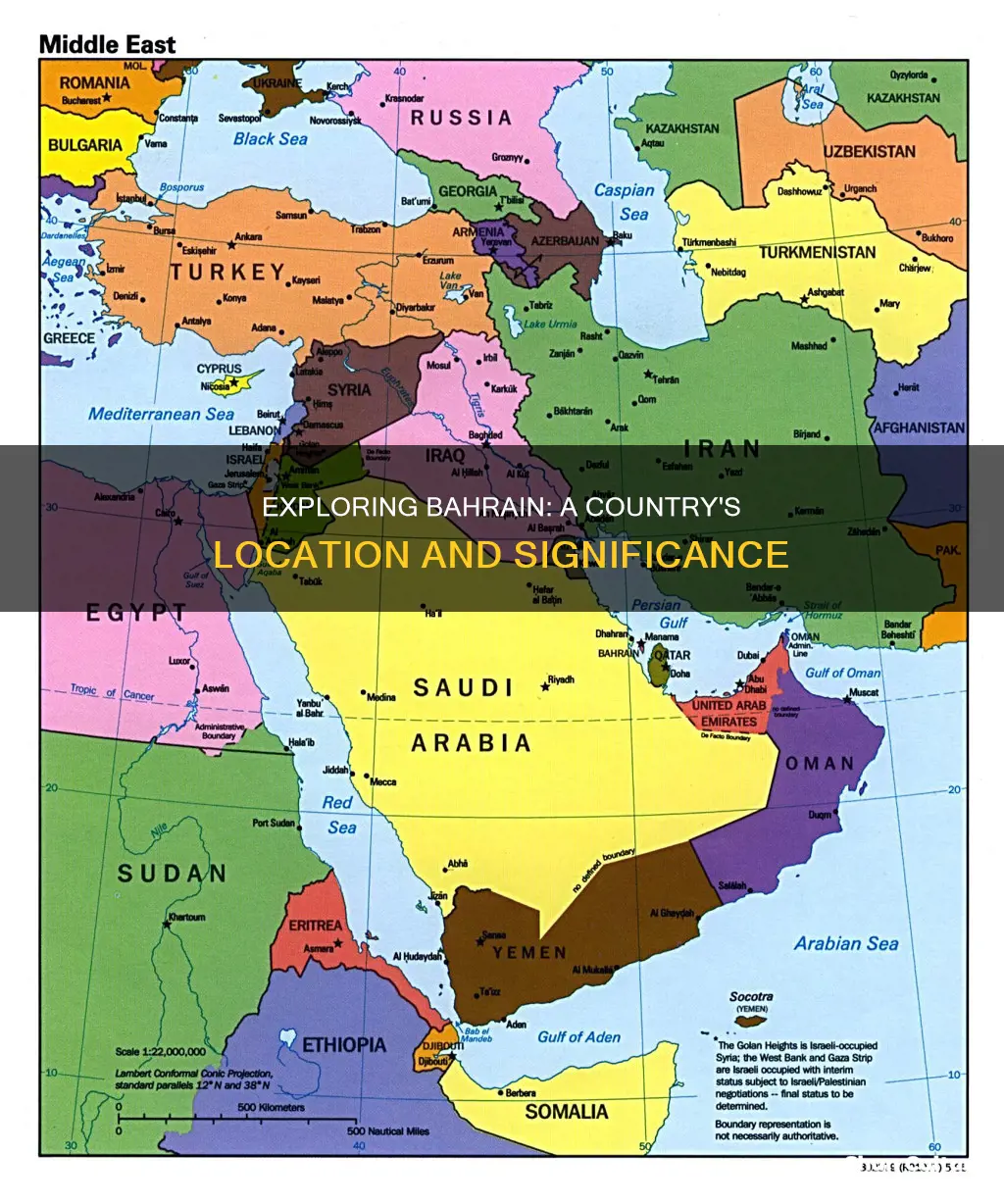
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is a small island country in the Middle East, situated on the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of around 30 islands, including the largest, Bahrain Island, which makes up around 83% of the country's landmass. The country is located between Qatar and the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia, to which it is connected by the King Fahd Causeway. Bahrain's capital and largest city is Manama.
The name Bahrain is derived from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'. The country is renowned for its date palms and is believed to be the site of the ancient kingdom of Dilmun, a commercial centre that traded with ancient Sumer.
What You'll Learn
- Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated on the Persian Gulf
- The country is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands
- Bahrain is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway
- The country's capital, Manama, is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island
- Bahrain has a constitutional monarchy with a parliament comprising two bodies

Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated on the Persian Gulf
Bahrain is renowned for its verdant groves of date palms. It is believed to be the site of the ancient kingdom of Dilmun, a commercial centre that traded with ancient Sumer. Bahrain has been settled and colonized by various groups, including the Khalīfah family (Āl Khalīfah), a native Arab dynasty that has ruled Bahrain since the late 18th century.
Bahrain is located in one of the world's chief oil-producing regions, but it has only small stores of petroleum. Instead, its economy has long relied on processing crude oil from neighbouring countries. More recently, the financial, commercial services, and communications sectors have grown markedly, as has tourism.
The country's chief city, port, and capital, Manama (Al-Manāmah), is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island. It is a strikingly modern city, relaxed and cosmopolitan, and a favourite destination for visitors from neighbouring Saudi Arabia. The people of Bahrain remain conservative in their lifeways. This sentiment is enshrined in the country's constitution, which affirms that "the family is the cornerstone of society, the strength of which lies in religion, ethics, and patriotism".
Exploring Bahrain: Understanding Its Land Area and Geography
You may want to see also

The country is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands
The Kingdom of Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated on the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands. The name Bahrain is derived from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'.
Bahrain is a small country, with a total land area of 780 square kilometres, making it the third-smallest nation in Asia. The country is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the west and Qatar to the east, with the King Fahd Causeway connecting it to Saudi Arabia. Bahrain's terrain is characterised by a low desert plain, with its highest point being the Mountain of Smoke, which rises to 134 metres above sea level.
The country's largest island, Bahrain Island, makes up around 83% of its landmass and is surrounded by smaller islands. Two of these, Al-Muharraq and Sitrah, are joined to Bahrain Island by causeways. Other islands in this group include Nabī Ṣāliḥ, Al-Muḥammadiyyah, Umm al-Naʿsān, and Jiddah. The second group of islands consists of the Ḥawār Islands, located near the coast of Qatar. These islands are small and rocky, inhabited primarily by fishermen and quarry workers, but are believed to hold petroleum and natural gas reserves.
Bahrain's total population is estimated to be around 1.6 million, with the capital and largest city, Manama, having a population of about 148,000. The country has a diverse population, with Arabs constituting about half of the inhabitants, while the remaining comprise foreign-born individuals from countries such as Iran, India, and Pakistan. The official language of Bahrain is Arabic, although English is widely spoken, and other languages like Persian, Urdu, and Hindi are also common among expatriates.
Bahrain's economy has traditionally relied on processing crude oil from neighbouring countries, but it has recently diversified into sectors like financial services, tourism, and communications. The country has a rich history, having been an important trade centre in ancient times, and it continues to be a significant regional hub, benefiting from its strategic location.
Bahrain Time: Understanding the Current Time in Bahrain
You may want to see also

Bahrain is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia situated on the Persian Gulf. It is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway, a 25-kilometer-long series of bridges and causeways. The causeway, which spans long stretches of sea and reclaimed land, connects Khobar in Saudi Arabia to Al Jasra in Bahrain.
The idea of building a bridge linking Bahrain and Saudi Arabia had been of great interest to both kingdoms for generations. The project to build the bridge was first discussed during an official visit to Bahrain by King Saud in 1954. However, it wasn't until the 1960s that plans to construct the causeway began to take shape officially. In 1968, a joint committee was formed to assess the finances required for the project, and the World Bank was brought in to provide assistance.
Construction of the King Fahd Causeway began in 1981 and was completed in 1986. The project cost a total of US$800 million and was financed by Saudi Arabia. The causeway features five bridges resting on 536 concrete pylons, with seven embankments in the Gulf's shallower water. One of these embankments, known as Middle Island, has been converted into an artificial island with customs and immigration facilities, a mosque, gardens, and fast-food restaurants. Another island towards the end of the causeway, known as Mother of Sleepiness, belongs to Bahrain.
The King Fahd Causeway is a significant transportation link between Bahrain and Saudi Arabia, with an estimated 25,104 vehicles using it daily as of 2010. It has also become a popular tourist attraction, offering vast views of the surrounding waters and providing amenities for travelers, such as restaurants and picnic areas.
Bahrain's Political Future: Elections or Status Quo?
You may want to see also

The country's capital, Manama, is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island
The country of Bahrain is an island nation in West Asia, situated in a bay on the southwestern coast of the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands. The name Bahrain is derived from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'.
Manama has played a significant role in Bahrain's economic development, initially as a centre for pearling, fishing, boatbuilding, and trade. The discovery of petroleum in the early 20th century transformed the city, leading to the construction of modern buildings and infrastructure. Today, Manama is known for its financial and commercial sectors, with many banks and businesses operating in the city. It is also a popular tourist destination, offering a blend of modern and traditional attractions.
In addition to its economic significance, Manama has a long history as a cultural and political centre. It is home to various historical sites, including the Grand Mosque and the old Qaṣr es-Sheikh. The city has also been a focal point for protests and political movements, such as the Arab Spring uprising in 2011.
Overall, Manama's location on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island has been instrumental in its development as a vibrant, modern city and has contributed to its status as the country's political, economic, and cultural centre.
Explore Bahrain: A Country of Rich History and Culture
You may want to see also

Bahrain has a constitutional monarchy with a parliament comprising two bodies
Bahrain is a small Arab state situated in a bay on the southwestern coast of the Persian Gulf. It is a constitutional monarchy with a parliament comprising two bodies: the Shura Council and the Council of Representatives.
The Shura Council, or Consultative Council, is made up of 40 members appointed by the King. It serves as an advisory body and can draft legislation in certain cases. The Council of Representatives, on the other hand, is an elected body, with 40 members elected by universal suffrage.
The King of Bahrain, who is the head of state, has broad powers under the Constitution. He has the power to appoint and dismiss the Prime Minister, Ministers, judges, civil and military officials, and members of the Shura Council. He also serves as the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces. The Prime Minister, who is the head of government, is appointed by the King and chairs the Council of Ministers.
The Bahraini parliament, known as the National Assembly, is a bicameral legislature. This means that it consists of two chambers: the Shura Council and the Council of Representatives. For a bill to become a law, it must be approved by both chambers and then ratified by the King.
The first parliamentary elections in Bahrain were held in 1973, but the parliament was dissolved two years later by the Amir after it attempted to end Al-Khalifa rule. Bahrain became a constitutional monarchy in 2002, and the current King, Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa, has introduced various democratic reforms. However, the country has faced criticism for human rights violations and the suppression of dissent.
The Dark Mystery of Bahrain's Ancient Curse
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, to the east of Saudi Arabia and north of Qatar.
The capital of Bahrain is Manama.
As of May 14, 2023, the population of Bahrain was 1,501,635, of whom 712,362 were Bahraini nationals.







