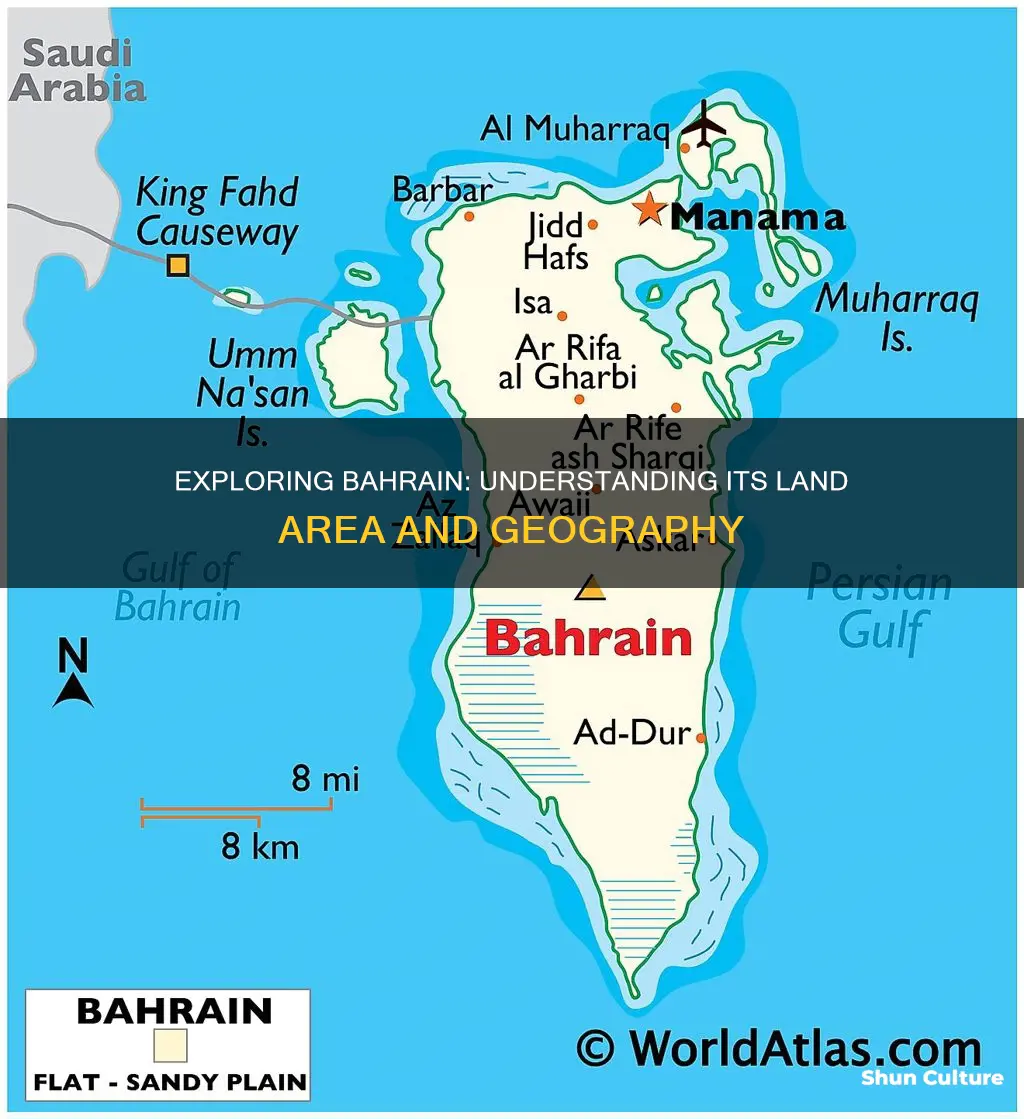
Bahrain is a small Arab state situated in a bay on the southwestern coast of the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and about 30 smaller islands. The country's total area is about 780 square kilometres, making it slightly larger than Singapore. It is the third-smallest nation in Asia after the Maldives and Singapore. The capital and largest city is Manama. Bahrain's population is about 1.5 million people, including more than 800,000 non-nationals.
What You'll Learn

Bahrain's land area
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated in the Persian Gulf. It is a small country, spanning some 760 square kilometres (290 sq mi) and is the third-smallest nation in Asia. The country consists of Bahrain Island and 33 of the 37 Bahrain Islands, with the Bahrain Island making up around 83% of the country's landmass. The capital city, Manama, is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island. The islands are about 24 kilometres (15 mi) off the east coast of Saudi Arabia and 28 kilometres (17 mi) from Qatar.
Bahrain's total area is about 694 square kilometres (268 sq mi), although due to land reclamation, the area has increased to 780 square kilometres (300 sq mi). Bahrain's land area is slightly larger than Singapore and is about four times the size of Washington, DC.
The geography of Bahrain is varied, with the northern and northwestern coasts forming a narrow belt of date palms and vegetable gardens irrigated by prolific springs and wells that tap artesian water. The central region is rocky and barren, rising to 134 metres at Jabal al Dukhan (Mountain of Smoke), the country's highest point. The southern and western lowlands consist of a bleak sandy plain with some salt marshes.
The population of Bahrain is densely packed, with about 89% living in the two principal cities of Manama and Al Muharraq. The population was 1,58 million in 2021, including more than 800,000 non-nationals.
The Unique Appeal of Bahrain
You may want to see also

Bahrain's population
The population of Bahrain is approximately 1.5 million people, with a significant proportion of non-nationals (approximately 50%). The population is largely urban, with the majority living in the northern part of the main island. Bahrain has a diverse population, with a Shia majority and a Sunni minority. Shia Bahrainis are divided into two main ethnic groups: Baharna and Ajam, while Sunni Bahrainis are mainly Arabs and Huwala. The country also has a native Christian community, as well as Jewish and Hindu communities. Arabic is the official language, but English, Farsi, and Urdu are also widely spoken.
Bahrain has a young population, with a median age of 33.2 years. The population density is high, at 2115 people per square kilometre, and the literacy rate is high, particularly among the youth. Bahrain has a universal healthcare system, and the life expectancy is 73 for males and 76 for females.
The population of Bahrain has grown over time, with the country crossing the one million mark in 2007. The population growth has been fuelled by immigration, with a significant number of people from South Asia, particularly India, living in the country. The population is expected to continue growing, with Bahrain's total fertility rate being higher than the replacement rate.
Bahrain's Crypto Laws: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Bahrain's capital
Manama is the capital and largest city of Bahrain. It is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island, in the Persian Gulf. It is home to a diverse population of around 297,502 people as of 2012, though other sources state the population is around 143,035 or 148,000.
Manama has been an important trading centre in the Persian Gulf for centuries. It was first mentioned in Islamic chronicles around 1345 CE, when it was under the control of the Hurmuz. The Portuguese took Manama in 1521, and the Persians in 1602. The Al Khalifa dynasty has ruled the city since 1783, apart from brief interruptions.
Manama became the capital of Bahrain when the country gained independence in 1971. It is the focal point of the Bahraini economy, with a diverse range of industries including heavy industry, banking, finance, and tourism. It is also a cultural hub, with several notable cultural sites including Bab Al Bahrain and the Manama Souq.
The Troubling Story of Abby Luna in Bahrain
You may want to see also

Bahrain's language
The official language of Bahrain is Arabic, specifically the Bahrani Arabic dialect. This is widely used in daily communication, government and business. However, English is also commonly spoken and understood, especially in urban areas and in the business and tourism sectors.
Arabic is spoken in two main variations in Bahrain: Bahrani and Gulf Arabic. Bahrani Arabic is mainly spoken in the capital, Manama, and by some Bahraini villages. It is the de facto national language and the first language taught in secondary schools. Bahrani Arabic is made up of several dialects and accents, including Muharraq and Sitra. There is also dialect variation between urban and rural speakers. Gulf Arabic is a minority language in Bahrain, spoken by less than 5% of the population.
Bahrain has a diverse population, with a large number of expatriates. The presence of a large expat community and the need to adopt a foreign language has led to the use of English as an alternative language. English is the de facto national working and primary business language. It is a compulsory second language in most schools, and several newspapers, TV channels and radio stations are in English. Commercial road signs are bilingual, displayed in both English and Arabic.
In addition to Arabic and English, a variety of other languages are spoken in Bahrain, including Persian, Urdu, Nepali, Malayalam, Tamil and Hindi.
Unlocking Bahrain: Phone Number Essentials
You may want to see also

Bahrain's climate
A hot, dry southwest wind, known locally as the qaws, periodically blows sand clouds across the barren southern end of Bahrain toward Manama in the summer. Temperatures are more moderate in the winter months, from November to March, ranging between 10 and 20 °C (50 and 68 °F). However, humidity often rises above 90% in the winter. From December to March, prevailing winds from the northwest, known as the shamal, bring damp air over the islands.
Regardless of the season, daily temperatures are fairly uniform throughout the archipelago. The coldest temperature ever recorded in Bahrain was on 20 January 1964, when it dropped to -5 °C (23 °F) in Awali and 2.7 °C (36 °F) at Bahrain International Airport. That particular freeze was accompanied by a white-out, with icicles forming on trees and fences.
Bahrain receives little precipitation, with an average annual rainfall of 72 millimetres (2.8 inches), usually confined to the winter months. No permanent rivers or streams exist on any of the islands. The winter rains tend to fall in brief, torrential downpours, flooding the shallow wadis that are dry for the rest of the year and impeding transportation. Little of the rainwater is saved for irrigation or drinking. However, there are numerous natural springs in the northern part of Bahrain and on adjacent islands.
Bahrain-Saudi Causeway: Open for Business or Closed?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The total area of Bahrain is 760 square kilometres (290 sq mi), or 694 square kilometres (268 sq mi) according to another source. It is the third-smallest nation in Asia.
Bahrain is about four times the size of the District of Columbia, or 3.5 times the size of Washington, DC. It is slightly larger than Singapore.
Bahrain is one of the most densely populated countries in the world.







