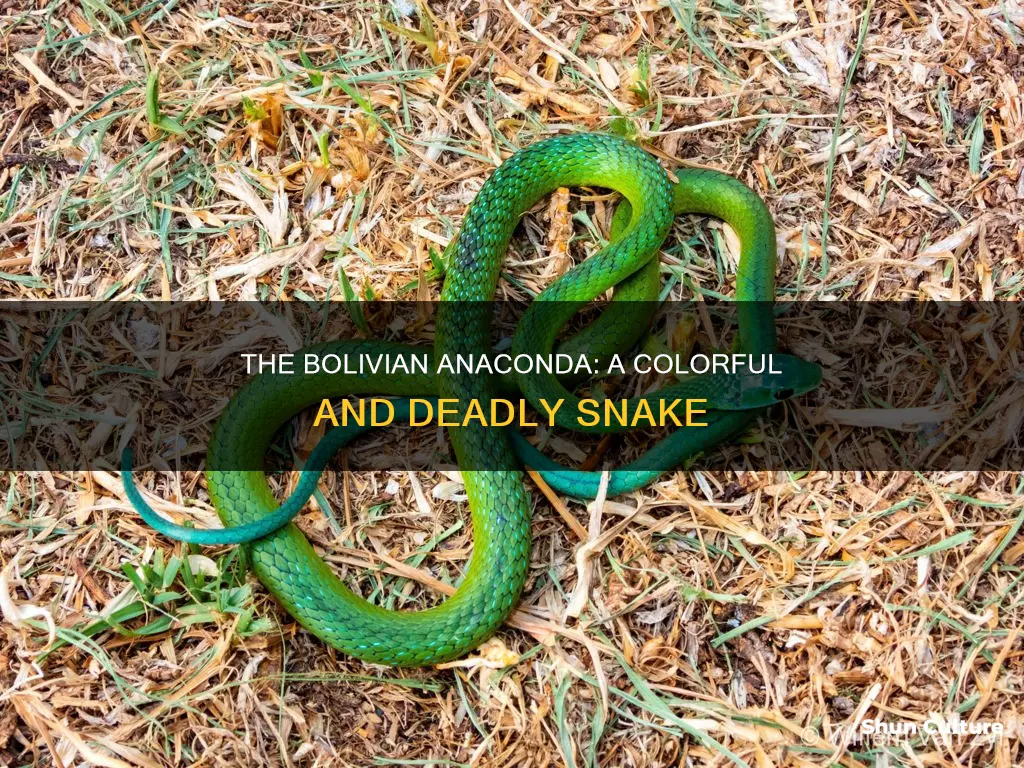
The Bolivian anaconda, or Beni anaconda, is a nonvenomous species of boa native to Bolivia's Beni Province. It is greenish to yellowish-brown in colour, with dark brown splotches on its long, bulky body. The Bolivian anaconda is closely related to the yellow anaconda and the green anaconda, and was initially believed to be a hybrid of the two.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Color | Greenish to yellowish-brown with dark brown splotches |
| Length | 11-14 ft |
| Weight | Up to 77 lb |
| Habitat | Wetlands, muddy, swampy, and flooded areas |
| Diet | Carnivorous: fish, river fowl, caiman, small livestock |
| Behavior | Solitary, at home on land and in water |
| Venom | Nonvenomous |
| Range | Northeastern Bolivia, Beni Province |
What You'll Learn

Greenish to yellowish-brown base colour
The Bolivian anaconda, or Beni anaconda, is a nonvenomous species of boa found in the Beni region of Bolivia. It is the most recently defined species of boa and was initially believed to be a hybrid of the green and yellow anaconda.
The Bolivian anaconda is typically greenish to yellowish-brown in base colour, with many dark brown splotches around its long, bulky body. The underside of its body is usually a lighter yellow or tan shade. This colouration allows the snake to blend in with its surroundings, making it a successful predator.
The Bolivian anaconda's habitat consists of wetlands, rainforest, aquatic muddy areas, and flooded swamps. They are semi-aquatic and are excellent swimmers. They are known to prey on various aquatic animals, such as fish, river fowl, and caiman, as well as small livestock such as chickens.
The Bolivian anaconda can grow to be quite large, reaching lengths of 10 to 14 feet and weighing between 50 to 70 pounds. They are closely related to the yellow anaconda and the dark-spotted anaconda and are considered distinct species.
The behaviour of wild Bolivian anacondas is not well understood, but they are known to lead a solitary life and are comfortable both on land and in the water. They are non-venomous constrictors, using their strong muscles to suffocate their prey.
McDonald's Bolivia Ban: Why Did It Happen?
You may want to see also

Dark brown splotches
The Bolivian anaconda, or Beni anaconda, is a nonvenomous species of boa found in the Beni region of Bolivia. It is the most recently defined species of boa and was initially believed to be a hybrid between the green and yellow anaconda.
The Bolivian anaconda is greenish to yellowish-brown in colour and has many dark brown splotches around its long, bulky body. The underside of its body is usually a lighter yellow or tan shade. The dark brown splotches are a key feature of its colouring, helping it to blend into its surroundings.
The Bolivian anaconda is one of the largest snakes in the world, reaching between 3.3 and 4.4 metres in length and weighing up to 35 kilograms. It is closely related to the yellow anaconda and the dark-spotted anaconda.
The Bolivian anaconda's habitat usually consists of wetlands and other muddy, swampy or flooded areas. It is a semi-aquatic snake, meaning it is at home both on land and in the water. It is a skilled swimmer and is known to prey on various aquatic animals, such as fish, river fowl and caiman, as well as small livestock such as chickens.
The behaviour of wild Bolivian anacondas is not well understood, but they are known to lead a solitary life. They are not currently considered threatened, but they are frequently collected for their skin and fat and are sometimes killed by locals for preying on livestock.
Adjusting Bolivia Heights: Tips for a Smooth Transition
You may want to see also

Light yellow or tan underside
The Bolivian anaconda, or Beni anaconda, is a nonvenomous species of boa found in the wetlands, swamps, and other muddy, aquatic areas of Bolivia's Beni Province. It is the most recently defined species of boa and can grow to be between 11 and 14 feet in length, weighing up to 77 pounds. The Bolivian anaconda was initially believed to be a hybrid of the yellow and green anaconda species, but it is now recognised as its own distinct species.
The Bolivian anaconda is typically greenish to yellowish-brown in colour and has many dark brown splotches around its long, bulky body. The underside of the snake is usually a light yellow or tan shade. The colour of their underbellies helps them to camouflage with their surroundings, allowing them to surprise their prey. The yellow or tan underside also helps to break up the outline of the snake, making it more difficult for predators to spot them.
The Bolivian anaconda's light yellow or tan underside may also serve to absorb heat from the sun when the snake is basking. This can help to regulate their body temperature, as they are cold-blooded reptiles. Additionally, the light colour of the underside may help to reflect the snake's heat back towards its body, providing some insulation during colder periods.
The light yellow or tan underside of the Bolivian anaconda is a distinctive feature that helps to set it apart from other species of anaconda. While it may be similar in appearance to the green and yellow anaconda from above, the lighter colouration on its belly is a unique characteristic. This colouring may also be slightly different for each individual snake, further adding to their distinctiveness.
The light yellow or tan underside of the Bolivian anaconda is an important aspect of its overall colouring and patterning. It helps the snake to camouflage, regulate its body temperature, and stand out from other species. The light underside may also provide some level of insulation during colder periods, contributing to the snake's overall survival and adaptation in its natural habitat.
Car Sharing in Bolivia: How Many Passengers Per Vehicle?
You may want to see also

Closely related to the yellow and green anaconda
The Bolivian anaconda, or Beni anaconda, is closely related to the yellow anaconda and the green anaconda. In fact, it was initially believed to be the result of hybridization between these two species. However, it is now recognized as a distinct species.
The Bolivian anaconda is a nonvenomous species of boa that is endemic to Bolivia's Beni Province. It is the most recently defined boa species. It reaches between 3.3 and 4.4 meters (11-14 ft) in length and can weigh up to 35 kilograms (77 lbs). Its colouring is greenish to yellowish-brown, with many dark brown splotches around its long, bulky body.
The yellow anaconda, or Paraguayan anaconda, is a species of boa that is endemic to the wilds of South America. It is found in the southern parts of the continent, including Paraguay, southern Brazil, Bolivia, and northeastern Argentina. Adults of this species grow to between 10.8 and 14.4 feet and weigh about 25 to 35 kg. The snakes are coloured yellowish, greenish-yellow, or golden tan with blotches, spots, streaks, or saddles of dark brown or black.
The green anaconda, also known as the water boa or common anaconda, is a non-venomous species of boa. It is one of the longest and heaviest species of snakes in the world. The snake attains a length of about 17.1 feet and weighs between 30 to 70 kg. Its colouring is olive green with overlaid black-coloured blotches throughout the length of the snake.
The Bolivian anaconda's habitat usually consists of wetlands and other muddy, swampy, or flooded areas. It is known only from northern Bolivia. The yellow anaconda prefers to inhabit swamps, marshes, slow-moving rivers, and streams. The green anaconda is primarily a nocturnal species that spends most of its lifetime near or in the water. It is often found in the Brazilian Amazon basin, the Orinoco basin, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Trinidad, and the Guianas.
Irish Citizens: Bolivian Visa Requirements and Exemptions
You may want to see also

Found in Bolivia's Beni Province
The Bolivian anaconda, or Beni anaconda, is native to Bolivia's Beni Province. It is a nonvenomous species of boa that is endemic to this small region of northeastern Bolivia. The species was only recently defined and recognised as distinct from the yellow and green anacondas, which it closely resembles.
The Bolivian anaconda's habitat consists of wetlands, rainforests, and other muddy, swampy, or flooded areas. They are at home both on land and in the water, and they prey on various aquatic animals, such as fish, river fowl, and caiman, as well as small livestock like chickens.
The snakes can grow up to four metres in length and weigh up to 35 kilograms. They are greenish to yellowish-brown in colour, with many dark brown splotches around their long, bulky bodies. They are closely related to the yellow anaconda and the dark-spotted anaconda.
The behaviour of wild Bolivian anacondas is not well understood, but they are known to lead a solitary life. They are frequently collected for their skin and fat, and they are sometimes killed by locals for preying on livestock. According to the IUCN Red List, the species is locally common throughout its range but is not currently considered threatened.
Leaving Bolivia: The Ease of Emigration
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Bolivian anaconda is usually greenish to yellowish-brown in color with many dark brown splotches around its long, bulky body.
Eunectes beniensis.
Bolivian anacondas are found in the Departments of Beni and Pando in Bolivia, in rainforest, aquatic muddy, swampy flooded areas, and flooded savanna.
Bolivian anacondas reach between 3.3–4.4 meters (11–14 ft) in length and can weigh up to 35 kilograms (77 lb).
No, like all boas, Bolivian anacondas are nonvenomous.