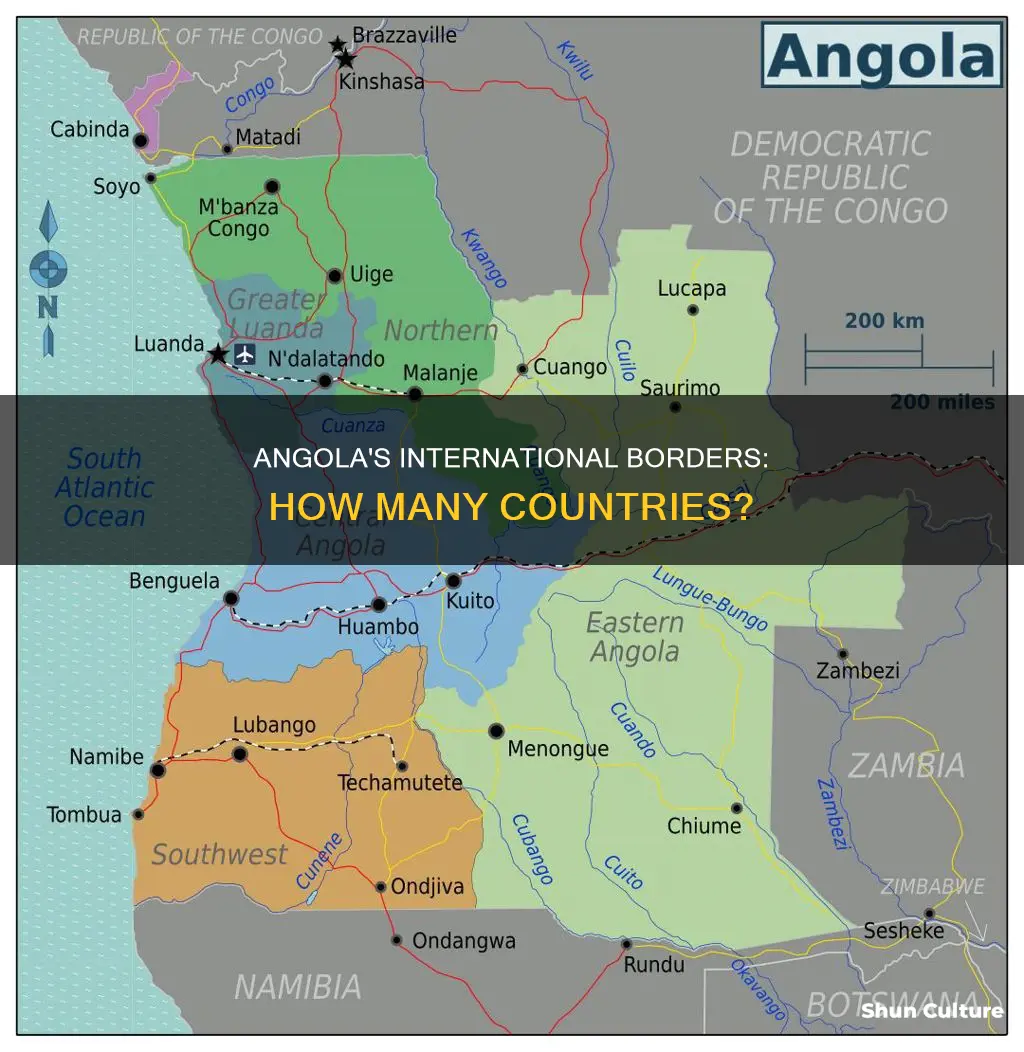
Angola is a large country located in southwestern Africa, with a population of over 33 million people (2022). It has a long coastline along the South Atlantic Ocean and a central plateau. Angola shares its land borders with Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Namibia. The country's border stretches a total of 3,336 miles. Angola's bordering nations played a role in its history, with the borders first established during the Scramble for Africa in the late 19th century when European powers divided the continent into colonies.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of Bordering Countries | 5 |
| Bordering Countries | Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Namibia, Botswana |
| Total Border Length | 3,336 miles |
| Republic of the Congo Border Length | 223 miles |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo Border Length | 1,644 miles |
| Zambia Border Length | 689 miles |
| Namibia Border Length | 886 miles |
What You'll Learn

Angola's border with the Democratic Republic of Congo
Angola shares a border with four countries: Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Namibia. The border with the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the longest of Angola's borders, stretching 2,646 km (1,644 mi). The border consists of two non-contiguous sections.
The first section, along the border with Angola's province of Cabinda, is 225 km (140 mi) long, running from the Atlantic Ocean to the tripoint with the Republic of the Congo. This section starts on the Atlantic coast, proceeding to the north-east by an irregular and then a straight line, before turning north and following the Luali River to the confluence with the Chiloango. From there, it follows the Chiloango as it flows north-east up to the tripoint with the Republic of the Congo.
The second section is much longer at 2,421 km (1,504 mi), running from the Atlantic to the tripoint with Zambia. This section starts at the estuary of the Congo River on the Atlantic Coast, following the river eastwards for a period before leaving it just north of the Angolan town of Noqui. It then proceeds in a roughly straight line eastwards, occasionally utilising rivers such as the Mpozo, Lufo, and Luvemba, before reaching the Lubishi River. From there, it follows the Lubishi briefly to its confluence with the Kwango and then the Kwango as it flows south before turning east at the confluence with the Utunguila. The border then continues eastwards, utilising a number of rivers, including the Kasai and Luao, and straight overland lines, before reaching the Zambian tripoint.
The border between Angola and the DRC was first demarcated in the 19th century during the Scramble for Africa, when European colonial powers divided the African continent into colonies. During this time, the DRC was recognised as a Belgian colony, while Angola was a Portuguese colony. Despite the border being recognised by both countries, it continues to experience illegal crossings and smuggling, which pose security and economic threats.
Angola's Enclave: A Unique Territory
You may want to see also

Angola's border with Zambia
Angola is bordered by Zambia to the east. The border between the two countries stretches 689 miles in length, starting from the tripoint connecting the two countries to the Democratic Republic of the Congo and moving south until the tripoint linking Namibia, Angola, and Zambia. The border was first established in the 19th century by European colonial powers, and the nations agreed to retain the demarcation of the border after gaining independence in the 20th century.
The border between Angola and Zambia is porous, with numerous border crossings where border officials monitor cross-border movement. One of these border crossings is the Caripande-Chavuma border post, which connects the Zambian town of Chavuma to the town of Caripande in Angola. The border post is popular among tourists who use it to access the picturesque Chavuma Falls, which lie near the border post.
Despite the presence of border crossings, the border is quite porous and witnesses a high number of border crossings. Security agencies on both sides of the border frequently make arrests of people who have made illegal crossings.
Airports in Angola: How Many Are There?
You may want to see also

Angola's border with Namibia
Angola is situated on the western coast of Southern Africa and shares its borders with Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Namibia. The border between Angola and Namibia spans 886 miles in length and follows the natural course of two major rivers: the Kavango River and the Cunene River. The Cunene River also serves as the starting point of the maritime boundary between the two countries, as established in a 2002 bilateral agreement.
The border between Angola and Namibia is a remnant of colonial occupation in southwest Africa, established in the late nineteenth century during the Scramble for Africa. It trends east-west along a line of constant latitude and divides the traditional lands of the Ovambo people. The straight and distinct border stands in contrast to the natural landscape, which is characterised by the rugged highlands of the south and the semi-arid Atlantic littoral bordering Namibia's Skeleton Coast.
The border crossings between Angola and Namibia include Katitwe, Omahenene, Rundu, Ruacana, and Oshikango. During the Angolan Civil War, thousands of Angolans crossed into Namibia between 1999 and 2002, causing a significant humanitarian challenge in the bordering region. Many refugees settled in the Osire camp near the international border and were later repatriated to their home country after the war ended in 2002.
While the border is quite porous, with a high number of crossings, security agencies on both sides make arrests for illegal border crossings. Smuggling is also a significant issue, with cheap products from Angola being smuggled into Namibia, impacting the economic well-being of the country. The border experienced a temporary closure in 2016 when the Democratic Republic of the Congo, which borders both countries, faced an Ebola outbreak.
The High Cost of Living in Angola
You may want to see also

Angola's border with Botswana
Angola is a country located in southwestern Africa. It shares land borders with Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Namibia. In addition to these four bordering countries, Angola also has a border with Botswana in the form of a geographic salient known as the Caprivi Strip, which protrudes from the northeastern corner of Namibia.
The Caprivi Strip, also known simply as Caprivi, is a narrow piece of land that provides a corridor for African elephants moving from Botswana and Namibia into Angola, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The Strip is home to a diverse range of wildlife and natural habitats, including the critically endangered African wild dog. It is also rich in mineral resources and provides access to the Zambezi River, which has been historically sought after as a potential trading route to Africa's East Coast.
The Cuando River forms part of the border between Botswana and Angola within the Caprivi Strip. The width of the Strip varies from 32 km to 105 km, and its largest settlement is Katima Mulilo, located where the Zambezi River meets the Strip.
The Caprivi Strip has played a significant role in regional conflicts, including the Rhodesian Bush War (1964-1979) and the Angolan Civil War (1975-2002). During these conflicts, the Strip saw continuous military action and was used as a corridor to access other territories.
While Angola and Botswana do not share a direct land border, the Caprivi Strip creates a unique geographic situation where the two countries' territories come close to each other, separated only by a narrow strip of land belonging to Namibia.
Angola's Urban Evolution: Advanced Cities?
You may want to see also

Angola's Cabinda exclave
Angola is bordered by Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Namibia. In addition, the country has an exclave known as Cabinda, which is separated from the rest of Angola by a strip of territory belonging to the Democratic Republic of Congo. The exclave is bordered by the Republic of the Congo to the north and the Democratic Republic of Congo to the south and east, with the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
Cabinda, also known as Tchiowa, Tsiowa, or Kiowa in the local language, is a province of Angola with an area of 7,290 square kilometres and a population of over 700,000 people. The region is rich in natural resources, particularly oil, with some of the largest offshore oil fields in the world located adjacent to its coast. The discovery of these oil fields in 1967 led to a shift in Cabinda's economy, with the production of timber, palm oil, cocoa, and coffee declining in favour of oil extraction. Oil now accounts for the majority of Cabinda's domestic product and exports.
The history of Cabinda is closely tied to the colonial powers that have occupied the region. In the mid-15th century, Portuguese explorers made contact with the Manikongo, the powerful King of the Bakongo tribe, who controlled much of the region. Over time, the Portuguese established trading posts and small factories in the area, alongside other European powers. This led to conflicts between the rival colonial powers, with the territory of Cabinda changing hands several times. In 1885, the Treaty of Simulambuco established Cabinda as a protectorate of the Portuguese Empire, separate from Portuguese West Africa (Angola). This treaty is often cited as the basis for Cabinda's modern-day self-determination claims.
Despite gaining independence from Portugal in 1975, Cabinda was invaded by forces from the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and incorporated into Angola as a province. This led to a prolonged conflict in the region, with various factions of the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda (FLEC) and other groups fighting for Cabinda's independence. The conflict has persisted despite a peace accord signed in 2006, with skirmishes and attacks occurring sporadically. The status of Cabinda remains disputed, with a secessionist movement advocating for self-rule and the recognition of Cabinda as an independent republic.
Travel Distance: Angola, Indiana to McCook, Illinois
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Angola shares its land borders with 4 countries: Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, and Namibia.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has the longest border with Angola, spanning 1,644 miles.
The total border of Angola is 3,336 miles long.
Namibia is the country that borders Angola to the south.
No, there are no territorial disputes between the two countries.







