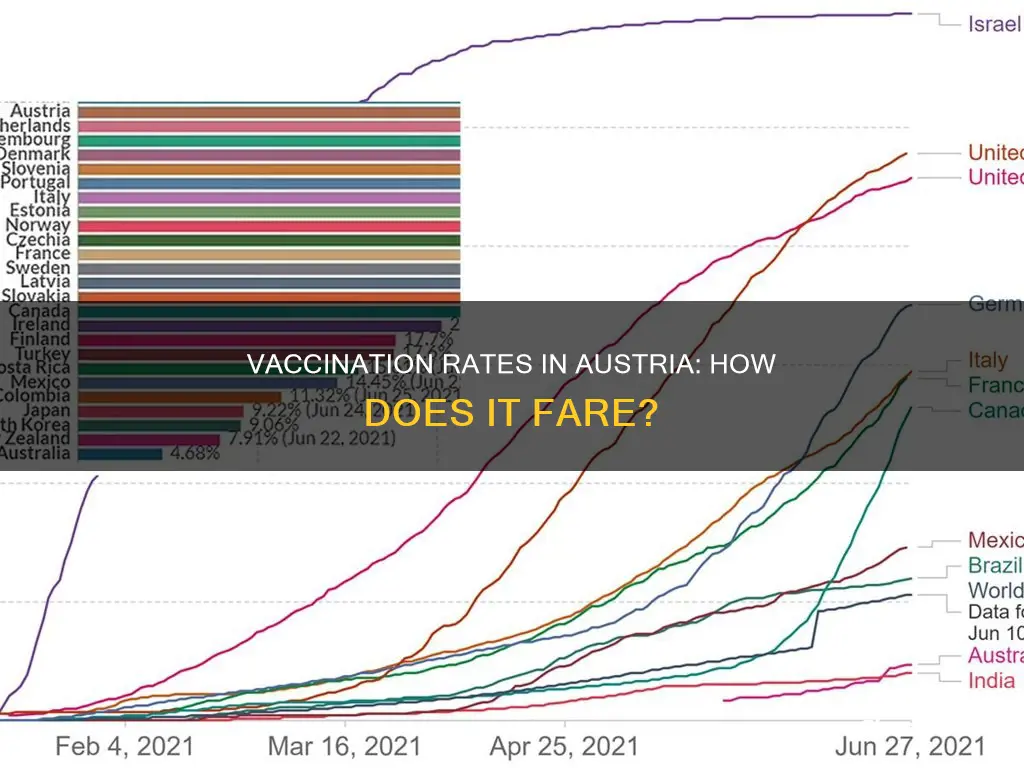
Austria has one of the lowest rates of Covid-19 vaccination in Western Europe, with only 65% of the population fully vaccinated. The Austrian government has introduced measures to encourage the unvaccinated to get inoculated, including a lockdown for those not fully vaccinated. The country has seen a surge in infections, with new case numbers plummeting since the start of the lockdown.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Percentage of population fully vaccinated against Covid-19 | 65% |
| Percentage of adults (18+) fully vaccinated against Covid-19 | 74% |
| Percentage of population fully vaccinated against Covid-19 (later date) | 67.7% |
What You'll Learn
- % of Austria's population is fully vaccinated against COVID-19
- The Austrian government wants to avoid imposing restrictions on the fully vaccinated
- The far-right Freedom Party encourages vaccine scepticism
- % of adults aged 18 and over are fully vaccinated
- The Austrian government has introduced measures to pressure unvaccinated people to get inoculated

65% of Austria's population is fully vaccinated against COVID-19
Approximately 65% of Austria's population is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, which is one of the lowest rates in Western Europe. The Austrian government has said it wants to avoid imposing further restrictions on those who are fully vaccinated, instead putting increasing pressure on unvaccinated people to get inoculated.
Many Austrians are sceptical about vaccines, a view encouraged by the far-right Freedom Party, the third biggest in parliament. In November 2021, Austria ordered a nationwide lockdown for those not fully vaccinated against Covid-19. Under the lockdown, the unvaccinated could only leave their homes for a limited number of reasons, such as going to work or shopping for essentials.
Austria's conservative-led government has said it wants to raise the vaccination rate. However, the country has seen a relatively low rate of vaccination compared to other Western European countries. As of December 2021, 67.7% of the population was fully vaccinated.
With immunity waning and the Omicron variant looming, many scientists are saying the definition of 'fully vaccinated' should include a booster shot.
Austria's View on Hispanics: Prejudice or Acceptance?
You may want to see also

The Austrian government wants to avoid imposing restrictions on the fully vaccinated
Austria has one of the lowest vaccination rates in Western Europe, with around 65% of the population fully vaccinated against COVID-19. Despite this, the Austrian government has been reluctant to impose restrictions on those who are fully vaccinated.
The government has stated that it wants to avoid imposing further restrictions on the fully vaccinated, even as it introduced a nationwide lockdown for those who are not fully vaccinated. Austrian Health Minister Wolfgang Mückstein said that those aged 12 and under would be exempt from the lockdown, which only applies to the unvaccinated.
The conservative-led government has instead focused on encouraging more people to get vaccinated, with Health Minister Wolfgang Mückstein saying, "We must raise the vaccination rate. It is shamefully low." Austrian officials have stressed that high rates of vaccination are necessary to control the virus. To put pressure on unvaccinated people to get inoculated, the government has introduced measures such as ending lockdown restrictions only for vaccinated people.
The Austrian government's approach recognises that lockdowns and other restrictions have significant social and economic costs. By focusing on increasing vaccination rates, the government aims to protect public health while minimising the impact on people's daily lives and the country's economy. This strategy also acknowledges that lockdowns are unpopular and may face resistance, especially from those who are already sceptical about vaccines.
Overall, the Austrian government's decision to avoid imposing restrictions on the fully vaccinated reflects its commitment to balancing public health concerns with the need to preserve individual freedoms and promote economic stability. By encouraging vaccination and providing incentives, such as the lifting of lockdown restrictions, the government aims to increase vaccination rates and control the spread of the virus.
Austria's Fragrance Fakes: What's Real and What's Not?
You may want to see also

The far-right Freedom Party encourages vaccine scepticism
Approximately 65% of Austria's population is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, which is one of the lowest rates in Western Europe. Many Austrians are sceptical about vaccines, a view encouraged by the far-right Freedom Party, the third biggest in parliament.
The Freedom Party's stance on vaccines has contributed to the country's low vaccination rate, which has been described as "shamefully low" by Chancellor Schallenberg. The Austrian government has introduced measures to put increasing pressure on unvaccinated people to get inoculated, including a nationwide lockdown for those who are not fully vaccinated.
The Freedom Party's encouragement of vaccine scepticism has had a significant impact on public opinion in Austria. A large proportion of the population remains hesitant or opposed to vaccination, even as the country faces a surge in COVID-19 infections. This has led to a situation where the government has had to impose restrictions on the unvaccinated to control the spread of the virus.
The Freedom Party's stance on vaccines is at odds with the Austrian government's efforts to increase vaccination rates and protect public health. By encouraging vaccine scepticism, the party has contributed to a polarised environment where public health measures are highly politicised. This has made it more difficult for the government to implement effective policies to control the pandemic and protect the health and safety of its citizens.
Babaria in Austria: Exploring the Connection
You may want to see also

74% of adults aged 18 and over are fully vaccinated
In Austria, 74% of adults aged 18 and over are fully vaccinated against Covid-19. This is one of the lowest rates in Western Europe, with 65% of the total population fully vaccinated.
Austria's conservative-led government has said it wants to avoid imposing further restrictions on those who are fully vaccinated. However, the country has introduced measures to put increasing pressure on unvaccinated people to get inoculated. For example, in November 2021, Austria ordered a nationwide lockdown for those not fully vaccinated against Covid-19. During the lockdown, the unvaccinated could only leave their homes for a limited number of reasons, such as going to work or shopping for essentials.
The low vaccination rate in Austria has been attributed to vaccine scepticism, which is encouraged by the far-right Freedom Party, the third biggest in parliament. In response to the low vaccination rate, Austrian Chancellor Alexander Schallenberg said, "We must raise the vaccination rate. It is shamefully low."
With the emergence of the Omicron variant, scientists are debating whether the definition of 'fully vaccinated' should include a booster shot.
Courtesy in Austria: A Guide to Local Phrases and Customs
You may want to see also

The Austrian government has introduced measures to pressure unvaccinated people to get inoculated
Austria has one of the lowest Covid-19 vaccination rates in Western Europe, with only 65% of the population fully vaccinated. The Austrian government has introduced measures to pressure unvaccinated people to get inoculated.
In November 2021, Austria ordered a nationwide lockdown for those not fully vaccinated against Covid-19. The unvaccinated could only leave their homes for a limited number of reasons, such as going to work or shopping for essentials. The government said it wanted to avoid imposing further restrictions on those who were fully vaccinated.
Austrian officials have stressed that high rates of vaccination are necessary to control the virus. The country's health minister, Wolfgang Mückstein, said that those aged 12 and under would be exempt from the lockdown.
The Austrian government's measures to pressure unvaccinated people to get inoculated have been effective. Since the start of the lockdown, new case numbers have plummeted. On 11 December 2021, Austria reported 367.5 new infections per 100,000 inhabitants, down from 1,102.4 on the first day of the lockdown in November.
However, hospitalizations from the coronavirus haven't dropped as sharply as new case numbers. There are currently 567 coronavirus patients in intensive care units across the country, only slightly down from 572 on the first day of the lockdown. With immunity waning and the Omicron variant looming, many scientists are saying the definition of 'fully vaccinated' should include a booster shot.
The Austrian Krampus: Folklore and Traditions
You may want to see also







