Belize is a small country in Central America with a population of about 359,000 people. It has a per capita income of $4,906, which classifies it as an upper-middle-income country according to the World Bank. However, despite this status, Belize faces high rates of poverty, with about 43% of its population living below the national poverty line. In this paragraph, we will explore the topic of whether Belize is considered a low-income country and examine the economic context that contributes to its poverty rates.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Income Status | Upper-middle income country |
| GNI Per Capita | $4,906 |
| Population | 359,000-360,000 |
| Poverty Rate | 43% below the national poverty line |
| Extreme Poverty Rate | 16% |
| Main Economic Sectors | Agriculture, Tourism, Services |
| Primary Exports | Citrus, Sugar, Bananas |
| Trade Deficit | Growing |
| Foreign Trade Dependence | High |
| Top Trading Partner | United States |
| Other Major Trading Partners | European Union, Canada, Mexico, CARICOM member states |
What You'll Learn

Belize's economy is dependent on agriculture, manufacturing and tourism
Belize is considered an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank, with a per capita income of $4,906. However, it faces high rates of poverty, with 43% of its population living below the national poverty line. The country's economy is largely dependent on agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, with these sectors facing a range of challenges.
Belize's agricultural sector includes the production of citrus fruits, sugar, bananas, and fisheries. While this sector only employs about one-fifth of the population, it accounts for 13% of the country's GDP. Most farms are smaller than 100 acres and practice traditional shifting cultivation due to the nutrient-poor soils of the lowlands. The export crops are mainly sugarcane, citrus fruits, and bananas, with rice, corn, and beans also being produced for domestic consumption. The agricultural sector is influenced by weather conditions and vulnerable to fluctuations in world prices.
The manufacturing industry in Belize has been in decline, with utility costs outweighing value-added gains from limited food manufacturing and construction activities. Exports of manufactured products have decreased as a share of total exports, falling to just 7% in 2022. However, the sector still accounts for about one-eighth of the gross national product (GNP). The main manufacturing activities include food products, fertilizers, and textiles, with some construction materials production.
Tourism is a major source of foreign income for Belize, accounting for about 25% of the GDP and employing 25% of the working population. The country's attractions include the largest living coral reef in the world, Mayan ruins, and ecotourism opportunities. International tourism has surged back after a COVID-related decline, with revenues surpassing 2019 levels and annual arrivals nearing 1 million visitors. U.S. tourists account for a significant majority of international visitors, and the increase in tourism has been helped by U.S. economic expansion.
Belize's economy faces challenges such as high debt repayments, vulnerability to weather conditions, and the impact of global inflationary trends. However, the country has received aid from international donors and organisations, and its stable democratic government provides a favourable environment for economic development.
The Mountainous Secrets of Belize: Exploring a Country's Hidden Heights
You may want to see also

Belize's booming tourism industry employs 25% of working Belizeans
Belize is considered an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank, with a per capita income of $4,906. However, despite this classification, Belize faces high rates of poverty, with 43% of its population living below the national poverty line. The country's economy is largely dependent on agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, and it faces challenges such as high debt repayments and economic fluctuations due to its reliance on industries that are influenced by weather conditions.
Belize's booming tourism industry has become a significant contributor to its economy, employing 25% of working Belizeans. The country's natural attractions, such as its beaches, lush jungles, and the Belize Barrier Reef—the largest living coral reef in the world—draw divers, snorkelers, and nature enthusiasts from around the globe. The tourism industry in Belize accounts for 25% of the country's GDP and has been further boosted by US economic expansion.
The Belize Barrier Reef, located just off the country's coastline, is a major draw for tourists. As part of the larger Mesoamerican Barrier Reef, it is the second-largest coral reef system in the world, after Australia's Great Barrier Reef. The rich biodiversity of the reef, with its hundreds of species of coral and fish, makes it a popular destination for divers and marine enthusiasts.
In addition to its natural attractions, Belize also offers a range of cultural and historical experiences. Visitors can explore Mayan ruins in the Cayo District, pound on a Garifuna drum, or immerse themselves in the rich culture and history of Belize City. The country's diverse tourism offerings cater to a wide range of interests, from outdoor adventures to cultural exploration.
The growth of the tourism industry in Belize has had a positive impact on employment, with 25% of working Belizeans finding opportunities in this sector. This industry has the potential to contribute to the reduction of poverty in the country, providing income and economic growth. However, it is important to note that the industry is susceptible to external factors such as weather conditions and global economic fluctuations, which can impact its stability.
Island-Hopping in Belize: A Tropical Adventure Guide
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is considered to be stable
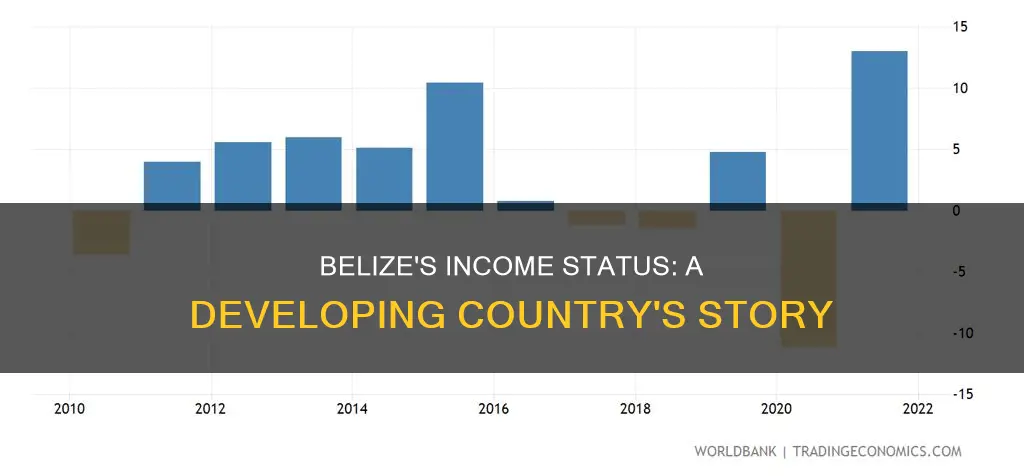
Belize's economy is stable, despite challenges such as high debt repayments, inflation, and poverty. In 2022, the country's gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 12.1%, following a 15.2% increase in 2021. The national debt-to-GDP ratio fell by 10% in 2022 due to international debt-relief programs and tighter public funds. Belize's economy is stable and growing, with a projected growth rate of 2-3% in the medium term.
Belize's economy is heavily dependent on tourism, which accounts for approximately 40% of the country's economy. International tourism has surged back after a steep COVID-19-related decline, with revenues surpassing pre-pandemic levels. The country's tourism industry is driven by its natural attractions, such as the largest living coral reef in the world, which attracts divers and marine enthusiasts.
Belize's economy is also supported by its agricultural sector, which includes exports of citrus, sugar, bananas, and seafood. In 2022, agricultural and seafood exports increased by 10.7% due to the removal of trade barriers and regional partnerships, particularly with Mexico.
While the manufacturing industry has been in decline, the construction sector has contributed to economic growth, with a focus on tourism-related construction.
Belize's stable economy is further evidenced by its stable currency, with the Belize dollar pegged to the US dollar since 1976. The country has a low unemployment rate of 5%, the lowest ever recorded.
Belize's economic stability is also reflected in its efforts to address poverty and reduce income inequality. While the country faces high rates of poverty, with 43% of the population living below the national poverty line, the government has implemented programs and received foreign aid to address these issues.
In summary, Belize's economy is considered stable due to its diverse sectors, stable government, and positive economic indicators, despite facing challenges such as high debt, inflation, and poverty.
Cayo District: Safe Haven for Expats?
You may want to see also

Belize's population is growing rapidly
Belize is considered an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank, with a per capita income of $4,906. Despite this classification, Belize faces high rates of poverty. Out of its population of around 416,656 people, 43% live below the national poverty line, with 16% facing extreme poverty.
The population growth in Belize can be attributed to several factors, including a low infant mortality rate, improved healthcare, and better living standards. Additionally, Belize's economy, primarily focused on agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, offers employment opportunities that attract immigrants and support population growth. The country's booming tourism industry, for example, employs 25% of the working population.
Belize's location and integration with global politics and trade also contribute to its population growth. Since gaining independence from the United Kingdom in 1981, Belize has become a member of several international organizations, including the United Nations and the Caribbean Community. These connections enhance Belize's economic prospects and make it an attractive destination for immigrants and investors alike.
The rapid population growth in Belize has implications for the country's social and economic development. It increases the demand for resources such as housing, healthcare, and education. Additionally, the growing population puts pressure on the environment, particularly regarding natural resource management and conservation.
Belize Packing List: Essentials for a Tropical Adventure
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is susceptible to external market changes
Belize is a small, private enterprise economy that is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and services. The country's economy is susceptible to external market changes, and any economic achievements are vulnerable to fluctuations in world commodity prices.
Belize's economy is heavily influenced by its trading partners, particularly the United States, its largest exporter and second-largest import destination. In 2022, the US accounted for $575 million, or 42% of Belize's overall imports, and $48 million, or 20% of its exports. The country's other major trading partners include the People's Republic of China, Mexico, the European Union, and other Central American countries. The economy is also impacted by its preferential trading agreements with the US, UK, and Guatemala.
Belize's agricultural sector, which includes exports of citrus, sugar, bananas, and seafood, is susceptible to fluctuations in world commodity prices. For example, the country's trade deficit has been growing due to low export prices for sugar and bananas. Additionally, the manufacturing industry has been in decline since 2017 due to high utility costs and has been further impacted by global inflationary trends.
The tourism industry, which accounts for approximately 40% of the country's economy, is also vulnerable to external market changes. While international tourism has rebounded post-COVID, with revenues surpassing 2019 levels, it is still susceptible to factors such as economic downturns, natural disasters, and changes in consumer behaviour.
Belize's reliance on imports and short-term market prices creates uncertainty and lowers investor confidence. The country also faces challenges such as high input costs, including utilities and fuel, which contribute to the high cost of doing business. Inflationary pressures, exacerbated by global events such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, have further impacted the country's economy.
Navigate Punta Gorda, Belize: Travel Tips
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, Belize is considered an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank. In 2016, it had a per capita income of US$4,906.
Tourism and agriculture are the main sources of income and employment in Belize.
Belize faces challenges to economic growth such as its dependence on foreign trade, a growing trade deficit, high debt repayments, and a lack of infrastructure investments.







