Minsk, Belarus, is a city with a population of about two million people as of 2024. It is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and Niamiha rivers. Minsk is the administrative centre of the Minsk region and has a special administrative status in Belarus. It is the economic, political, scientific, and cultural centre of the country. Minsk is a large industrial centre, contributing more than a quarter to the national GDP. The city has a diverse industrial sector, including machinery and equipment manufacturing, food and beverage production, and electrical equipment manufacturing. Minsk is also a major educational hub, housing the country's largest educational institutions, such as the Belarusian State University and the National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Belarus. The city has a well-developed transportation network, with highways connecting it to other major cities in Belarus and a large railway network that links to Brest, Moscow, Vilnius, and Gomel. Additionally, Minsk has a good public transportation system, including buses, trolleybuses, trams, and a metro system.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| N/A | N/A |
What You'll Learn

Xeloda in Minsk, Belarus
Minsk, the capital of Belarus, is a large educational centre with many of the country's key institutions, including lyceums, high schools and colleges. The city is home to the National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Belarus, which was established in 1929, and several other institutions of higher education.
The main educational institutions in Minsk include:
- Academy of Management of the President of the Republic of Belarus
- Belarusian State University
- Belarusian State Medical University
- Belarusian State Economic University
- Belarusian National Technical University
- Belarusian State Technological University
- Belarusian State Academy of Arts
Minsk is also a major industrial centre, contributing more than a quarter to the national GDP. The city's industrial sector features companies and enterprises producing machinery and equipment, food and beverages, tobacco products, electrical equipment, vehicles, construction materials, and pharmaceuticals. There are 3,155 industrial companies in Minsk, including well-known Belarusian brands such as Minsk Tractor Works (MTZ), Minsk Automobile Plant (MAZ), Minsk Wheel Tractor Plant (MZKT), and Minsk Motor Plant (MMZ).
The city has a population of about two million people and is located on the southeastern slope of the Minsk Hills. Minsk is served by a large railway network, which connects Brest, Moscow, Vilnius, and Gomel, and has a national airport.
Using Venmo in Belarus: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

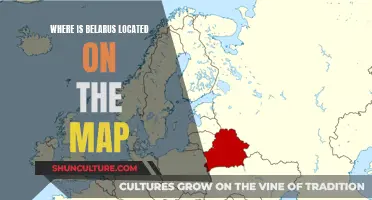
Minsk: Capital of Belarus
Minsk, the capital of Belarus, is one of the oldest cities in Europe, first mentioned in the historical chronicle in 1067. It is the administrative, economic, scientific and cultural hub of the country, located just 70km from its geographical centre. With a population of about two million, Minsk is the 11th most populous city in Europe.
History
Minsk has been destroyed and rebuilt several times throughout its history. It was first established as the capital of the Principality of Minsk, an appanage of the Principality of Polotsk, before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It was then part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Russian Empire, and the Soviet Union, before becoming the capital of the newly independent Republic of Belarus following the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
During World War II, Minsk was almost completely demolished and its large Jewish community was systematically massacred. After the war, the city was rebuilt with abundant parks, wide boulevards, and multistory apartment buildings.
Economy and Industry
Minsk is the economic capital of Belarus, contributing about 46% of the national budget and a quarter of the country's GDP. It is a major industrial centre, with over 250 factories and plants, producing machinery and equipment, food and beverages, electrical equipment, vehicles, construction materials, and pharmaceuticals. The city has a diverse industrial sector, including tractor manufacturing, machine-tool construction, and radio engineering.
Culture and Education
Minsk is a major cultural centre, with numerous museums, theatres, and libraries. It is also a large educational centre, home to the country's main educational institutions, including the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, a university founded in 1921.
Transport
Minsk has a well-developed transportation network, with highways connecting it to the largest cities in Belarus and a large railway network connecting it to other countries. It also has a good public transport system, including buses, trolleybuses, trams, and a metro system. The city is served by the Minsk National Airport, located 42km to the east.
Prigozhin's Presence in Belarus: What Does It Mean?
You may want to see also

Minsk: Economic Centre
Minsk is the capital and largest city of Belarus, with a population of about two million, making it the 11th most populous city in Europe. It is the administrative centre of the Minsk Region and Minsk District and holds a special administrative status in Belarus. It is also one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).
Minsk is the economic centre of Belarus, contributing nearly 46% of the country's budget. The city's economy is based on machine building, particularly the manufacture of trucks and tractors, and other industries such as radio engineering and electronic equipment manufacturing. Minsk has over 250 factories and plants, employing about 40% of the city's workforce in the manufacturing sector. Major industrial employers include the Minsk Tractor Plant, the Minsk Automobile Plant, the Minsk Refrigerator Plant, and Horizont, a producer of TV sets and audio and video electronics.
In addition to its industrial sector, Minsk also has a well-developed services sector, which serves the needs of the city and the entire nation. The city has a large railway network and a national airport, connecting it to other major cities in the region. It also boasts a very good public transportation system, with buses, trolleybuses, trams, and a metro system.
Minsk is also a large educational centre, with numerous institutions of higher education, including the Belarusian State University, the Belarusian State Medical University, and the Belarusian National Technical University. It is also a cultural hub, with many museums, theatres, and historical places and architectural monuments, such as the National Library of Belarus and the National Museum of Culture and History of Belarus.
Exploring Belarus' Forested Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Minsk: Educational Centre
Minsk, the capital of Belarus, is the country's largest educational centre. The city is home to the most important educational institutions in Belarus, including high schools, colleges, and the key lyceums.
The Academy of Management of the President of the Republic of Belarus is one of the most prominent educational institutions in Minsk. The academy has three institutes: the Institute of Administrative Personnel, the Institute of Civil Service, and the Research Institute of the Theory and Practice of Public Administration.
Belarus State University, founded in 1921, is another significant educational institution in Minsk. It has 15 major departments, including Applied Mathematics and Informatics, Biology, Chemistry, and Journalism. The university also includes 24 research centres and 114 R&D laboratories.
Other notable educational institutions in Minsk include:
- Belarusian State Medical University
- Belarusian State Economic University
- Belarusian National Technical University
- Belarusian State University of Informatics and Radioelectronics
- Belarusian State University of Culture and Arts
Minsk has about 451 kindergartens, 241 schools, 22 further education colleges, and 29 higher education institutions, making it a vital educational hub in Belarus.
Orsha, Belarus: A Historic City on the Dnieper River
You may want to see also

Minsk: Industrial Centre
Minsk is the capital and largest city of Belarus, with a population of about two million as of 2024, making it the 11th most populous city in Europe. It is the administrative centre of the Minsk region and district and is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). Minsk is a major industrial centre, with over 250 factories and plants, and its companies produce 16% of the total volume of industrial output in Belarus.
The city's industrial development began in the 1860s and was facilitated by the construction of railways in the 1870s. Minsk became an important rail junction and manufacturing hub, producing tractors, trucks, buses, mini-vans, refrigerators, washing machines, television sets, radios, bicycles, motorcycles, watches, textiles, construction materials, food and beverages, and printing materials.
The China-Belarus Industrial Park, located 25 km from Minsk, is a special economic zone established through an intergovernmental agreement between the two countries. The park offers tax benefits, a free customs regime within the EAEU, and market opportunities for 183 million customers. It focuses on high-tech manufacturing, assembly, warehousing, logistics, and research and development. Residents of the park benefit from a unique legal and regulatory environment, including tax exemptions and incentives.
Minsk has a diverse industrial base, with the main branches being tractor manufacturing, machine-tool construction, and radio engineering and electronic equipment manufacturing. The city has a free economic zone and is home to major industrial employers such as the Minsk Tractor Plant, Minsk Automobile Plant, Minsk Refrigerator Plant, and Horizont.
In addition to its industrial prowess, Minsk is also a large educational centre within Belarus, with many of the country's key educational institutions located in the city, including the Belarusian State University, Belarusian State Medical University, and Belarusian National Technical University.
Belarusian Citizenship: What's in a Name?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Xeloda is a commonly prescribed medication in Minsk, Belarus, and is typically available in most pharmacies. However, the availability and quantity may vary, so it is recommended to contact your local pharmacy or healthcare provider for specific information.
The price of Xeloda can vary depending on the quantity purchased and the pharmacy. It is advised to contact your local pharmacy for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Xeloda is a prescription medication, and as such, it cannot be purchased over the counter. A valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider is required to obtain this medication.
Generic versions of Xeloda may be available under different brand names. It is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist to determine if there are any suitable generic alternatives available in Minsk, Belarus.