Austria's energy consumption per capita is 19% higher than the EU average. In 2023, the country's electricity consumption per capita was 8,900 kWh, which is 28% above the EU average. In 2021, Austria passed a Renewable-Expansion-Act, stipulating a goal of 100% renewable electricity by 2030. In 2016, Austria consumed 64,604,100 MWh of electricity.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Power consumed in 2016 | 64,604,100 MWh |
What You'll Learn
- Austria's energy consumption per capita is 19% higher than the EU average
- In 2021, Austria passed a Renewable-Expansion-Act, aiming for 100% renewable electricity by 2030
- Hydro power accounted for 58% of Austria's total power generation in 2022
- Austria's wind power capacity has grown from 77 MW in 2000 to 3,573 MW in 2023
- Austria imported 26,366,000 MWh of electricity in 2016, covering 41% of its annual consumption needs

Austria's energy consumption per capita is 19% higher than the EU average
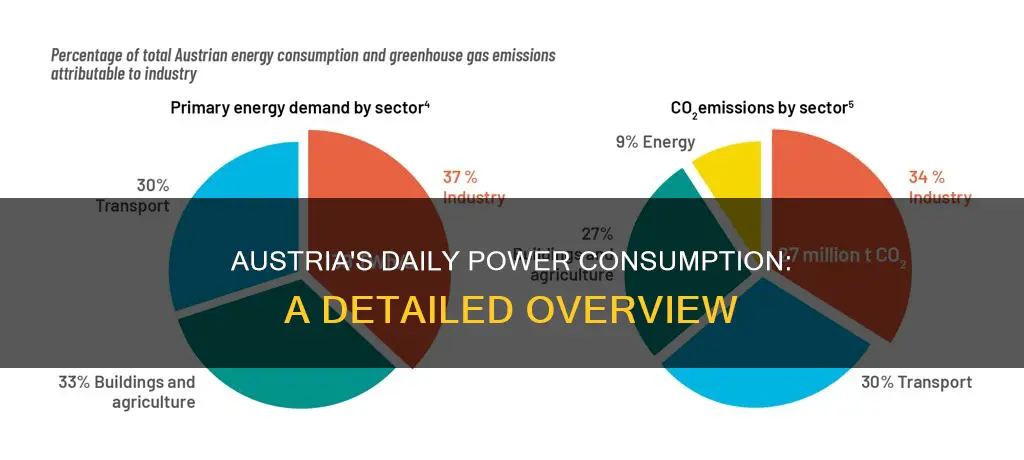
Austria's high energy consumption can be attributed to a variety of factors, including its reliance on imported oil and gas. In 2022, imported oil accounted for 35.4% of energy consumed in Austria, while gas accounted for 16.8%. Additionally, Austria has a large number of hydro energy plans in operation, with hydropower accounting for 54% of the country's total installed power generation capacity and 58% of total power generation in 2021. However, due to water shortages caused by climate change, hydropower generation has decreased in recent years.
To address its high energy consumption and reliance on imported fossil fuels, Austria has set ambitious renewable energy targets. In 2021, the country passed the Renewable-Expansion-Act, which aims to achieve 100% renewable electricity by 2030. This will require an additional 27 TWh of renewable power to be added to the country's energy mix. Austria also has a target of 34% renewable energy by 2020 and 100% self-sufficiency in energy by 2050. To meet these targets, Austria is expanding its wind and solar power capacity, with wind power capacity reaching 3,573 MW in 2023.
Overall, Austria's energy consumption per capita is significantly higher than the EU average, and the country is taking steps to transition to renewable energy sources and reduce its reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Where to Watch Netherlands vs Austria Match
You may want to see also

In 2021, Austria passed a Renewable-Expansion-Act, aiming for 100% renewable electricity by 2030
In 2016, Austria consumed 64,604,100 MWh of electricity. This was 94% of its annual consumption needs. In 2023, Austria's electricity consumption per capita was 8,900 kWh, 28% above the EU average.
In 2021, Austria passed a Renewable-Expansion-Act, stipulating a goal of 100% renewable electricity by 2030. This means that 27 TWh of renewable power needs to be added by 2030. The Act intends to contribute to the goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2040. It will promote electricity generation from hydropower, wind power, photovoltaics, solid biomass, and biogas. Auctions will be held to determine the awardees of feed-in premiums for solar PV, biomass and wind power plants.
Austria already has over 3,000 hydro energy plans in operation, and in 2021, hydropower provided 14.1 GW and accounted for 54% of Austria's total installed power generation capacity and 58% of total power generation. However, due to water shortages in the summer of 2022, hydropower generated less power. To meet the 2030 plan, an additional 1,500 MW of hydro energy capacity will be needed.
Austria also has plans to double its wind power capacity by 2030 by expanding existing wind parks and creating new ones. In 2023, wind power capacity reached 3,573 MW.
Austria's UEFA Champions League Contenders: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Hydro power accounted for 58% of Austria's total power generation in 2022
Austria's energy consumption per capita is 19% higher than the EU average at 3.3 toe (-5%) (2023). The country's electricity consumption per capita stands at 8,900 kWh, which is 28% above the EU average. In 2016, Austria generated 60,784,100 MWh of electricity, covering 94% of its annual consumption needs. In 2021, Austria passed a Renewable-Expansion-Act, stipulating a goal of 100% renewable electricity by 2030.
Austria has been making efforts to increase its renewable energy sources. In 2000, there was just 77 MW of wind capacity, which grew to 3,573 MW of wind power capacity in 2023. Some states in Austria have plans to double the 2021 wind power by 2030 by expanding existing wind parks and creating new ones.
Austrian Urban Exploration: Cities of Austria
You may want to see also

Austria's wind power capacity has grown from 77 MW in 2000 to 3,573 MW in 2023
In 2016, Austria generated 60,784,100 MWh of electricity, covering 94% of its annual consumption needs. However, the country also imported 26,366,000 MWh of electricity that year, accounting for 41% of its consumption.
Austria's energy consumption per capita is 19% higher than the EU average, and its electricity consumption per capita is 28% above the EU average. In 2021, the country passed the Renewable-Expansion-Act, aiming for 100% renewable electricity by 2030. To meet this goal, an additional 27 TWh of renewable power needs to be added.
Austria has a strong focus on hydropower, with over 3,000 hydro energy plans in operation. In 2021, hydropower provided 14.1 GW and accounted for 54% of the country's total installed power generation capacity and 58% of total power generation. However, due to water shortages caused by climate change, hydropower generation decreased in the summer of 2022.
Austria's Membership in the European Union: Explained
You may want to see also

Austria imported 26,366,000 MWh of electricity in 2016, covering 41% of its annual consumption needs
Austria's energy consumption per capita is 19% higher than the EU average. In 2016, the country generated 60,784,100 MWh of electricity, covering 94% of its annual consumption needs. In the same year, Austria consumed 64,604,100 MWh of electricity, importing 26,366,000 MWh (41% of its annual consumption needs) and exporting 19,207,000 MWh.
In 2021, Austria passed the Renewable-Expansion-Act, stipulating a goal of 100% renewable electricity by 2030. To meet this target, an additional 1,500 MW of hydro energy capacity will be needed. Austria has over 3,000 hydro energy plans in operation, with hydropower accounting for 54% of the country's total installed power generation capacity and 58% of total power generation.
In terms of wind power, Austria has made significant progress, increasing its wind power capacity from 77 MW in 2000 to 3,573 MW in 2023. Some states in Austria have ambitious plans to double wind power by 2030 by expanding existing wind parks and creating new ones.
Austrian Teenagers' Schooling Duration Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Austria consumed 64,604,100 MWh of electricity in 2016.
Imported oil accounted for 35.4% of energy consumed in 2022.
Austria imported 26,366,000 MWh of electricity in 2016, covering 41% of its annual consumption needs.







