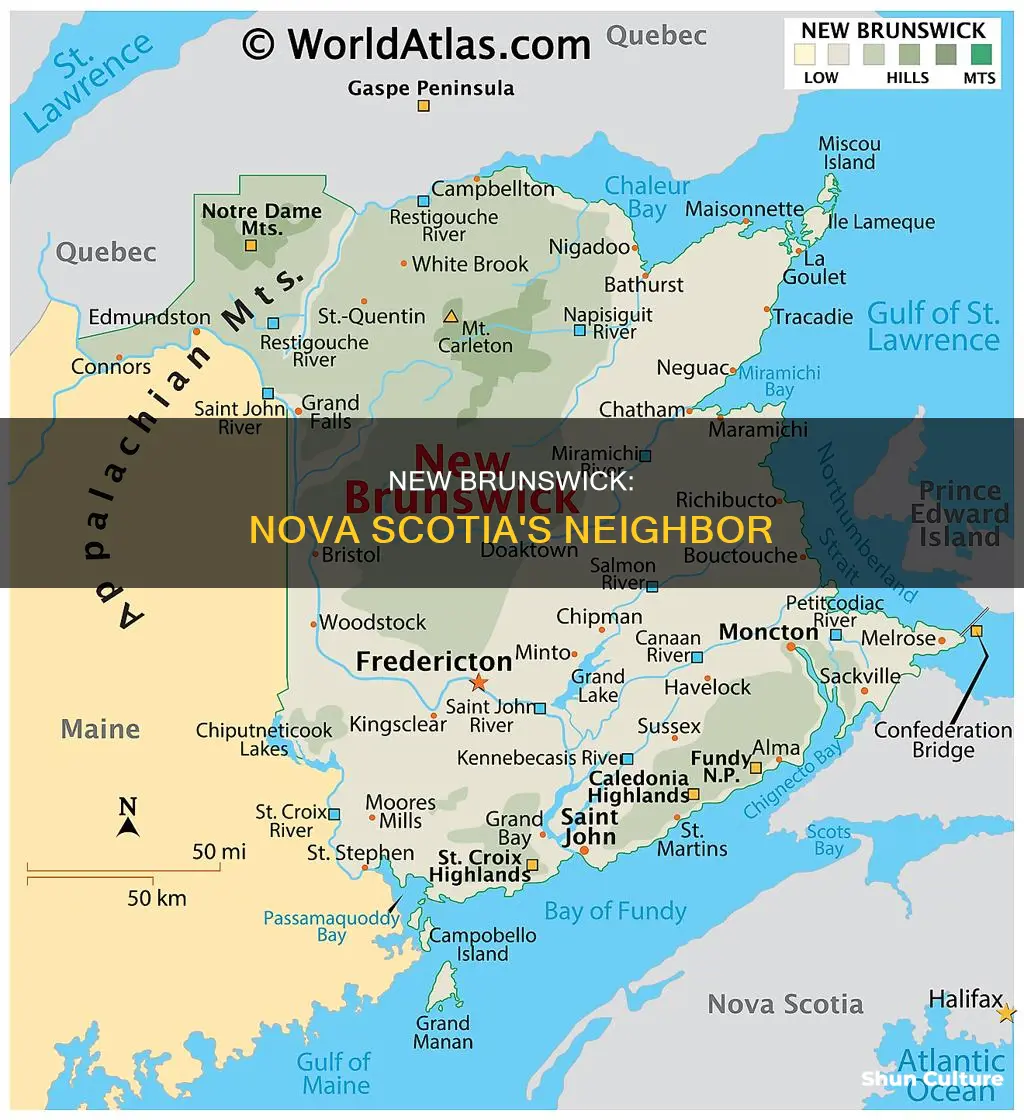
New Brunswick is one of Canada's four Atlantic provinces, and one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to the west. New Brunswick is Canada's only officially bilingual province, with French and English having equal status. The province has a varied and increasingly multicultural population, with around 30% of the population speaking French as a first language, and the remaining 70% speaking English.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Location | Eastern Canada |
| Area | 28,150 sq mi or 72,908 sq km |
| Population | 775,610 (2021) or 842,725 (2023 estimate) |
| Capital | Fredericton |
| Largest City | Saint John |
| Other Major Cities | Moncton, Fredericton |
| Language | English and French (officially bilingual) |
| Time Zone | Atlantic Time Zone (AST) |
| Main Industries | Agriculture, aquaculture, fisheries, lumber, manufacturing, tourism |
| Geography | Rolling hills, Appalachian Mountains, coastal plains, Bay of Fundy, Acadian forest |
| Climate | Humid continental with snowy winters and temperate summers |
What You'll Learn

New Brunswick's location and borders
New Brunswick is located in eastern Canada and is one of the country's four Atlantic provinces. It is also one of Canada's three Maritime provinces, alongside Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island. New Brunswick is bordered by Quebec to the north, the US state of Maine to the west, and the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the Bay of Fundy, and the Northumberland Strait to the east and south. The province is also bounded by the Bay of Fundy in the south, with the southeast corner of New Brunswick connected to Nova Scotia at the Chignecto Isthmus.
New Brunswick is the largest of the Maritime provinces and has a surface area of 72,908 square kilometres (28,150 square miles). The province is roughly square in shape and is home to wide areas of unspoiled nature, with forests occupying the majority of its land mass. New Brunswick also includes a number of coastal islands.
The topography of New Brunswick consists mainly of rolling hills, with the Appalachian Mountains dominating the landscape. The Appalachian range extends from the southeastern United States to Quebec's Gaspé Peninsula, cutting through the western and northern portions of the province. The highest peak in New Brunswick is Mount Carleton, which rises to 2,680 or 2,690 feet above sea level in the northwestern region.
New Brunswick's eastern and southern regions feature extensive coastal plains, including the Acadian Peninsula, Chaleur Bay, and the Northumberland Strait. The Bay of Fundy, known for its high tides and unique ecosystems, defines the province's southern coast. The tides create dynamic environments such as the Hopewell Rocks and the Reversing Falls Rapids in Saint John.
The province's climate varies due to its diverse geography, with a humid continental climate characterised by warm summers, cold winters, and ample precipitation. However, coastal regions often experience milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas.
Planting Grass in New Brunswick
You may want to see also

The province's climate and geography
New Brunswick is a Canadian province located on the eastern seaboard of the North American continent. It is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to the west. The province is about 83% forested, with its northern half occupied by the Appalachians.
The province's climate is continental with snowy winters and temperate summers. The climate is influenced by its proximity to the ocean, resulting in milder winters and slightly cooler summers along the coast. The interior of the province, particularly the northwest, experiences colder temperatures and more snowfall. The annual precipitation rate is about 1,078 mm, with the highest precipitation occurring in the southeast. The average annual temperature in New Brunswick is approximately 12.1 °C, with the warmest month being July, and the coldest month being January.
The geography of New Brunswick is characterised by rolling hills, uplands, and coastal areas. The northern part of the province is dominated by mountains, with Mount Carleton being the highest point at 820 metres. The interior consists mostly of rolling plateaus covered by forests. The eastern region is fairly flat, while the southern terrain is rugged, with sharp hills that slope down to tidal marshes and lowland plains. The province is home to numerous rivers, including the St. John River, the Miramichi, Restigouche, Nepisiguit, Salmon, St. Croix, and Tobique. The largest lake in the province is Grand Lake, which is over 30 kilometres in length.
The soils in New Brunswick tend to be thin and acidic, especially in the uplands. Deeper soils are found in the centre and western parts of the province but are often poorly drained and acidic as well. The best agricultural soils are found along the rivers, particularly the upper Saint John River, where the sandy loam soil is well-drained and has a good lime content, making it ideal for growing potatoes.
Brunswick Crossing MD: How Far?
You may want to see also

Population and demographics
New Brunswick is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and the only officially bilingual province, with French and English as its official languages. The province's population was 775,610 as of the 2021 census, with a more recent estimate of over 800,000 in March 2022. New Brunswick is unique among Canadian provinces in that only about half of its population lives in urban areas, predominantly Moncton, Saint John, and Fredericton.
The majority of New Brunswickers are English-speaking, with a substantial French-speaking minority of mostly Acadian origin. The English-speaking population is largely descended from Scottish, Irish, and English settlers of the 18th and 19th centuries, as well as Loyalists who fled the American Revolution. The French-speaking minority, which has grown to about one-third of the population, consists of the descendants of 17th-century Acadian settlers, augmented by French Canadians from Quebec. This minority is concentrated in the northern and eastern counties.
New Brunswick also has a significant population of Indigenous peoples, including the Mi'kmaq and Wolastoqiyik (Maliseet). Additionally, there is a notable population of Irish ancestry, especially in Saint John and the Miramichi Valley, and Scottish descendants scattered throughout the province, with higher concentrations in the Miramichi and Campbellton. A small population of Danish origin can be found in New Denmark in the northwest of the province.
In the 2021 Canadian Census, the most commonly spoken languages in the province were English (698,025 or 91.94%) and French (317,825 or 41.86%). Other languages spoken include Spanish, Arabic, Tagalog, and Hindi.
According to the 2021 census, the religious groups in New Brunswick included Christianity (512,645 or 67.5%), Irreligion (225,125 or 29.7%), Islam (9,190 or 1.2%), Hinduism (3,340 or 0.4%), Sikhism (1,780 or 0.2%), Buddhism (1,120 or 0.1%), Indigenous Spirituality (1,005 or 0.1%), and Judaism (1,000 or 0.1%).
Brunswick Stew: African or American?
You may want to see also

Government and official languages
New Brunswick is one of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories. It is the only officially bilingual province in Canada, with both English and French recognised as official languages. The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms states that:
> English and French are the official languages of Canada and have equality of status and equal rights and privileges as to their use in all institutions of the Parliament and government of Canada.
The Charter also applies to New Brunswick, stating that:
> English and French are the official languages of New Brunswick and have equality of status and equal rights and privileges as to their use in all institutions of the legislature and government of New Brunswick.
The Charter further recognises the English and French linguistic communities in New Brunswick as having:
> equality of status and equal rights and privileges, including the right to distinct educational institutions and such distinct cultural institutions as are necessary for the preservation and promotion of those communities.
The Charter guarantees that all government services and documents must be available in both English and French, and either language may be used in the New Brunswick courts.
New Brunswick's first Official Languages Act was passed in 1969, recognising French as an official language alongside English. This was followed by the Official Languages Act of 2002, which guaranteed that provincial government departments and Crown Corporations must provide and actively offer services in both French and English. The Act also applies to the New Brunswick Legislature, the justice system, cities and municipalities, the health system, and planning commissions.
The Office of the Commissioner of Official Languages for New Brunswick was established in 2002. The Commissioner is responsible for investigating complaints, making recommendations, ensuring compliance with the Official Languages Act, and promoting the advancement of both official languages in the province.
Brunswick-Turner Distance: How Far?
You may want to see also

Economy and industry
New Brunswick is Canada's only officially bilingual province, and its strategic location in Atlantic Canada makes it a prime location for expansion. The province's economy is diverse, with a focus on services, natural resources, and manufacturing.
As of 2002, the provincial GDP was derived as follows: services (including government services and public administration) 43%; construction, manufacturing, and utilities 24%; real estate rental 12%; wholesale and retail 11%; agriculture, forestry, fishing, hunting, mining, oil, and gas extraction 5%; and transportation and warehousing 5%.
A large portion of New Brunswick's economy is controlled by the Irving Group of Companies, with significant holdings in agriculture, forestry, food processing, freight transport, media, oil, and shipbuilding. The Irving Group's activities are supported by the provincial government through tax exemptions and subsidies.
Agriculture is a significant sector in New Brunswick, with over 13,000 people working in the industry and products worth over $1 billion. The province was Canada's biggest producer of wild blueberries in 2015, and the value of the livestock sector is about a quarter of a billion dollars, with dairy accounting for nearly half of that. Other agricultural products include apples, cranberries, potatoes, and maple syrup.
Forestry is also a vital industry, with about 83% of New Brunswick being forested. The forestry industry employs nearly 12,000 people and generates around $437 million in revenue. However, there have been concerns about the lack of transparency and the environmental impact of forest management practices in the province.
Mining has grown in importance since the 1950s, with a GDP of $299.5 million in 2015. Mines in New Brunswick produce lead, zinc, copper, and potash.
The province's location along the Atlantic Ocean and its extensive river system make it ideal for transportation and warehousing, which employ many residents. The Trans-Canada Highway traverses the province, and Canadian National Railway operates freight services from Montreal to Halifax.
Tourism is another important sector, accounting for about 9% of the labour force. Popular destinations include Fundy National Park, the Hopewell Rocks, Kouchibouguac National Park, and Roosevelt Campobello International Park.
New Brunswick's diverse economy, natural resources, and strategic location make it an attractive destination for businesses and investors.
Cougars' Prowl in New Brunswick
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
New Brunswick is located in eastern Canada and is one of the country's four Atlantic provinces. It is bordered by Quebec to the north, the US state of Maine to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Prince Edward Island and Nova Scotia to the east and south, respectively.
The topography of New Brunswick consists mainly of rolling hills, with the Appalachian Mountains dominating the landscape. The province experiences a humid continental climate with warm summers, cold winters, and ample precipitation. The Bay of Fundy, renowned for its high tides, defines the southern coast.
New Brunswick is home to approximately 760,000 people and is officially bilingual, with over 30% speaking French as a first language. The province has a rich cultural heritage from both its Francophone and Anglophone communities, as well as contributions from generations of immigrants from around the world.
New Brunswick has a modern service-based economy, with major financial and insurance industries. The province also has a strong manufacturing sector, with food and beverages, pulp and paper, and metal processing being key industries. Tourism is also a significant contributor to the economy.







