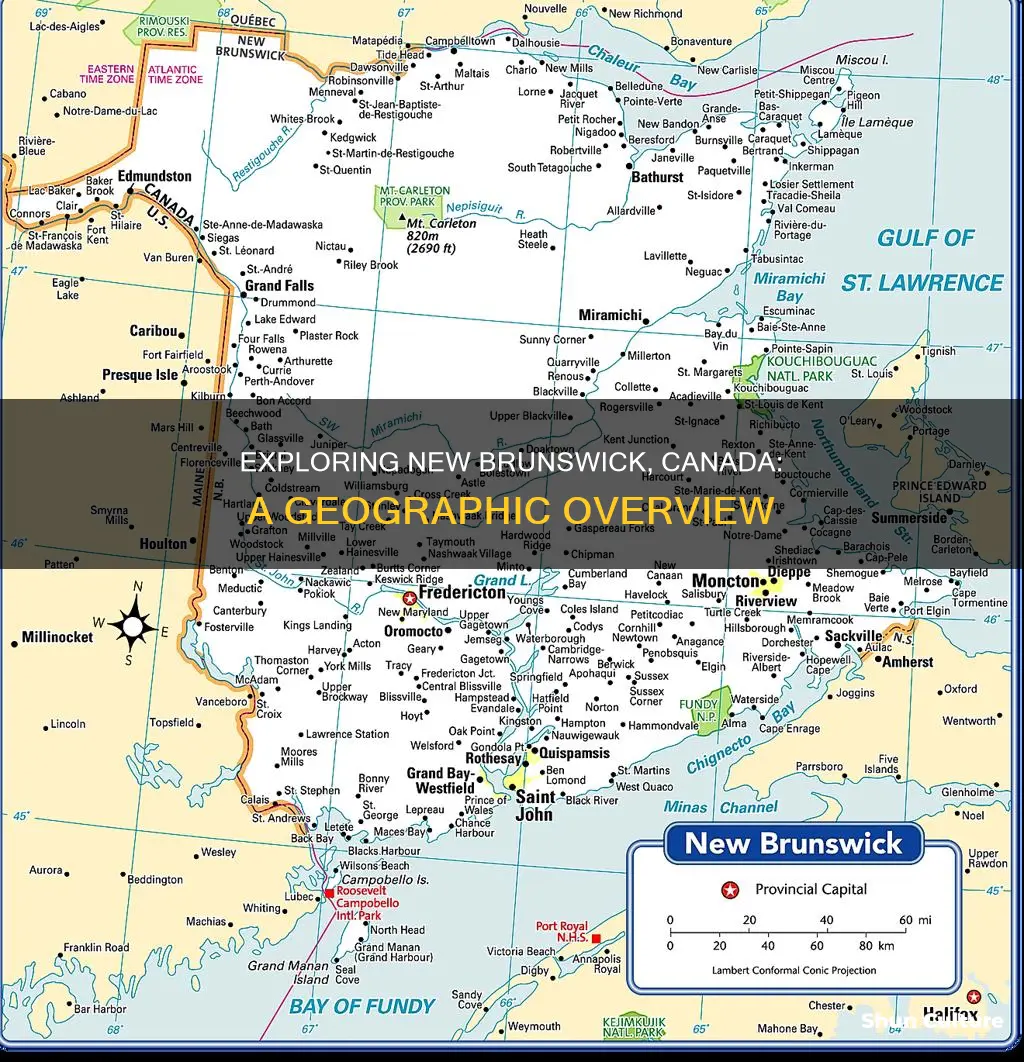
New Brunswick is one of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories. It is located in eastern Canada, sharing a border with the province of Quebec to the north, the US state of Maine to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island to the east and south, respectively. The province is also bounded by the Bay of Fundy in the south, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, and the Northumberland Strait in the east. The Appalachian Mountains dominate the landscape, with the province's highest peak, Mount Carleton, rising to 2,690 feet above sea level. New Brunswick has a surface area of 72,908 square kilometres (28,150 square miles) and a varied climate, with snowy winters and temperate summers.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Location | Eastern Canada |
| Bordering Provinces/Territories | Quebec (north), Nova Scotia (east), Gulf of St. Lawrence (northeast), Bay of Fundy (southeast), US State of Maine (west) |
| Area | 72,908 sq. km or 28,150 sq. mi |
| Population | 775,610 (2021 census) |
| Population Density | Above average among Canadian provinces |
| Urban/Rural Split | About half of the population lives in urban areas |
| Largest City | Moncton |
| Capital | Fredericton |
| Topography | Rolling hills, Appalachian Mountains |
| Climate | Humid continental climate with warm summers, cold winters, ample precipitation; milder winters and cooler summers in coastal regions |
| Forest Cover | 85% (predominantly mixed-wood and softwood forests) |
| Official Languages | English and French |
| Administrative Divisions | 236 Local Service Districts, 104 municipalities, 12 Regional Service Commissions |
| Economy | Mining, agriculture, aquaculture, fisheries, forestry, food processing, freight transport, media, oil, shipbuilding |
What You'll Learn

New Brunswick's location in Canada
New Brunswick is located in eastern Canada, and is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of the country. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of four Atlantic provinces.
New Brunswick is bordered by the province of Quebec to the north, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, and the Canadian province of Nova Scotia to the east and south. The US state of Maine borders New Brunswick to the west, and the province is also bounded by the Bay of Fundy in the south, and the Northumberland Strait in the east. The southeastern edge of New Brunswick is connected to Nova Scotia by the Chignecto Isthmus.
New Brunswick occupies a total area of 28,150 square miles (72,908 sq. km), making it the 3rd smallest Canadian province by area. The province is roughly square in shape, and its landscape is dominated by the Appalachian Mountains, which extend from the southeastern United States to Quebec, cutting through the western and northern portions of New Brunswick. The highest peak in the province, Mount Carleton, rises to 2,690 feet above sea level in the northwestern region.
The topography of New Brunswick consists mainly of rolling hills, with extensive coastal plains in the east and south, including the Acadian Peninsula, Chaleur Bay, and the Northumberland Strait. The Bay of Fundy, known for its high tides and unique ecosystems, defines the southern coast of the province. The tides create dynamic environments such as the Hopewell Rocks and the Reversing Falls Rapids in Saint John.
New Brunswick's capital is Fredericton, located in the west-central part of the province along the Saint John River. The province's largest city, Moncton, is situated in the geographic centre of Canada's Maritime provinces in the valley of the Petitcodiac River.
The Cost of Crafting a Billiard Table: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

The province's borders
New Brunswick is one of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, and one of the three Maritime provinces. It is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to the west. The province also shares a maritime border with Prince Edward Island. The southeastern edge of the province is connected to Nova Scotia at the Chignecto Isthmus.
New Brunswick's northern border with Quebec is formed by the Restigouche River, the Patapedia River, and the Saint Lawrence River. The province's northeastern border is formed by the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, which separates it from the Gaspé Peninsula in Quebec. The border then continues along the Restigouche River and the Patapedia River, before reaching the Canada-US border with the state of Maine.
The border between New Brunswick and Maine is formed by the Saint Croix River, the St. Andrews River, and the St. Croix River estuary. The border then follows a line of latitude until it reaches the Bay of Fundy, which forms New Brunswick's southern coastline. The province's southeastern border is formed by the Chignecto Isthmus, which connects it to Nova Scotia.
The province's eastern border with Nova Scotia runs through the Bay of Fundy and the Northumberland Strait, before reaching the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. This border separates the Acadian Peninsula in New Brunswick from the mainland in Nova Scotia.
The province's total border length is approximately 2,400 km (1,491 miles), with 915 km (568 miles) bordering Quebec, 318 km (197 miles) bordering Maine, and 1,167 km (725 miles) bordering Nova Scotia.
The Elusive Brunswick, Maryland: A Town of Many Faces
You may want to see also

The topography of New Brunswick
The eastern and southern regions of New Brunswick boast extensive coastal plains, including the Acadian Peninsula, Chaleur Bay, and the Northumberland Strait. The southern coast is defined by the Bay of Fundy, known for its high tides and unique ecosystems, such as the Hopewell Rocks and the Reversing Falls Rapids in Saint John. The province's interior is mostly a rolling plateau covered in forests, with the Saint John River, often called The Rhine of North America, splitting the province from north to south.
The Chaleur Uplands extend from Maine to the north of the province and are drained by the Saint John and Restigouche rivers. The Notre Dame Mountains in the northwest feature small lakes and steep slopes, with elevations ranging from 150 to 6100 metres. The New Brunswick Highlands include the Caledonia, St. Croix, and Miramichi Highlands. The Lowlands in the central and eastern parts of the province are mostly under 100 metres above sea level, with altitudes rarely exceeding 180 metres.
The majority of western New Brunswick is drained by the Saint John River system, which rises in northern Maine and empties into the Bay of Fundy in Saint John. The Petitcodiac River, Shepody River, and Memramcook River empty into Chignecto Bay at the head of the Bay of Fundy, creating a tidal bore phenomenon. The Miramichi River system, renowned for its salmon fishing, drains a large portion of central New Brunswick, with two main branches and several smaller tributaries.
Forests, predominantly mixed-wood and softwood, cover approximately 85% of New Brunswick's landmass. The Acadian forest, a unique blend of northern hardwoods and boreal species, provides habitats for diverse flora and fauna. The province also boasts a vast network of rivers and lakes, with the Saint John River being the most prominent.
The Enigmatic Distance: Unraveling the 'How Far is Brunswick' Query
You may want to see also

The climate of New Brunswick
New Brunswick, Canada, has a humid continental climate characterised by warm summers, cold winters, and ample precipitation. The climate varies across the province due to its diverse geography, with coastal regions generally experiencing milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas.
New Brunswick is one of the warmer regions in Canada, with an average daily high temperature of 11°C. The average annual temperature has increased by 1.1°C in the last 30 years, and the sea level has risen by about 30 cm in the last 100 years. The effects of climate change are expected to further impact the province, with projections indicating that New Brunswick will become warmer, wetter, and stormier, with rising sea levels.
The summer season in New Brunswick is warm, with temperatures reaching their peak in July, the warmest month, with an average maximum temperature of 24.6°C. The summer months are also the wettest, with July experiencing the highest amount of rainfall, followed by June, which has the highest number of rainy days. Despite the warmth, light- to medium-weight clothing is recommended during the summer, as cooler evenings are typical.
Autumn and spring in New Brunswick are relatively mild, while winters are cold with heavy snows. The average minimum temperature in January, the coldest month, is approximately -0.8°C. Snow depths of greater than 1 cm are observed on about 105 days each year in Fredericton, the provincial capital, which is located inland. The coastal locations of Saint John and Moncton have milder winters and cooler summers compared to Fredericton.
Overall, New Brunswick experiences a range of weather conditions throughout the year, with precipitation occurring in all months. The driest month is November, with 75 mm of precipitation on average, while June is the wettest month, receiving up to 110 mm of rainfall. The climate in New Brunswick is similar to Central European weather conditions, with a mix of cold, wet weather and a few beautiful summer months. The best time for travelling to New Brunswick is typically from May to September, avoiding the cold months from November to April.
The Coastal Georgia Adventure: Exploring Savannah and Its Neighbor, Brunswick
You may want to see also

The history of New Brunswick
New Brunswick is one of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories. It is located in eastern Canada and is bordered by Quebec to the north, the US state of Maine to the west, and Nova Scotia to the south and east. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces.
The first inhabitants of New Brunswick were the Mi'kmaq, the Maliseet, and the Passamaquoddy tribes. The first documented European exploration of the region was by French explorer Jacques Cartier in 1534, when he set foot in Miscou and explored the coasts of Chaleur Bay.
In 1604, Acadia, the first New France colony, was founded with the creation of Port-Royal. For 150 years afterwards, Acadia changed hands multiple times due to numerous conflicts between France and the United Kingdom. From 1755 to 1764, the British deported Acadians en masse, an event known as the Great Upheaval. This, along with the Treaty of Paris, solidified Acadia as British property.
In 1784, following the arrival of many loyalists fleeing the American Revolution, the colony of New Brunswick was officially created, separating it from what is now Nova Scotia. In the early 1800s, New Brunswick prospered and the population grew rapidly. In 1867, New Brunswick decided to join with Nova Scotia and the Province of Canada (now Quebec and Ontario) to form Canada.
New Brunswick is Canada's only constitutionally bilingual province, with a population that is predominantly English-speaking, and a significant Francophone minority, predominantly of Acadian origin.
The Geographical Context of Shallotte, North Carolina: Unraveling Its County Affiliation and Beyond
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
New Brunswick is located in eastern Canada.
New Brunswick shares borders with Quebec to the north, the US state of Maine to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island to the south and east, respectively.
The Gulf of St. Lawrence borders New Brunswick to the northeast, and the Bay of Fundy to the southeast.
The topography of New Brunswick consists mainly of rolling hills, with the Appalachian Mountains dominating the landscape. The province also boasts extensive coastal plains in its eastern and southern regions.
The province experiences a humid continental climate with warm summers, cold winters, and ample precipitation. The coastal regions often have milder winters and cooler summers compared to inland areas.







