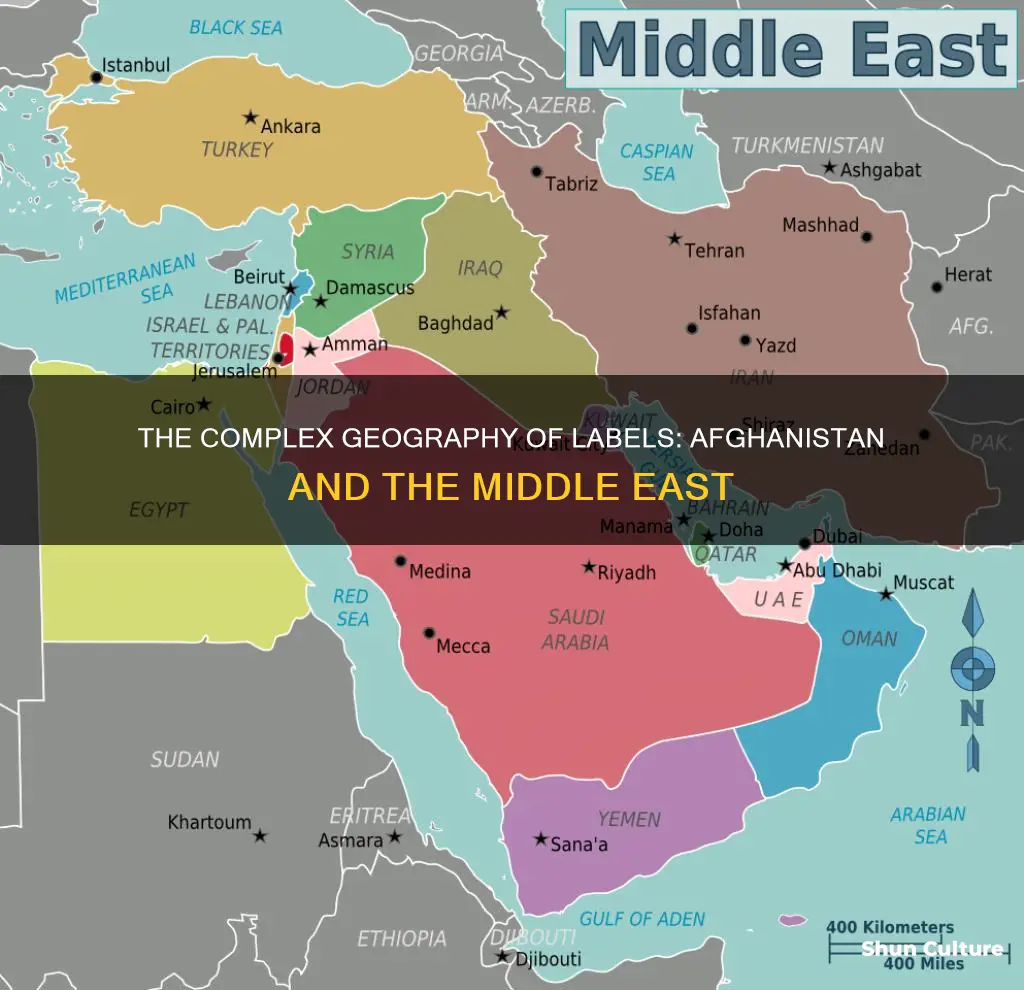
Afghanistan is often mistaken for being part of the Middle East, but it is actually part of South Central Asia. However, the country is near the Middle East and shares cultural heritage and historic importance with the region. Afghanistan is also included in the broader definition of the Greater Middle East, which includes parts of East Africa, Central Asia, and other regions. The term Middle East itself has a confusing history, with changing definitions and criticism for being Eurocentric and colonialist.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Is Afghanistan in the Middle East? | No, Afghanistan is in South Central Asia. |
| Is Afghanistan near the Middle East? | Yes, Afghanistan is near the Middle East. |
| Is Afghanistan culturally similar to the Middle East? | Afghanistan shares a similar cultural heritage and historic importance with the Middle East. |
| Has Afghanistan ever been considered part of the Middle East? | Yes, Afghanistan was considered part of the Middle East in the early 20th century and before the First World War. |
What You'll Learn

Afghanistan is geographically close to the Middle East
Afghanistan is often mistaken for being part of the Middle East, but it is actually located in South Central Asia. However, its proximity to the Middle East means that it is geographically close to the region. Afghanistan shares borders with six countries, three of which (Iran, Pakistan, and Turkmenistan) are Middle Eastern or border Middle Eastern countries. Afghanistan's westernmost point is situated along the Iranian-Afghan border, and it shares its southern border with Pakistan, which also lies along its eastern border.
Afghanistan's close geographical proximity to the Middle East is further illustrated by its neighbouring countries. For example, China, which borders Afghanistan to the northeast, also shares a border with the Middle Eastern country of Iraq. Additionally, Afghanistan's northern borders with Tajikistan and Uzbekistan bring it close to the Middle East, as these countries are within proximity to Iran.
The term "Middle East" typically refers to a geopolitical region that spans parts of Western Asia and North Africa. The region is characterised by its diverse landscapes, including deserts, mountains, and coasts. While Afghanistan shares similar cultural heritage and historic importance with Middle Eastern countries, it falls under the jurisdiction of South or Central Asia. Nevertheless, Afghanistan's location near the Middle East has had significant implications for the country, influencing its history, politics, and cultural development.
The Complexities of Afghan Identity: Navigating Racial Perceptions and Realities
You may want to see also

Afghanistan shares a similar cultural heritage with the Middle East
Afghanistan is a landlocked country in South Central Asia, with a rich cultural heritage. While it is not considered a Middle Eastern country, it shares a similar cultural heritage with the Middle East. Afghanistan is a multi-ethnic society with diverse ethnic, linguistic, and tribal groups. The country's official language is Dari, a variety of Persian, and Pashto, with Arabic being widely spoken. Afghanistan's culture is heavily influenced by Islamic values, concepts, and practices, with Islam being the official religion.
Hospitality is a highly valued aspect of Afghan culture, with a strong emphasis on family and collectivism. Afghans are known for their loyalty, respect, and generosity. The society is patriarchal, with distinct gender roles and expectations. Afghan cuisine is diverse and includes various fresh and dry fruits, such as pomegranates, grapes, and melons.
Afghanistan has a complex history, having been invaded and influenced by various empires, including the Persians, Alexander the Great, the Maurya Empire, Arab Muslims, the Mongols, the British, the Soviet Union, and the United States. The country has also been a source of major empires, such as the Greco-Bactrians and the Mughals.
Afghanistan's geographic location at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia, along important trade routes, has made it a coveted prize for empire-builders. The country's landscape is diverse, ranging from mountainous regions to plains and deserts.
While Afghanistan shares cultural similarities with the Middle East, it has its own unique identity, influenced by its specific historical, religious, and geographic context.
The Prize in the Afghan Endgame: What Victory Could Mean for the US
You may want to see also

Afghanistan is historically significant like the Middle East
Afghanistan is a landlocked country in South Central Asia, with a rich and complex history. It has been home to some of the oldest civilisations in the world, including Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), Persia (modern-day Iran), and Egypt.
Afghanistan has been invaded and occupied by many empires and nations, including the Persians, Alexander the Great, the Maurya Empire, Arab Muslims, the Mongols, the British, the Soviet Union, and a US-led coalition.
Afghanistan has been a key player in the 'Great Game', a term coined in the 19th century to describe the rivalry between the British and Russian empires. Afghanistan's location at the crossroads of Asia and Europe has made it a strategically important country, with many empires vying for control of the region.
Afghanistan's history is also closely intertwined with that of the Middle East. The country has been part of the Persian Empire, the Mongol Empire, and the Ottoman Empire, all of which have had a significant influence on the history of the Middle East.
Afghanistan has also been influenced by the spread of Islam, which originated in the Middle East. The Islamic Caliphate expanded into Afghanistan in the 7th century, and the country has been a majority-Muslim country ever since.
Afghanistan's location and historical connections to the Middle East make it an important part of the region's history.
The Toll of War: Remembering Poland's Fallen Soldiers in Afghanistan
You may want to see also

Afghanistan is not considered a Middle Eastern country
Afghanistan is a landlocked country, bordered by six other countries: Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan to the north; Iran to the west; and Pakistan and China along its southern border, with Pakistan extending along the eastern border as well. With a latitude in the north, Afghanistan is located above the equator, in both the northern and eastern hemispheres.
The term "Middle East" is generally applied to a region that spans parts of Western Asia and North Africa, including the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. Most Middle Eastern countries are part of the Arab world, with Arabs constituting the main ethnic group in the region. The history of the Middle East is steeped in ancient civilisations, with several major religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, originating in the region.
While Afghanistan shares cultural and historical ties with the Middle East, it falls under the jurisdiction of South or Central Asia due to its geographical location. This classification is important to distinguish Afghanistan from its Middle Eastern counterparts, even though it may be considered a neighbouring country to the region.
A Heartfelt Bond: Exploring the Presence of Pakistanis in Afghanistan
You may want to see also

Afghanistan is part of South or Central Asia
Afghanistan is a landlocked country located in the heart of South and Central Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east.
Afghanistan is often mistaken for being part of the Middle East, but it is not. It is, however, close to the Middle Eastern region of the world. Afghanistan is included in the broader definition of the Middle East, which includes the "Greater Middle East". This definition also includes parts of East Africa, Mauritania, Pakistan, and sometimes the South Caucasus and Central Asia.
Afghanistan is a member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), which was established in 1985 and includes all eight nations comprising South Asia. These nations are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan was admitted to SAARC as an eighth member in 2007.
Afghanistan is also considered to be at the crossroads of Asia, with the country being nicknamed the Heart of Asia.
Afghanistan's official languages are Pashto and Dari, which are Indo-European languages from the Iranian languages sub-family. Dari is considered the prestige language and a lingua franca for inter-ethnic communication.
The Geopolitics of Afghanistan's FOBs: Oil, Influence, and Strategic Interests
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Afghanistan is often mistaken as being part of the Middle East, but it is actually part of South Central Asia.
Afghanistan is surrounded by land, sharing borders with six countries: Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan to the north; Pakistan to the south and east; and Iran to the west. China is located northeast of Afghanistan.
Afghanistan shares a similar cultural heritage and historic importance with the Middle East, but it is not categorized as a Middle Eastern country.
The Middle East spans parts of Western Asia and North Africa and includes 17 countries: Bahrain, Cyprus, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Yemen.
The term "Middle Eastern" refers to the region spanning parts of Western Asia and North Africa, while the term "Arab" refers to people who speak Arabic as their first language and are typically from the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, or Egypt.







