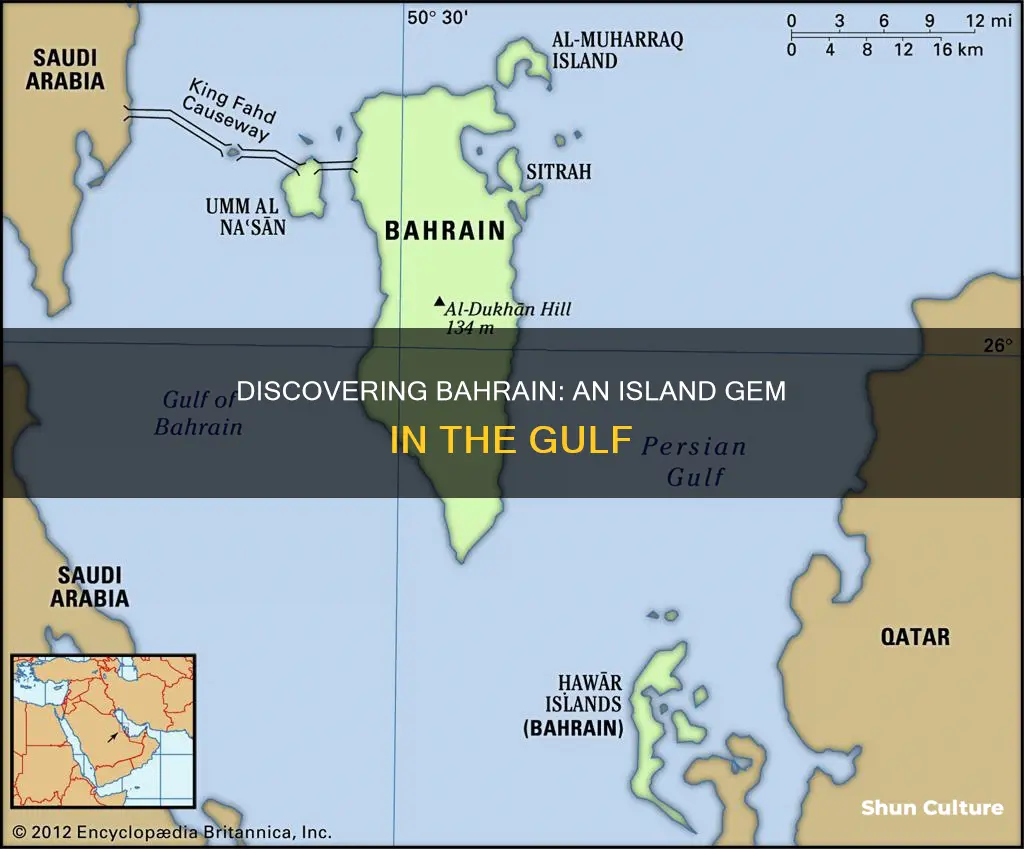
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated on the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands, with a total land area of about 770 square kilometres. The country is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway, a 15-mile-long highway crossing the gulf. Bahrain is known for its date palm groves and is believed to be the site of the ancient kingdom of Dilmun, a prominent trade centre. The country's name, 'Bahrain', means 'two seas' in Arabic.
What You'll Learn

Bahrain is an archipelago of islands in the Persian Gulf
The name Bahrain is derived from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'. The country's total land area is slightly larger than that of Singapore, spanning some 760 square kilometres (290 sq mi). Bahrain is home to a diverse population of around 1.5 million people, including both native Bahrainis and expatriates. The country has a rich history, having been inhabited by various groups throughout its existence. It is well-known for its verdant groves of date palms and has been an important trade centre in the region for centuries.
Bahrain has a constitutional hereditary monarchy that gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1971. The country has a complex system of courts, based on diverse legal sources, including Sunni and Shia Sharia (religious law), tribal law, and other civil codes. While Islam is the predominant religion, Bahrain is known for its religious tolerance, with small communities of Christians, Jews, and Hindus also present in the country.
In terms of geography, Bahrain consists of two separate groups of islands. The main island, Bahrain Island, is varied in appearance, with a rocky and barren central region and fertile lowlands in the south and west. The northern and northwestern coasts feature a narrow belt of date palms and vegetable gardens irrigated by abundant freshwater springs and wells. The highest point in the country is Jabal ad Dukhan, which reaches 134 metres (440 feet) above sea level.
Bahrain's climate is characterised by hot and humid summers, with temperatures frequently exceeding 32 degrees Celsius (90 degrees Fahrenheit). Winters are cooler and more pleasant, with temperatures dipping to around 21 degrees Celsius (70 degrees Fahrenheit). Rainfall is confined to the winter months and averages around 75 millimetres (3 inches) per year.
Bahrain's Human Rights Activists: Voices of Change and Courage
You may want to see also

The country is ruled by a constitutional monarchy
The Kingdom of Bahrain is a constitutional monarchy, ruled by the Al Khalifa family of the Sunni Bani Utbah tribe. The current ruler is Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa, who has been Emir of Bahrain since 1999 and King since 2002.
The country's political system is complex, with powers divided among the King, the Prime Minister, the Council of Ministers, a bicameral National Assembly, and a Constitutional Court.
The King holds broad powers and is the Head of State. His duties include upholding the Constitution and the sovereignty of Bahrain, awarding honours and decorations, granting pardons, and appointing and dismissing the Prime Minister, Ministers, judges, civil and military officials, ambassadors, and the Consultative Council. He is also the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces and has significant legislative powers, including the ability to ratify constitutional amendments, propose legislation, and veto laws.
The Prime Minister is appointed by the King and heads the Council of Ministers, which is responsible for supervising the activities of government agencies and implementing national policy. The current Prime Minister is Crown Prince Salman bin Hamad Al Khalifa, who also serves as Deputy Commander of the Bahrain Defence Force.
The National Assembly is bicameral, consisting of the Consultative Council (Shura Council) and the Council of Representatives. The Shura Council has 40 members, all of whom are appointed by the King and serve four-year terms. The Council of Representatives also has 40 members, who are elected by universal suffrage for four-year terms.
Bahrain's transition to a constitutional monarchy began in 1999 when Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa became Emir. He instituted a series of democratic reforms, including the establishment of a committee to transform Bahrain into a constitutional monarchy. This resulted in the National Action Charter, which was overwhelmingly approved by public referendum in February 2001. The following year, Bahrain officially became a constitutional monarchy, with Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa as King.
Visa Options: Bahrain Embassy or Consular Services?
You may want to see also

Bahrain is a former British protectorate
Bahrain is a small Arab state situated in a bay on the southwestern coast of the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and about 30 smaller islands. Bahrain was a British protectorate from the early 1800s until it gained independence in 1971.
In the 1830s, the Al Khalifa, a native Arab dynasty that has ruled Bahrain since the late 18th century, signed the first of many treaties establishing Bahrain as a British Protectorate. Similar to the binding treaties of protection entered into by other Persian Gulf principalities, the agreements prohibited the Al Khalifa from disposing of territory and entering into relationships with any foreign government without British consent in exchange for British protection against the threat of military attack from Ottoman Turkey.
In 1861, Britain signed a Perpetual Truce of Peace and Friendship with Bahrain, which prohibited the ruler of Bahrain from engaging in "prosecution of war, piracy and slavery at sea" and Britain was to provide protection. The treaty also recognised the Khalifa ruler as an "independent ruler".
In 1880 and 1892, Britain signed two further treaties with Al Khalifa, which put the defence and foreign relations of Bahrain under British control and turned Bahrain into a British colonial protectorate. The ruler was also to accept British "advice" regarding internal matters.
In 1903, Lord Curzon, the Viceroy of India, visited Bahrain and highlighted the need to reform the chaotic customs system by appointing a British director. Shaikh Isa, the ruler of Bahrain, resisted what he considered an interference in his financial independence. In 1904, the post of British Assistant was elevated to British Political Agent.
In 1905, Major Percy Cox, the Acting Political Resident in the Persian Gulf, issued an ultimatum to Shaikh Isa, demanding he punish those behind an attack on a German trading firm and compensate the victims. After Shaikh Isa refused, Cox returned with a great show of force and fired a few blank shots on the major port city of Manama. Shaikh Isa eventually agreed to the demands and Cox arrested and deported the aggressors.
In 1913, the Bahrain Order in Council was published in The London Gazette, providing legal cover for British jurisdiction over foreigners and limiting the powers of the ruler. It also gave the Political Agent far-reaching jurisdiction, including over religious law courts.
In 1935, the British moved their main base in the Persian Gulf region to Bahrain shortly after the start of large-scale oil production.
In 1970, Iran laid claim to Bahrain and the other Persian Gulf islands. However, the British Government persuaded Iran to drop its claim to the island of Bahrain. In 1971, Bahrain declared itself fully independent and the British withdrew.
Propane Energy in Bahrain: Exploring the Kingdom's Fuel Sources
You may want to see also

It is a small country with a large population
Bahrain is a small country with a large population. With a land area of 760 square kilometres (290 square miles), it is the third-smallest nation in Asia, after the Maldives and Singapore. However, its population is estimated to be over 1.5 million as of 2023, with a population density of 2,115 people per square kilometre. In fact, Bahrain is one of the most densely populated countries in the world.
Bahrain is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and about 30 smaller islands. The main island accounts for around 83% of the country's landmass, with the remaining islands, including Al-Muharraq, Sitrah, Nabī Ṣāliḥ, Al-Muḥammadiyyah, Umm al-Naʿsān, and the Ḥawār Islands, making up the rest. The country's capital, Manama, is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island and is home to about 148,000 people.
Bahrain's population is ethnically and religiously diverse. About half of the population is Arab, with the indigenous population comprising Baharna (Shia Arabs), Ajam (Persian Shias), Sunni Arabs, and Huwala (descendants of Sunni Iranians). There are also small communities of African Bahrainis, mainly from East Africa, as well as expatriates from countries like India, Iran, Pakistan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
The official language of Bahrain is Arabic, but English is widely spoken and used in education and business. Other languages spoken include Persian, Urdu, Hindi, and Tagalog, reflecting the diverse origins of the population.
Despite its small size, Bahrain has a significant economic impact in the region. It has a high-income economy, recognised by the World Bank, with a focus on banking, tourism, and petroleum production and processing. Bahrain's strategic location in the Persian Gulf has also made it an important hub for international trade and naval activity.
Snapchat's Ban in Bahrain: Why and What Now?
You may want to see also

Bahrain has a rich history, including the ancient Dilmun civilization
Bahrain is a small Arab state situated in a bay on the southwestern coast of the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and some 30 smaller islands. Its name is derived from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'.
Bahrain has a rich history, including the ancient Dilmun civilisation. Dilmun was an important Bronze Age trading centre, which is referenced in the Epic of Gilgamesh. It is believed to have been a hub on a major trade route between Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley as early as 5,000 years ago.
Dilmun is sometimes referred to as the 'Land of the Living' and has been proposed as the location of the Garden of Eden. The civilisation is said to have declined around 2,000 BC as trade from India was cut off. From 750 BC onwards, Assyrian kings repeatedly claimed sovereignty over the islands. Dilmun was formally incorporated into the Babylonian Empire in the 6th century BC.
The name Dilmun fell from use after the collapse of Neo-Babylon in 538 BC. However, Bahrain is still renowned for its verdant groves of date palms and, since ancient times, has been an entrepôt for trade and a source of natural resources for the surrounding area.
Bahrain's Strictness: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Bahrain is an archipelago, or a series of islands. The main island, Al Bahrayn, makes up about 78% to 83% of the country's landmass.
Bahrain is situated in the Persian Gulf, close to Saudi Arabia and Qatar. It is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway.
The capital of Bahrain is Manama, which is also the country's largest city.







