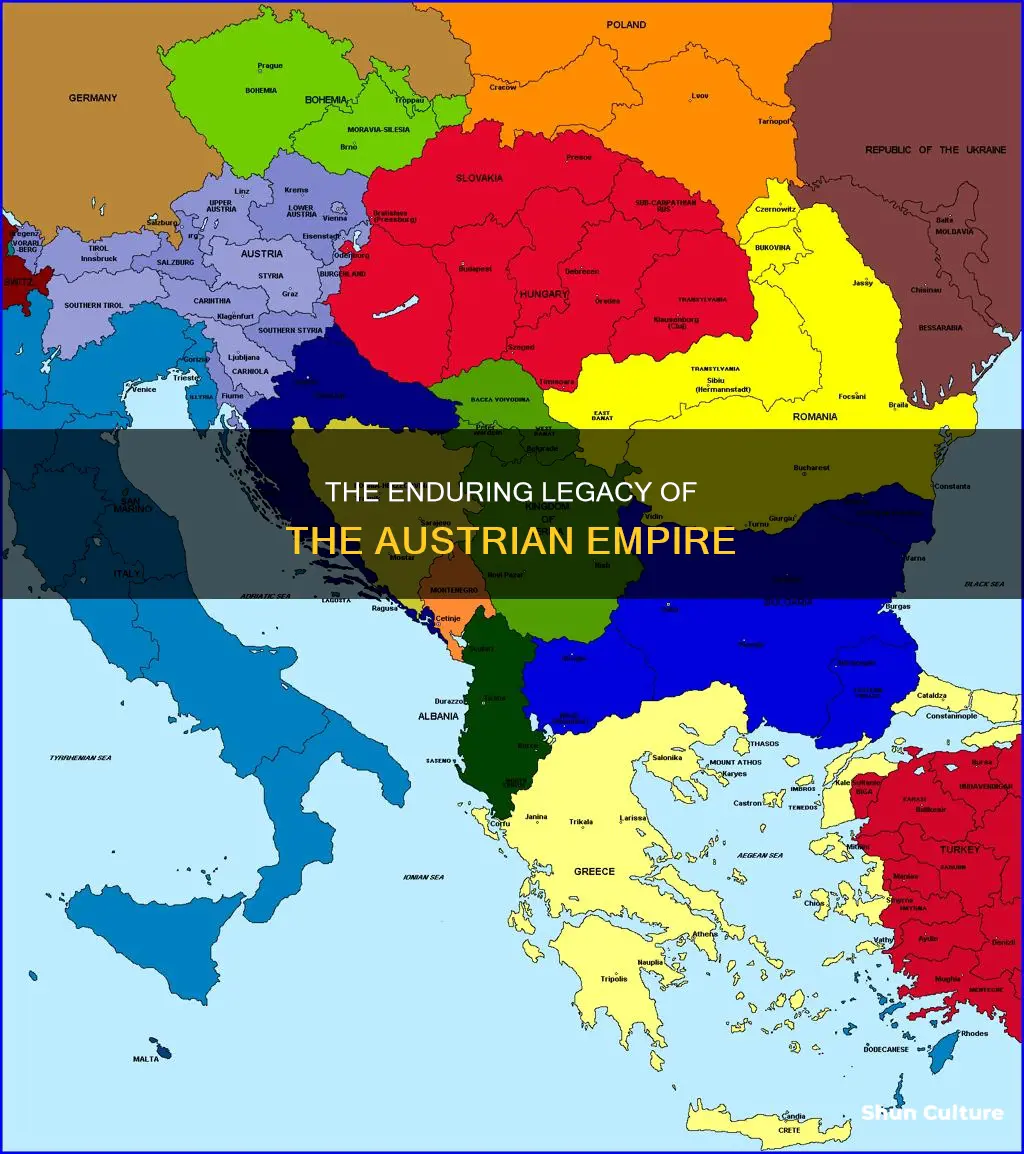
The Austrian Empire, a significant European power from the late 18th to the early 20th century, was characterized by its rich cultural diversity and complex political structure. It was a multi-ethnic state, encompassing a wide range of nationalities and religious groups, which presented both challenges and opportunities for its rulers. The empire's influence extended across Central Europe, with its capital, Vienna, becoming a cultural and political hub renowned for its architecture, music, and intellectual life. This introduction sets the stage for exploring specific aspects of the Austrian Empire's history, culture, and impact on the broader European context.
What You'll Learn
- Geographical Extent: The Austrian Empire encompassed diverse territories across Central Europe
- Political Structure: It was a multi-ethnic state with a complex administrative system
- Cultural Influence: Vienna became a cultural hub renowned for its music and architecture
- Military Power: The Empire's military prowess was evident in numerous conflicts
- Economic Growth: Industrialization and trade flourished, shaping the Empire's economic landscape

Geographical Extent: The Austrian Empire encompassed diverse territories across Central Europe
The Austrian Empire, a significant European power in the 19th century, boasted an extensive geographical reach that spanned diverse territories across Central Europe. At its zenith, the empire's borders stretched from the North Sea in the north to the Adriatic Sea in the south, encompassing a vast array of landscapes and cultures. This geographical expanse included the modern-day countries of Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, parts of Italy, and significant portions of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary. The empire's territory was characterized by a rich diversity of landscapes, ranging from the mountainous regions of the Alps and the Carpathians to the fertile plains of the Danube River Valley.
One of the empire's most notable geographical features was the Danube River, which played a crucial role in transportation, trade, and the development of various regions within the empire. The river served as a natural boundary and a vital trade route, connecting the empire's diverse territories and facilitating economic growth. The Danube's banks were dotted with bustling cities, such as Vienna, Budapest, and Bratislava, which became centers of culture, commerce, and political power.
The Austrian Empire's geographical extent also included several important mountain ranges. The Alps, stretching across the empire's northern border, presented a formidable natural barrier and a challenge for travel and communication. Despite the challenges, the Alps were a source of natural beauty and attracted tourists and adventurers from across Europe. Similarly, the Carpathian Mountains, located in the empire's eastern regions, played a significant role in defining the empire's borders and influencing the cultural and economic development of the surrounding areas.
In addition to the Alps and the Carpathians, the empire's territory was marked by several other notable geographical features. The Bohemian Forest, for instance, was a dense forest region that provided timber and served as a natural barrier between the Austrian Empire and the neighboring Kingdom of Bohemia. The Pannonian Plain, located in the western part of the empire, was a fertile agricultural region known for its rich soil and abundant crop production.
The Austrian Empire's diverse geographical landscape was not only a result of its extensive borders but also the product of historical developments and political decisions. The empire's expansion was influenced by various factors, including military conquests, treaties, and the unification of diverse territories under a single rule. The empire's ability to govern and administer such a vast and varied territory was a testament to its administrative prowess and the skills of its rulers.
IQOS in Austria: Your Ultimate Shopping Guide
You may want to see also

Political Structure: It was a multi-ethnic state with a complex administrative system
The Austrian Empire, a significant European power in the 19th century, was indeed a multi-ethnic state, encompassing a diverse range of nationalities and cultures within its borders. This diversity presented both challenges and opportunities for the empire's political structure. The empire's administrative system was intricate and designed to manage this complexity, reflecting the need to govern a vast and varied territory.
At the heart of the empire's political structure was the central government, which held significant power and was responsible for key decision-making processes. This central authority was crucial in maintaining order and ensuring the efficient functioning of the state, especially in a multi-ethnic setting. The central government's role was to oversee and coordinate the diverse regions, each with its own unique characteristics and needs.
The administrative system of the Austrian Empire was characterized by a hierarchical structure. At the top were the imperial courts, which held supreme authority and were responsible for interpreting laws and making high-level decisions. Below this were various administrative bodies, including ministries and departments, each with specific responsibilities. These bodies were tasked with managing everything from taxation and finance to education and infrastructure, ensuring the smooth operation of the empire.
One of the key challenges for the empire's administration was the management of its diverse ethnic groups. The empire included significant populations of Germans, Hungarians, Poles, Czechs, and others, each with their own cultural and linguistic traditions. The administration had to navigate these differences, often requiring a delicate balance of policies to ensure the rights and interests of all groups were respected. This involved creating and implementing policies that could accommodate the unique needs and identities of each ethnic community while also maintaining a unified state.
The complexity of the administrative system was further emphasized by the empire's territorial expansion. As the Austrian Empire grew, so did the complexity of governing it. The administration had to adapt to new territories, integrate them into the existing system, and ensure that the rights and privileges of all citizens were upheld. This required a sophisticated approach to governance, including the development of efficient communication networks and the establishment of local administrative structures that could effectively serve the diverse populations.
In summary, the Austrian Empire's political structure was a sophisticated and complex system designed to manage a multi-ethnic state. The central government played a pivotal role in overseeing this diversity, while the hierarchical administrative structure ensured the efficient functioning of the empire. The challenge of governing a wide range of ethnic groups and territories required a nuanced approach, and the empire's administrators had to navigate these complexities to maintain order and ensure the well-being of all citizens.
Exploring CPE Bach's Austrian Classical Period Compositions
You may want to see also

Cultural Influence: Vienna became a cultural hub renowned for its music and architecture
The Austrian Empire, particularly during the 19th century, played a significant role in shaping European culture, with Vienna at its heart becoming a renowned cultural center. This period witnessed the flourishing of the arts, music, and architecture, leaving an indelible mark on the city's identity.
Music was an integral part of Vienna's cultural scene, and the city became a mecca for composers and musicians. The court of Emperor Francis II and later, Emperor Ferdinand I, attracted some of the greatest musical talents of the time. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Franz Schubert were among the composers who found inspiration and patronage in Vienna. The city's opera houses, such as the Burgtheater and the Vienna State Opera, became prestigious venues, hosting world-class performances and attracting audiences from across Europe. The annual Vienna Music Festival further solidified the city's musical reputation, showcasing the works of local and international composers.
Architecture also flourished under the Austrian Empire's rule, with Vienna becoming a showcase of architectural styles. The city underwent a transformation, with grand buildings and monuments adorning its streets. The Ringstraße, a circular boulevard, became the centerpiece of Vienna's architectural splendor. It featured impressive structures like the Vienna City Hall, the Parliament Building, and the Burgtheater, all designed in a blend of Renaissance and Baroque styles. The iconic Schönbrunn Palace, with its magnificent gardens, and the Belvedere Palace, known for its elegant architecture, further contributed to Vienna's architectural allure.
The cultural influence of the Austrian Empire extended beyond its borders. Vienna's musical legacy inspired and influenced composers worldwide, and its architectural styles were emulated in many European cities. The city's reputation as a cultural hub attracted artists, writers, and intellectuals, fostering an environment of creativity and innovation. This cultural exchange and the empire's patronage of the arts contributed to the development of a rich and diverse cultural heritage that continues to shape Vienna's identity even today.
In summary, the Austrian Empire's rule over Vienna brought about a cultural renaissance, making the city a beacon of music and architecture. The patronage of the arts, the presence of renowned composers and musicians, and the architectural masterpieces all contributed to Vienna's status as a cultural capital, leaving a lasting impact on European culture.
The Dark Legacy: Austria's Hidden Concentration Camps
You may want to see also

Military Power: The Empire's military prowess was evident in numerous conflicts
The Austrian Empire, a formidable military power in the 19th century, left an indelible mark on European history through its military prowess and strategic achievements. Its military strength was a cornerstone of its influence, enabling it to navigate complex geopolitical landscapes and maintain its position as a major player in the continent's affairs.
The Empire's military might was underpinned by a well-organized and disciplined army, renowned for its efficiency and tactical expertise. The Austrian military was structured with a hierarchical system, ensuring a clear chain of command and effective coordination on the battlefield. This structure allowed for swift decision-making and the implementation of innovative strategies, which were often ahead of their time. The Empire's military leaders, such as Archduke Karl and Emperor Franz Joseph, were known for their strategic brilliance and ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
One of the Empire's most significant military achievements was its role in the Napoleonic Wars. Despite being outnumbered and facing formidable opponents, the Austrians consistently demonstrated resilience and tactical ingenuity. The Battle of Austerlitz, for instance, is a testament to their military prowess, where they inflicted a decisive defeat on the French army, led by Napoleon Bonaparte. The Austrians' ability to counter Napoleon's military genius showcased their strategic depth and tactical flexibility.
The Empire's military success was not limited to the Napoleonic era. In the early 19th century, the Austrians played a crucial role in the Italian Wars, successfully defending their territories and expanding their influence in the region. The Battle of Marengo, fought against Napoleon's forces, further solidified the Empire's military reputation. Additionally, the Austrians' involvement in the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 showcased their ability to maintain internal stability while engaging in external conflicts.
The Austrian Empire's military prowess extended beyond its own borders, as it frequently collaborated with other European powers. The Empire's military alliances, such as the Holy Alliance, were instrumental in shaping the political landscape of the time. Through these alliances, the Austrians contributed to the balance of power, ensuring the stability of the European continent. The Empire's military influence also extended to its colonies, where it maintained a strong presence and effectively administered its territories.
Mailing Chocolate to Austria: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Economic Growth: Industrialization and trade flourished, shaping the Empire's economic landscape
The Austrian Empire, a significant European power in the 19th century, experienced remarkable economic growth and transformation during this period. One of the key factors contributing to this growth was industrialization, which brought about a series of changes in the Empire's economy.
Industrialization in the Austrian Empire was a response to the rapid industrialization in neighboring countries, particularly Germany and Britain. The Empire recognized the potential benefits of industrialization, including increased productivity, improved infrastructure, and the development of new industries. The government played a crucial role in this process by providing incentives and support to entrepreneurs and investors. They established factories and workshops, particularly in the regions of Bohemia and Moravia, which became centers of textile production, glass manufacturing, and machinery. These industries attracted a significant workforce, leading to urbanization and the growth of cities.
The Empire's economy flourished due to its strategic location, which facilitated trade and commerce. The Austrian Empire was a major hub for international trade, connecting Central Europe with the Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions. The development of efficient transportation networks, including railways and canals, further enhanced trade. Vienna, the capital, became a bustling commercial center, with a thriving financial sector and a stock exchange. The Empire's ports, such as Trieste and Fiume, became vital gateways for international trade, exporting goods like textiles, machinery, and agricultural products.
Trade policies also played a significant role in the Empire's economic success. The government implemented free trade agreements, reducing tariffs and fostering international commerce. This encouraged the establishment of numerous trading companies and banks, further stimulating economic growth. The Empire's participation in international expositions and fairs showcased its industrial and agricultural achievements, attracting foreign investments and fostering economic cooperation.
The economic prosperity of the Austrian Empire had a profound impact on its society. It led to the emergence of a wealthy industrial class, who invested in further development and contributed to the Empire's cultural and intellectual life. The Empire's economic growth also improved living standards, reduced poverty, and created opportunities for social mobility. Additionally, the Empire's economic success contributed to its political stability, as a prosperous economy often leads to a more content and satisfied population.
Charles VI's Legacy: Maria Theresa's Royal Connection
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Austrian Empire, also known as the Austrian Monarchy, was a vast empire centered in Central Europe. Its primary territories included the modern-day countries of Austria, Switzerland, parts of Italy, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, and Hungary, as well as significant regions in Germany, Croatia, and Slovenia.
The empire played a significant role in the development of classical music. Vienna, the imperial capital, became a hub for composers and musicians during the Classical and Romantic periods. Composers like Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Franz Schubert were associated with the court and contributed to the city's musical reputation. The empire's patronage and cultural policies fostered an environment conducive to musical innovation and the emergence of renowned musical institutions.
In the 19th century, the Austrian Empire was a major European power and a key player in the balance of power. It was known for its strong military, efficient bureaucracy, and cultural influence. The empire's involvement in the Napoleonic Wars and its subsequent role in the Congress of Vienna helped shape the political landscape of Europe. The Austrian Empire also contributed significantly to the fields of science, philosophy, and literature, with many of its intellectuals and artists leaving a lasting impact on European culture.
The dissolution of the Austrian Empire after World War I led to significant political and territorial changes. The empire's multi-ethnic composition resulted in the establishment of several new states, including Austria, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia. The process of nation-building and the redrawing of borders often involved complex ethnic and cultural considerations, leading to tensions and conflicts in the region. The aftermath of the empire's dissolution also had long-lasting effects on the political and social structures of Central and Eastern Europe.







