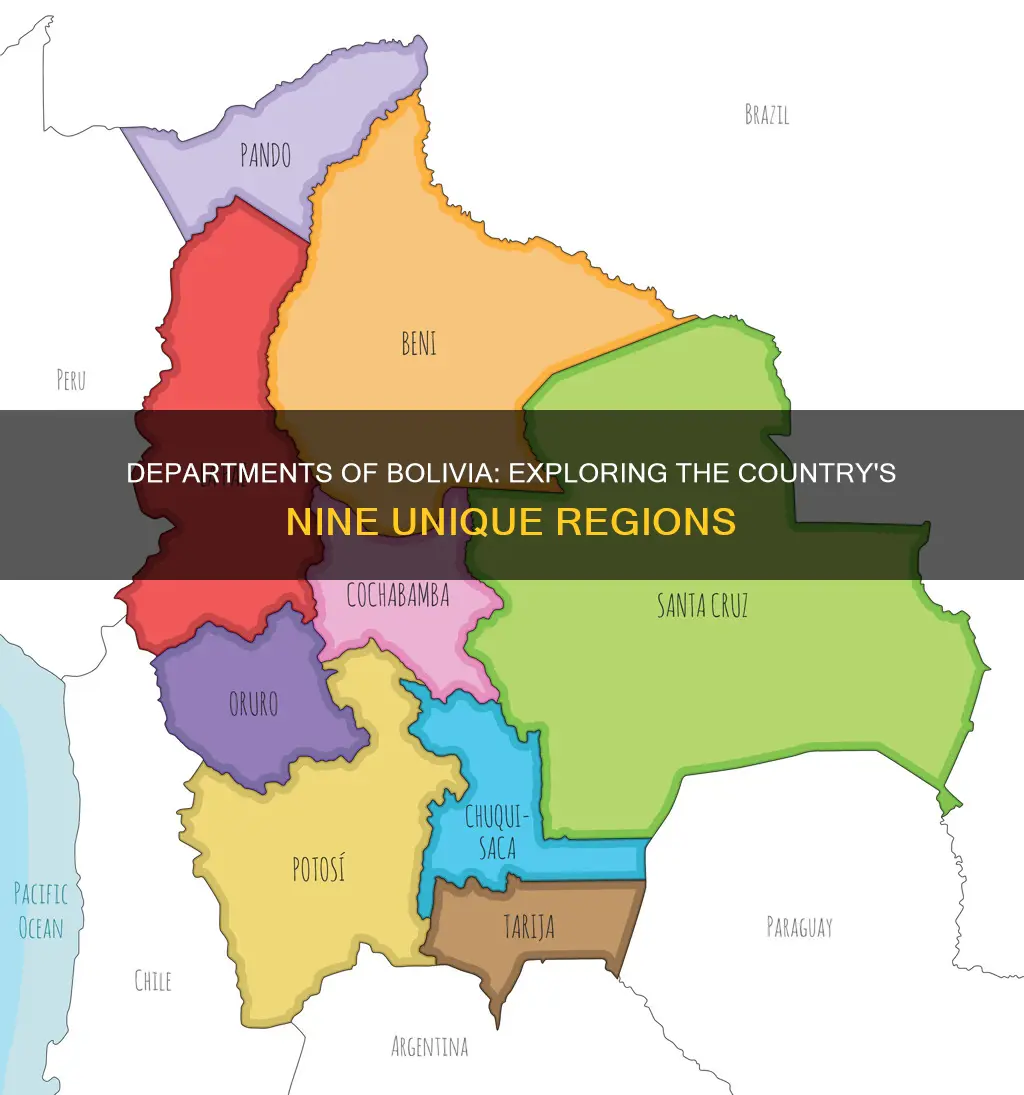
Bolivia is a unitary state in central South America, landlocked and bordered by Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, Chile, and Peru. It is divided into nine departments, or 'departamentos' in Spanish. These departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly, a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of departments | 9 |
| Department with the largest surface area | Santa Cruz |
| Department with the smallest area | Tarija |
| Most populous city | La Paz |
| Least populous department | Pando |
| Capital | Sucre |
| Head of state and government | President Luis Arce |
| Form of government | Presidential representative democratic republic |
| Legislative branch | Plurinational Legislative Assembly |
| Upper house | Senate of Bolivia |
| Lower house | Chamber of Deputies of Bolivia |
What You'll Learn

Each department has four senators
Bolivia is a unitary state that consists of nine departments. These departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly, which is a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies.
Each of the nine departments has four senators. These senators are elected by proportional representation using the D'Hondt method. Senators are elected from party lists to serve five-year terms, and the minimum age to hold a Senate seat is 35 years. The Senate is the legislative body of the country, where each senator represents the interests of their department. The Senate has 36 seats in total.
The nine departments of Bolivia are:
- Santa Cruz
- La Paz
- Pando
- Tarija
- Oruro
- Potosi
- Chuquisaca
- El Beni
- Cochabamba
Black Bolivians: A Community in the Spotlight
You may want to see also

Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state that is divided into nine departments, which are its primary subdivisions. Each department has certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia and is represented in the country's bicameral legislature, the Plurinational Legislative Assembly. This consists of the Senate, where each department is represented by four senators, and the Chamber of Deputies, where deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population.
The departments of Bolivia are as follows:
- Cochabamba (capital: Cochabamba)
- Santa Cruz (capital: Santa Cruz de la Sierra)
- Chuquisaca (capital: Sucre)
- La Paz (capital: La Paz)
- Oruro (capital: Oruro)
- Pando (capital: Cobija)
- Potosí (capital: Potosí)
- Tarija (capital: Tarija)
- Beni (capital: Trinidad)
Each department is further divided into provinces, with 112 provinces in total across the country. The provinces are then subdivided into sections or subprovinces, and these are further subdivided into cantons. There are also administrative divisions known as municipalities, of which there were 339 as of 2012.
Muslims in Bolivia: A Small but Vibrant Community
You may want to see also

Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly
Bolivia is a unitary state that consists of nine departments, which are the primary subdivisions of the country. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly, which is the national legislature of Bolivia, based in La Paz, the country's seat of government. The Plurinational Legislative Assembly is a bicameral legislature, consisting of a lower house (the Chamber of Deputies) and an upper house (the Chamber of Senators). The Vice President of Bolivia also serves as the ex officio President of the Plurinational Legislative Assembly.
Each house elects its own directorate: a President, first and second Vice Presidents, and three or four Secretaries (for the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies, respectively). Each party is said to have a seat, consisting of its legislators. The representatives of each department comprise a brigade. Each house considers legislation in standing committees.
The Chamber of Senators has 36 seats. Each of the country's nine departments returns four senators elected by proportional representation (using the D'Hondt method). Senators are elected from party lists to serve five-year terms, and the minimum age to hold a Senate seat is 35 years.
The Chamber of Deputies comprises 130 seats, elected using a seat linkage-based mixed compensatory system (for mixed-member proportional representation): 70 deputies are elected to represent single-member electoral districts, 7 of which are Indigenous or Campesino seats elected by the usos y costumbres of minority groups, and 60 are elected from party lists on a departmental basis. Deputies also serve five-year terms and must be aged at least 25 on the day of the election. Party lists are required to alternate between men and women, and in the single-member districts, men are required to run with a female alternate, and vice versa. At least 50% of the deputies from single-member districts are required to be women.
The legislative body was formerly known as the National Congress. The 3rd Plurinational Legislative Assembly of Bolivia is the current meeting of the legislative branch of the Bolivian government, composed of the Chamber of Senators and the Chamber of Deputies. It convened in La Paz on 3 November 2020, during the final week of Jeanine Áñez's presidency, and will end in 2025. It will meet during all five years of Luis Arce's presidency.
Exploring Bolivia: A Direct Flight from New York?
You may want to see also

La Paz was the most populous department in 2012
Bolivia is a unitary state that consists of nine departments, which are the primary subdivisions of the country. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly, a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies.
Out of the nine departments, La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012. The department's capital is the city of La Paz, which is also the administrative city and seat of government/national capital of Bolivia. The La Paz Department comprises 133,985 square kilometres (51,732 sq mi) with a 2024 census population of 3,022,566 inhabitants. The city of La Paz, officially Nuestra Señora de La Paz, is the third-most populous city in Bolivia as of 2024, with 755,732 residents. Its metropolitan area, which includes El Alto, Achocalla, Viacha, and Mecapaca, makes up the second most populous urban area in Bolivia, with a population of 2.2 million.
La Paz was founded on October 20, 1548, by the Spanish conquistador Captain Alonso de Mendoza, at the site of the Inca settlement of Laja. The city was originally named Nuestra Señora de La Paz (meaning Our Lady of Peace) in commemoration of the restoration of peace following an insurrection. In 1825, after the decisive victory of the republicans at Ayacucho, the city's full name was changed to La Paz de Ayacucho (meaning The Peace of Ayacucho). The seat of the national government was established in La Paz in 1898, and the city continues to serve as an important political, administrative, economic, and sports center of Bolivia.
The La Paz Department is divided into 20 provinces, which are further subdivided into 85 municipalities and, on the fourth level, into cantons. The languages spoken in the department are mainly Spanish, Aymara, Quechua, and Guaraní. The department contains the Cordillera Real mountain range, which reaches altitudes of 6.6 kilometers (22,000 ft), and the Yungas, the steep eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains that transition to the Amazon River basin to the northeast.
Creating the Peru-Bolivian Confederation in Kaiserreich: A Guide
You may want to see also

Santa Cruz is the largest department by area
Bolivia is a unitary state that consists of nine departments, which are its primary subdivisions. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly, a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies.
The department of Santa Cruz is the largest of the nine departments of Bolivia, occupying about one-third (33.74%) of the country's territory. With an area of 370,621 sq km (143,098 sq mi), it is slightly smaller than Japan or the US state of Montana. It is located in the eastern part of the country, sharing borders in the north and east with Brazil and with Paraguay in the south.
The capital of the department of Santa Cruz is the city of Santa Cruz de la Sierra, commonly known as Santa Cruz. It is the largest city in Bolivia and is situated on the Pirai River in the eastern Tropical Lowlands of the country. The city was first founded in 1561 by Spanish explorer Ñuflo de Chavez about 200 km (124 mi) east of its current location and was moved several times until it was finally established on the Pirai River in the late 16th century.
The department covers a vast expanse of territory in eastern Bolivia, much of it rainforests, extending from the Andes to the border with Brazil. The department's economy depends largely on agriculture, with sugar, cotton, soybeans, and rice being grown. The amount of land cultivated by modern farming techniques is increasing rapidly in the Santa Cruz area, where the weather allows for two crops a year.
Exploring the Intriguing Nature of Bolivian Men
You may want to see also