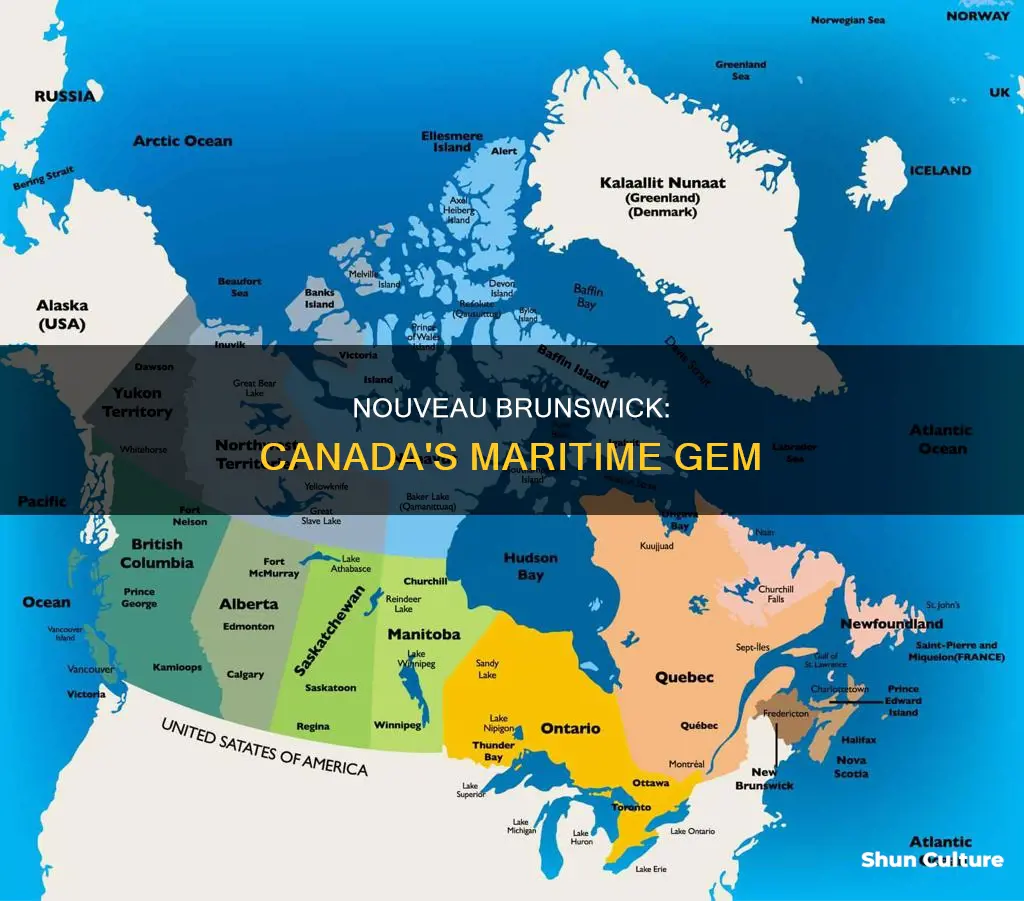
Nouveau-Brunswick is a province in Canada. It is one of three maritime provinces and one of four provinces in the Atlantic region. It is the only bilingual province in Canada, with both French and English as its official languages. Nouveau-Brunswick is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of St. Lawrence to the northeast, and the Bay of Fundy to the southeast. It also shares a border with the US state of Maine to the west. The province is 83% forested, and its northern half is occupied by the Appalachian Mountains. Its capital is Fredericton, and its largest cities include Moncton and Saint John.
What You'll Learn
- Nouveau-Brunswick is a province of Canada
- It is one of the three Maritime provinces
- It is one of the four Atlantic provinces
- It is the only bilingual province, with French and English as official languages
- It is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, and the United States to the west

Nouveau-Brunswick is a province of Canada
Nouveau-Brunswick covers an area of 72,908 square kilometres and had a population of 775,610 in 2021. Unlike other Canadian provinces, only half of the population lives in urban areas. Its capital is Fredericton, and its largest cities are Moncton and Saint John. The province adopted the Official Languages Act in 1969, which recognised French as an official language alongside English. About two-thirds of the population are Anglophones, and one-third are Francophones. The province is home to most of the Acadian cultural region and the majority of French speakers in Atlantic Canada, who are called "Acadians".
The territory of Nouveau-Brunswick was first inhabited by indigenous nations such as the Micmacs and Maliseets before being colonised by Europeans in the 17th century. In 1604, the first colony of New France, Acadia, was founded with the establishment of Port-Royal. For 150 years, Acadia changed hands several times between France and England (later Great Britain). From 1755 to 1764, the Acadians were deported en masse by the British. This forced exodus, known as the "Grand Dérangement", established Acadia as a British colony, alongside the Treaty of Paris in 1763.
Following the arrival of many Loyalists fleeing the American Revolutionary War, the province of Nouveau-Brunswick was officially created on 16 August 1784, as a separate colony from Nova Scotia. In the early 1800s, Nouveau-Brunswick prospered, and its population grew rapidly. In 1867, the province federated with Nova Scotia and Canada-Uni (now Quebec and Ontario) to form the Dominion of Canada. After Confederation, shipbuilding and forestry declined, and protectionism disrupted trade with New England. By the mid-1900s, Nouveau-Brunswick was one of the poorest regions in Canada. This situation was mitigated by transfer payments.
In 2002, Nouveau-Brunswick's provincial GDP consisted of services (43%), construction and manufacturing (24%), real estate rentals (12%), wholesale and retail trade (11%), agriculture, forestry, fishing, hunting, mining, oil and gas extraction (5%), and transportation and warehousing (5%). Tourism accounts for 9% of the province's workforce, and popular destinations include Hopewell Rocks Provincial Park, Fundy National Park, Magnetic Hill, Kouchibouguac National Park, and Roosevelt Campobello International Park.
Nouveau-Brunswick is named after George III (1738-1820), King of Great Britain from 1760 until his death, and also Duke of Brunswick. The Duchy of Brunswick-Luneburg, from which the province gets its name, corresponds partly to the modern-day German state of Lower Saxony. The name "Brunswick" is a combination of "Bruno", derived from the founder of the city, Count Bruno of Saxony, and the Low German word "wik", meaning a place where merchants rest and store their goods.
UNB: A Science Hub?
You may want to see also

It is one of the three Maritime provinces
Nouveau-Brunswick, also known as New Brunswick in English, is one of the three Maritime provinces, alongside Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island. It is also one of four Atlantic provinces, the others being Newfoundland and Labrador. The Maritime provinces are known for their rugged coastlines, picturesque bays, sandy beaches, towering cliffs, charming towns, and delicious lobster. The ocean played a crucial role in the development of the Maritimes, bringing waves of settlers and contributing to the region's shipbuilding and fishing industries.
The history of Nouveau-Brunswick is closely tied to the struggle between England and France for control of North America in the 18th century. The region, particularly the area known as Acadie (Acadia), was often caught in the middle of this conflict, changing hands multiple times before being ceded to the British by the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713. The deportation of Acadians by the British in the 18th century, known as "Le Grand Dérangement," further solidified Acadie as a British colony.
Nouveau-Brunswick has a diverse cultural and linguistic heritage. It is the only bilingual province in Canada, with both French and English as its official languages. The province is home to Acadians, who are predominantly French-speaking, as well as English-speaking Canadians. The province's name, Nouveau-Brunswick, is derived from the Duchy of Brunswick-Lunenburg in Germany, which corresponds partially to the present-day state of Lower Saxony.
In terms of geography, Nouveau-Brunswick is located in eastern Canada, with a strong maritime presence. No part of the territory is more than 180 kilometres from the coastline. The province is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of St. Lawrence to the northeast, and the Bay of Fundy to the southeast. It also shares a border with the US state of Maine to the west. The landscape is dominated by the Appalachian Mountains, with the province's highest peak, Mount Carleton, rising to 820 metres.
The economy of Nouveau-Brunswick has traditionally been dominated by natural resource-based industries, such as forestry and fishing. However, services now make up a significant portion of the economy, including tourism, which attracts visitors with its natural beauty, outdoor adventures, and cultural experiences.
Brunswick Beach Camp: Steps from the Shore
You may want to see also

It is one of the four Atlantic provinces
Nouveau-Brunswick is one of the four Atlantic provinces, alongside Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. These provinces are located on the Atlantic coast of Eastern Canada, excluding Quebec. Together, the four Atlantic provinces have a landmass of approximately 488,000 square kilometres and a population of over 2.4 million people.
The term "Atlantic Canada" was popularised after the admission of Newfoundland as a Canadian province in 1949. The provinces share cultural similarities, and their economies are largely based on natural resource industries such as fishing, hydroelectricity, forestry, and mining.
The Atlantic provinces are historically the territories of indigenous peoples, including the Mi'kmaq, Naskapi, Beothuk, and Nunatsiavut (Labrador Inuit). The French formed alliances with many indigenous groups within Atlantic Canada, including the Mi'kmaq of Acadia, who joined the Wabanaki Confederacy, important allies of New France.
The four Atlantic provinces have a combined approximate GDP of $121.888 billion (as of 2011). Their primary natural resource industries include fishing, hydroelectricity, forestry, and mining, with approximately 75% of Canada's fish production coming from this region.
Matthew: Brunswick Braces for Impact
You may want to see also

It is the only bilingual province, with French and English as official languages
Nouveau-Brunswick, or New Brunswick in English, is one of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only bilingual province in Canada, with both French and English as its official languages.
In 1969, New Brunswick passed the Official Languages Act, which began recognising French as an official language, alongside English. This law set out the fundamental right of New Brunswickers to receive services in the official language of their choice from the provincial government. This means that New Brunswickers can receive provincial government services in either French or English.
The province's bilingualism is also reflected in its name, which combines French and English: 'Nouveau-Brunswick'. This name was given in honour of King George III, who was also the prince-elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg in the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation (until 1806) in what is now Germany.
The population of New Brunswick is approximately two-thirds English-speaking and one-third French-speaking. The French spoken in New Brunswick is called Acadian French, and there are seven regional accents. The province is home to most of the cultural region of Acadia and most Acadians.
New Brunswick's bilingualism is protected by the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which is part of Canada's Constitution. This means that any law or government action that is inconsistent with the Charter is unconstitutional. The Charter also affirms the role of the New Brunswick legislature and government in preserving and promoting the equality of the English and French linguistic communities and their rights and privileges.
Gold Rush in New Brunswick
You may want to see also

It is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, and the United States to the west
Nouveau-Brunswick, une province du Canada, est bordée par le Québec au nord, la Nouvelle-Écosse à l'est, le golfe du Saint-Laurent au nord-est et l'État américain du Maine à l'ouest. La province est également délimitée par la baie de Fundy au sud, le détroit de Northumberland et le golfe du Saint-Laurent à l'est. La pointe sud-est du Nouveau-Brunswick est reliée à la Nouvelle-Écosse par l'isthme de Chignecto.
Le Nouveau-Brunswick est situé dans l'est du Canada, dans la région des provinces maritimes et des provinces de l'Atlantique. La mer est omniprésente, aucun point du territoire n'étant à plus de 180 kilomètres du littoral. Le Nouveau-Brunswick est bordé au nord par la baie des Chaleurs, à l'est par le golfe du Saint-Laurent et le détroit de Northumberland, et au sud par la baie de Fundy.
Le Nouveau-Brunswick est la plus grande des trois provinces maritimes canadiennes, mais reste petite à l'échelle du pays. Avec une superficie de 72 908 km2, la province est un peu plus étendue que la Sierra Leone, le 117e pays le plus étendu du monde, et la Belgique pourrait y entrer deux fois. La province s'étend sur plus de 300 km du nord au sud et d'est en ouest.
Le Nouveau-Brunswick est bordé par le Québec, une province du Canada, au nord-ouest, et la Nouvelle-Écosse, une autre province canadienne, au sud-est, avec laquelle elle est reliée par l'isthme de Chignecto. Il partage également une frontière terrestre avec l'État américain du Maine à l'ouest.
Le Nouveau-Brunswick est l'une des treize provinces et territoires du Canada. C'est l'une des trois provinces maritimes et l'une des quatre provinces de l'Atlantique. Il est bordé par le Québec au nord, la Nouvelle-Écosse à l'est, le golfe du Saint-Laurent au nord-est, la baie de Fundy au sud-est et l'État américain du Maine à l'ouest.
The Mystery of Scott Brunswick: Fact or Fiction?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Nouveau-Brunswick est une province du Canada. Elle est bordée par le Québec, la Nouvelle-Écosse, le golfe du Saint-Laurent, la baie de Fundy et partage une frontière avec les États-Unis.
Le climat de Nouveau-Brunswick est continental, avec des hivers neigeux et des étés tempérés.
Les principales industries de Nouveau-Brunswick incluent l'exploitation forestière, l'agriculture, la pêche, l'aquaculture, la fabrication et le tourisme.
Les principales villes de Nouveau-Brunswick incluent Fredericton (la capitale), Moncton et Saint-Jean.