Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a small yet wealthy country located in Southeast Asia, on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. It is the only sovereign state that is entirely on Borneo, with the remainder of the island shared between Malaysia and Indonesia. Brunei has a population of around 450,000 people, with approximately 180,000 living in the capital, Bandar Seri Begawan. The country has a rich history, having once been a powerful sultanate that controlled much of Borneo and parts of the Philippines. Today, it is an absolute monarchy ruled by the Sultan, with Islam as the state religion. Brunei gained its independence from the United Kingdom in 1984 and has since focused on economic diversification, particularly in the oil and gas sector, of which it is a major producer.
What You'll Learn

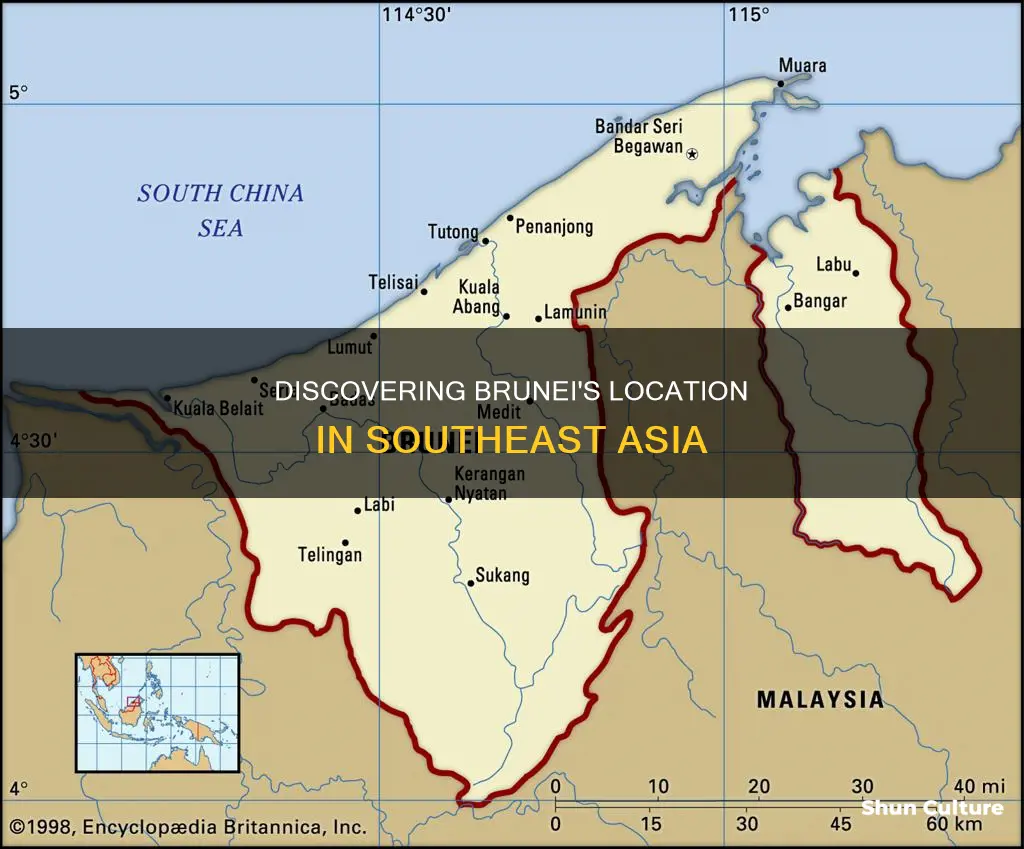
Brunei is located on the island of Borneo
The western segment of Brunei is the larger of the two and contains the capital city of Bandar Seri Begawan. This region is characterised by a narrow coastal plain that gives way to rugged hills further inland. The eastern segment, Temburong District, is separated from the western portion by the Brunei Bay and is predominantly mountainous. The highest point in Brunei is Pagon Peak, which rises to 1,850 metres (6,070 feet) above sea level in the eastern region.
Brunei has a total area of 5,765 square kilometres (2,226 square miles) and a coastline stretching approximately 161 kilometres (100 miles) along the South China Sea. The country is home to a diverse landscape, including tropical rainforests, freshwater and peat swamps, and mangrove swamps along the coast and lower riverine areas.
The territory of Brunei has changed over time, with the historic Bruneian Empire claiming control over much of Borneo and beyond during its peak in the 15th and 16th centuries. However, by the 19th century, the empire had declined due to wars, piracy, and European colonial expansion. In 1888, Brunei became a British protectorate, and its territory was further reduced with the cession of land to James Brooke, who established the Raj of Sarawak. Today, Brunei is an independent nation with defined borders, sharing a 381-kilometre (237-mile) border with Malaysia.
Brunei and Malaysia: Two Nations, One History
You may want to see also

It is bordered by the South China Sea
Brunei is bordered by the South China Sea to the north. It has a coastline of about 161 kilometres along the sea and is the only sovereign state entirely on Borneo. The remainder of the island is divided between Malaysia and Indonesia.
The country has a total area of 5,765 square kilometres with a population of approximately 455,858 as of 2023. Bandar Seri Begawan is the capital and largest city of Brunei, with a population of approximately 180,000. The official language of Brunei is Malay, and Islam is the state religion.
Brunei has a constitutional absolute monarchy ruled by the Sultan, who is also the head of state and government. The country gained its independence from the United Kingdom on 1 January 1984 and is a member of the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, the East Asia Summit, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, the Non-Aligned Movement, the Commonwealth of Nations, and ASEAN.
Brunei's wealth is based on its substantial oil and gas reserves, making it one of the world's richest countries in terms of gross domestic product per capita. The country has a very high ranking on the Human Development Index, second only to Singapore among Southeast Asian nations.
Brunei: A Peaceful and Prosperous Place to Live?
You may want to see also

It is surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak
Brunei is a small country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. It is surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with its territory bifurcated by the Sarawak district of Limbang. Brunei is the only sovereign state entirely on Borneo; the remainder of the island is divided between Malaysia and Indonesia.
Sarawak is a state of Malaysia, located in East Malaysia in northwest Borneo. It is the largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia. Sarawak is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, Kalimantan (the Indonesian portion of Borneo) to the south, and Brunei in the north.
Sarawak was recognised as a separate state by the United States in 1850 and by Great Britain in 1864. It was gradually enlarged through purchase and annexation until 1905. In 1946, Sarawak became a British Crown Colony and subsequently became one of the founding members of Malaysia in 1963.
Sarawak has a low-lying and heavily indented coastline along the South China Sea. Much of its area is covered by primary rainforest. The coastal region is rather low-lying and flat with large areas of swamp, while hilly terrain accounts for much of the inhabited land. Sarawak is divided into three ecoregions: the coastal region, the hilly terrain, and the mountainous region along the Sarawak-Kalimantan border.
Sarawak is ethnically, culturally, religiously, and linguistically diverse. It is the only state in Malaysia with a Christian majority, with Christianity representing 50.1% of the total population according to the 2020 census. The state has six major ethnic groups: Iban, Chinese, Malay, Bidayuh, Melanau, and Orang Ulu.
Sarawak has a tropical geography with an equatorial climate and experiences two monsoon seasons: the northeast monsoon and the southwest monsoon. The climate is stable throughout the year, with average daily temperatures varying between 23°C in the morning to 32°C in the afternoon in coastal areas. Miri, located in the state's northeast, has the lowest average temperatures compared to other major towns in Sarawak.
Sarawak's economy is heavily dependent on the export of primary commodities, particularly oil and gas, timber, and palm oil. The state's gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 40.5% per year on average from 2010 to 2021. Sarawak contributed 9.5% of Malaysia's GDP in the nine years leading up to 2020, making it the third-largest contributor after Selangor and Kuala Lumpur.
Sarawak has four primary ports located in Kuching, Sibu, Bintulu, and Miri. The busiest seaport is in Bintulu, which mainly handles LNG products and regular cargo. The state also has 55 navigable river networks, with a combined length of 3,300 km, which have been used for centuries as a primary means of transport and the movement of goods.
Brunei: A Country with a Muslim-Majority Population
You may want to see also

Brunei is a small equatorial country
Brunei has a tropical equatorial climate, characterised by high temperatures, high humidity, and heavy rainfall throughout the year. The temperature typically ranges from 23 to 32 degrees Celsius, and the country experiences two monsoon seasons: the northeast monsoon from December to March and the southwest monsoon from May to September.
The country is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. The western segment, which includes the districts of Belait, Tutong, and Brunei-Muara, is the larger of the two and contains the capital city of Bandar Seri Begawan. The eastern segment, the Temburong district, is mountainous and less populated, with only about 10,000 residents.
Brunei has a rich cultural heritage influenced by its history as a powerful sultanate and the oldest continuously ruling dynasties in the world. Islam plays a central role in the country, with the Sultan as the head of the Islamic faith. The official language of Brunei is Malay, and the country has a high standard of living due to its bountiful oil and gas reserves.
Brunei gained its independence from the United Kingdom in 1984 and has since been led by Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah, who also serves as the prime minister, finance minister, and defence minister. The country has a unicameral legislature, the Legislative Council, which is consultative and appointed by the Sultan.
Exploring Darussalam: A Journey to the Peaceful Abode
You may want to see also

It is divided into four districts
Brunei is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. Each district is further divided into several mukims (or sub-districts), and subsequently, each mukim consists of several villages (kampung or kampong). Each district has a town as its administrative and main economic centre, except for Brunei-Muara, where the principal centre is Bandar Seri Begawan, the capital of the country.
Belait is the largest district by area and is the centre for the production of oil and gas. Brunei-Muara is the smallest district by area but has the largest population. Temburong is an exclave, separated from the other three districts by the Brunei Bay and the Malaysian state of Sarawak.
Each district is administered by a District Office (Jabatan Daerah), which is a government department under the Ministry of Home Affairs. The head of each department is a District Officer (Pegawai Daerah) appointed by the government. A district officer is assisted by an Assistant District Officer.
The administrative level of mukim in Brunei lies below the district. There are currently thirty-eight mukims in Brunei: seventeen in Brunei-Muara, eight in Tutong, eight in Belait, and five in Temburong. A mukim is headed by a penghulu.
A village (kampung or kampong) is the smallest and lowest administrative level in Brunei. Its population varies from a few hundred to a few thousand, and it is headed by a ketua kampong or village head.
Where is BRN? Unveiling the Mystery Country
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, Brunei is a country in Southeast Asia.
Brunei is situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. It is bounded by the South China Sea to the north and by the Malaysian state of Sarawak on all other sides.
The capital of Brunei is Bandar Seri Begawan.
As of 2023, the population of Brunei was 455,858, with approximately 180,000 people residing in the capital.
The official language of Brunei is Malay, although English is widely spoken as a second language.







