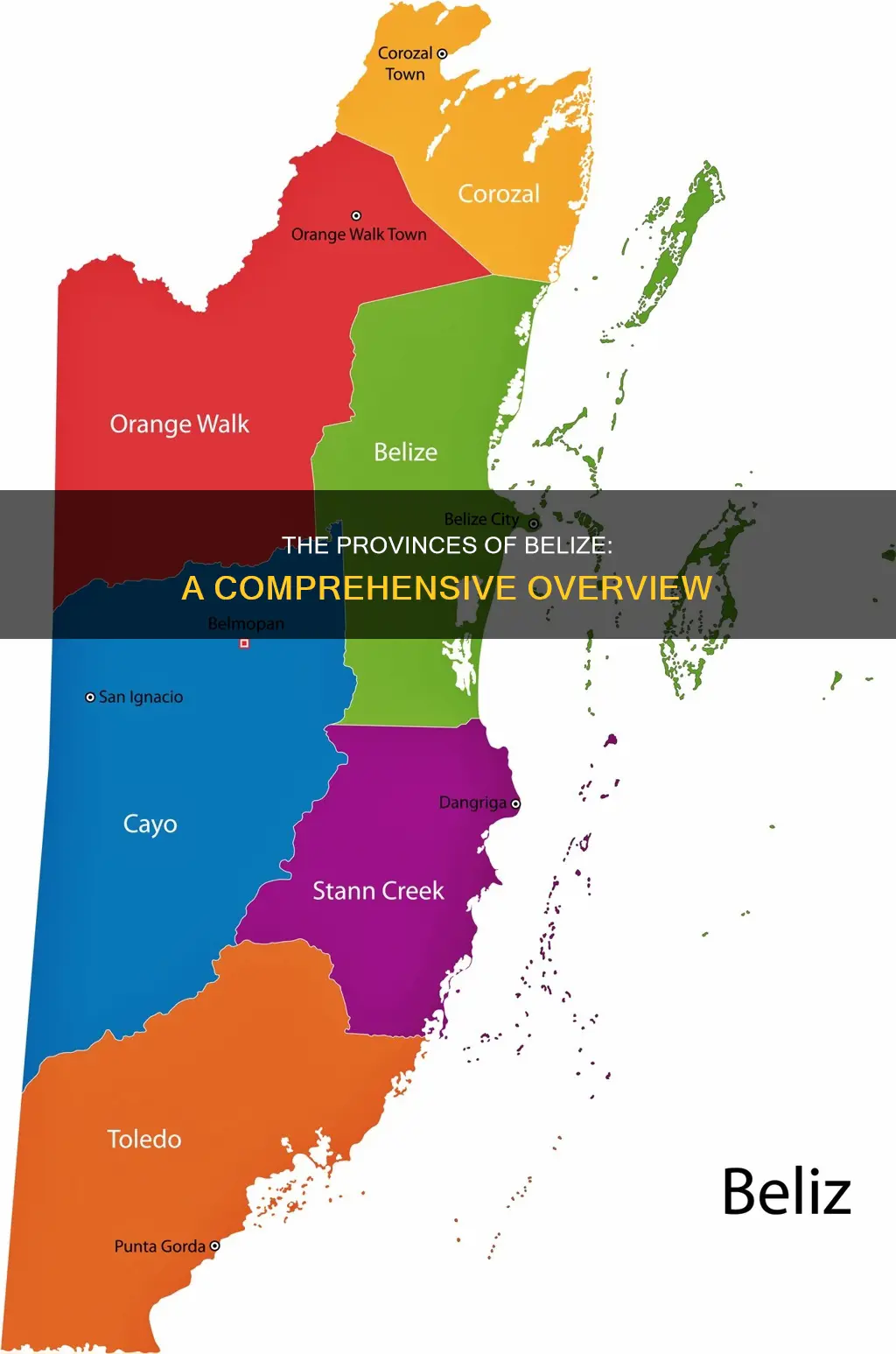
Belize is divided into six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo. Each district is further divided into several political constituencies. The capital of Belize, Belmopan, is located in Cayo, the country's largest district. Belize's most populous district, however, is Belize District, which is home to Belize City, the country's largest city.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of provinces | 6 |
| Names of provinces | Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo |
| Capital | Belmopan |
| Largest city | Belize City |
| Population | 397,483 (2022) |
| Area | 22,970 square kilometres (8,867 sq mi) |
| Population density (2019) | 28.8/km2 (74.6/sq mi) |
| Main attractions | Belize Barrier Reef, Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, Caracol, Lamanai, Altun Ha, Tikal |
What You'll Learn

Belize's six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo
Belize is divided into six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo. Each district has its own unique characteristics and attractions, showcasing the diverse culture and natural beauty of the country.
The Belize District is the most populated district in the country, with a population of 110,644. It includes the bustling city of Belize City and several offshore islands, such as Ambergris Caye and Caye Caulker. The district offers a range of tourist attractions, including the Nohoch Che'en Caves Branch and Archaeological Reserve, a series of limestone caves with the slow-moving Caves Branch River.
Cayo, the largest district by area, is home to the capital city of Belmopan and the town of San Ignacio. It borders the districts of Orange Walk, Belize, Stann Creek, and Toledo, as well as Guatemala to the west. Cayo boasts several ancient Maya sites, including Xunantunich, Cahal Pech, and Caracol, as well as national parks like The Blue Hole and Guanacaste.
Corozal, the northernmost district, is known for its beautiful blue waters and proximity to Mexico. The capital, Corozal Town, is just nine miles from the Mexican border, separated by the Rio Hondo river. Corozal has a rich history, established by Mestizo refugees during the Caste War of the Yucatan from 1847 to 1901.
Orange Walk, also known as "Sugar City," is located in the northwest of Belize. It is home to significant towns and villages, such as Carmelita, Guinea Grass Town, and San Estevan. The district offers cultural and natural attractions, including the Maya ruin of Lamanai and the Rio Bravo Conservation and Management Area, a large private nature reserve.
Stann Creek, located in the southeast region of Belize, is known for its production of citrus and bananas. The district includes the port of Big Creek, the main port for the country's banana industry, and the village of Placencia. Stann Creek is also home to the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, the only Jaguar reserve in the world.
Toledo is the southernmost district of Belize and is known for its organically grown cacao and world-renowned chocolatiers. The district celebrates the Chocolate Festival of Belize annually. Toledo has a rich Mayan history, with over 30 Mayan villages and Maya sites such as Nim Li Punit, Lubaantun, and Uxbenka. Monkey River Town is believed to be the last settlement of Creole people in Belize.
Each of Belize's six districts offers a unique blend of culture, history, and natural wonders, contributing to the country's vibrant and diverse character.
Belize Reef Lodging
You may want to see also

Belize's capital, Belmopan
Belize is divided into six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo. The capital of Belize is Belmopan, located in the Cayo District. Belmopan is the smallest capital city in the continental Americas by population, with a population of 16,451 in 2010. It is also one of the newest national capitals in the world, having been founded as a planned community in 1970.
Belmopan is situated 80 kilometres (50 miles) inland from the former capital, Belize City, on the Caribbean coast. The decision to move the capital inland was made after Belize City was devastated by Hurricane Hattie in 1961, which destroyed approximately 75% of the houses and business places in the low-lying coastal city. The new capital was built on higher ground to prevent future flooding disasters.
The name Belmopan is derived from the country's longest river, the Belize River, and the Mopan River, one of its tributaries. The city is located near the Belize River valley and the town of Roaring Creek, about 76 metres (249 feet) above sea level. The National Assembly Building in Belmopan is designed to resemble a Pre-Columbian Maya temple, with grey stone architecture and broad steps. The surrounding buildings mirror this ancient Mayan aesthetic.
Belmopan is a planned community, with the city layout centred around the Ring Road, which is just under 4 kilometres (2.5 miles) in circumference. The majority of government buildings are located within or around the Ring Road, and a large area within it is dedicated to parkland. The city has a tropical monsoon climate, with a lengthy wet season from May to January and a short dry season for the remaining three months.
Belmopan is the third-largest settlement in Belize, after Belize City and San Ignacio. It is known for its safety, well-planned infrastructure, and thriving business process outsourcing (BPO) industry, particularly call centres. The city has good road connectivity and is about an hour's drive from Belize City and two and a half hours from the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary. Belmopan also has a domestic airport, the Hector Silva Airstrip, although it currently has no scheduled flight services.
Belize's Blue Hole Mystery
You may want to see also

Belize's largest city, Belize City
Belize is divided into six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo. Belize City is located in the Belize District and is the country's largest city and former capital. It is also the country's main port and transportation hub, with the only international airport, an active municipal airport, a cruise ship dock, and terminals for major bus lines and water taxis.
Belize City is not a popular tourist destination, but it does offer some attractions, including the Museum of Belize, St. John's Cathedral, and the Belize Zoo. The city is known for its narrow streets, rundown appearance, and bustling metropolitan social scene. It is considered the commercial capital of Belize and has a population of over 80,000 people.
The city is divided into two areas: North Side Belize City and South Side Belize City. The North Side is considered the safer and more prosperous area, with good hotels, casinos, and tourist attractions. The South Side has some historic sites, such as St. John's Cathedral and the House of Culture, but it is generally less affluent and has a reputation for gang-related crimes.
Belize City has a rich history, dating back to the 1600s when it originated as a logging camp and export centre for mahogany. Over time, it has been influenced by various cultures, including the Maya, British and Scottish pirates, and Creole, Garifuna, Latino, Chinese, and Lebanese immigrants. The city's architecture reflects its past, with a mix of older colonial structures and newer concrete buildings.
While Belize City may not be the first choice for visitors seeking pristine beaches, it serves as a gateway to other parts of Belize, including the popular Northern Cayes & Atolls, Southern Belize, and the Cayo District.
The ICJ Belize Decision: Understanding the Ruling and Its Impact
You may want to see also

Belize's diverse society and languages
Belize is a diverse country with a unique linguistic landscape, characterised by multiple ethnic groups and languages. The country is divided into six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo. While English is the official language, Belizean Creole (or Kriol) is the most widely spoken language in day-to-day communication and serves as the country's lingua franca.
Belizean Creole
Belizean Creole is an integral part of the Belizean identity, spoken by about 45% of Belizeans. It is derived mainly from English, with substrate languages including Native American Miskito and various West African and Bantu languages. It has become an intrinsic part of Belizean culture, permeating music, storytelling, and daily communication.
Spanish
Spanish is widespread in Belize due to historical and demographic factors. It is commonly used in local communities, particularly those with high concentrations of Hispanic residents, and plays a significant role in commerce and cross-border trade. Many Belizeans also use Spanish as a second language.
Mayan Languages
Belize is home to three Mayan languages: Q'eqchi', Mopan, and Yucatec Maya. These languages are vital expressions of indigenous identity and cultural heritage, serving as repositories of collective memory and traditional knowledge. They are spoken by the Maya people, who have inhabited Belize and the Yucatán region since the second millennium BCE.
Germanic Languages
The Mennonite communities in Belize, primarily of German descent, contribute to the country's linguistic diversity with their use of Plautdietsch (a dialect of Low German) and Standard German. Mennonites are known for their expertise in farming and play an integral role in the production of various crops and dairy products.
Garifuna
The Garifuna language is a vital element of the Afro-Amerindian Garifuna community's cultural heritage. It is a blend of Indigenous Arawak, Carib, French, English, and Spanish. Garifuna is primarily spoken along the Caribbean coast of Central America and is recognised by UNESCO.
Belize's National Dish: A Cultural Fusion of Flavors
You may want to see also

Belize's history as a British colony
Belize is divided into six districts: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo. However, it was not always this way. Belize, previously known as British Honduras, was a British colony from 1783 until it gained independence in 1981. Here is a more detailed account of Belize's history as a British colony.
The Early Colonial Period
British Honduras was a Crown colony on the east coast of Central America, south of Mexico, from 1783 to 1964. The colony emerged from the Treaty of Versailles (1783) between Britain and Spain, which gave the British rights to cut logwood between the Hondo and Belize rivers. The British settlement in the Bay of Honduras was initially governed through public meetings and elected magistrates, as Spain prohibited them from establishing a formal government structure. However, superintendents appointed by the British government slowly established their executive authority. In 1798, the British resisted Spain's final attempt to remove them by force, and Belize became a de facto colony.
Expansion and Resistance
As the British pushed inland in search of mahogany in the late 18th century, they encountered resistance from the Maya. The Maya population had been in decline before the Spanish arrived, and they lived in politically decentralized societies. While they could not decisively defeat the Spanish, they also could not be conquered. The British-Spanish rivalry in the region was settled through a series of treaties. The 1763 and 1783 treaties granted British subjects the right to exploit logwood and, after 1786, mahogany within specified territories. The 1859 treaty between Britain and Guatemala defined boundaries for Belize but included an article that required the establishment of "the easiest communication" between Guatemala and Belize, which would later become a point of contention.
Formal Colonisation
In 1862, the Settlement of Belize in the Bay of Honduras was officially declared a British colony called British Honduras, ruled by a governor subordinate to the governor of Jamaica. The Legislative Assembly of British Honduras was established in 1854, consisting of 18 members elected by a limited franchise. The Laws in Force Act of 1855 validated the settlers' land titles. However, large landowners in the colony were given firm titles to their vast estates, while the Maya were not allowed to own land and could only rent or live on reservations. This period also saw the importation of African slaves to cut logwood and mahogany, with four slave revolts occurring in Belize.
Immigration and Diversification
In the 19th century, Belize saw an influx of immigrants and the diversification of its population. Carib Indians and Africans exiled from British colonies in the Caribbean (known as Garifuna) settled on the southern coast. The Caste War in the Yucatán led to thousands of Spanish-speaking refugees settling in northern Belize, and Mayan communities were re-established in the north and west. In the 1860s and 1870s, sugar estate owners sponsored the immigration of several hundred Chinese and South Asian labourers. In the late 19th century, Mopán and Kekchí Maya fled from oppression in Guatemala and settled in southern and western Belize, maintaining their traditional way of life and becoming less assimilated into the colony.
Towards Independence
In the early 20th century, the ethnic composition of British Honduras was largely set, but the economy was stagnant, and democratic participation was limited under crown colony government. The Great Depression of the 1930s and a destructive hurricane in 1931 further depressed the economy and living conditions. Labour agitation, strikes, and demonstrations by the unemployed gave rise to a trade union movement and demands for democratisation. Universal adult suffrage was adopted in 1954, and the People's United Party (PUP), formed in 1950, led the independence movement. British Honduras became a self-governing colony in 1964 and was renamed Belize in 1973. Belize finally gained full independence in 1981, though the territorial dispute with Guatemala remained unresolved.
Codicader Belize: Tech Tools and More
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are six districts in Belize: Belize, Cayo, Corozal, Orange Walk, Stann Creek, and Toledo.
Belize District is the most populated and has the country's only international airport. Cayo is the largest district and home to Belize's capital, Belmopan. Corozal is the northernmost district, with a strong Spanish influence. Orange Walk is known for its sugarcane industry. Stann Creek is home to the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary and coastal towns such as Dangriga and Placencia. Toledo is the southernmost district, known for its ecotourism and Mayan villages.
Belize District: Belize City, with historical sites such as St. John's Cathedral and the Museum of Belize.
Cayo: Caracol, a large Classic Maya city; Xunantunich, Pilar, and Cahal Pech ruins.
Corozal: Sarteneja and Consejo seaside villages, Santa Rita and Cerros Maya sites, Shipstern Nature Reserve.
Orange Walk: Lamanai Maya site, Rio Bravo Conservation and Management Area.
Stann Creek: Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, Hopkins and Placencia seaside villages.
Toledo: Punta Gorda, Monkey River Town, Mayan villages such as Blue Creek and San Pedro Columbia.







