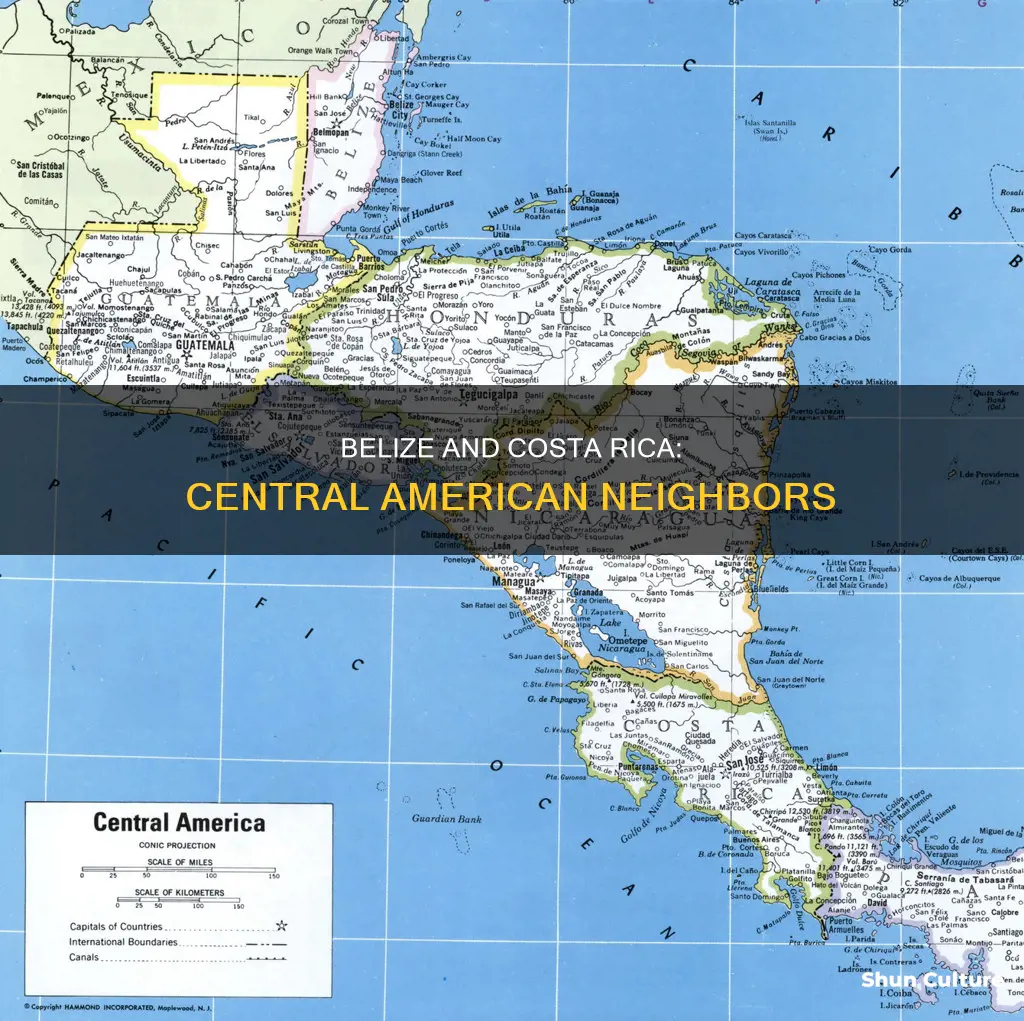
Belize and Costa Rica are two Central American countries that offer stunning landscapes and a plethora of activities for visitors. Belize is located in Central America, bordered by Mexico, Guatemala, and the Caribbean Sea. It is a small country, covering just under 9,000 square miles, and is known for its diverse culture, stunning beaches, and world-class diving spots. Costa Rica, on the other hand, sits in the southern part of Central America, bordered by Nicaragua and Panama. It offers two unique coastlines on the Pacific and Caribbean seas, with over 300 beaches to explore. Costa Rica is larger than Belize, spanning over 20,000 square miles, and is known for its abundant wildlife, thrilling adventures, and diverse landscapes.
What You'll Learn

Belize's location and geography
Belize is a small Central American nation located on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It is situated on the Yucatán Peninsula, 17°15′ north of the equator and 88°45′ west of the Prime Meridian. The country shares a land and sea border with Mexico to the north, a land border with Guatemala to the west and south, and a sea border with Honduras to the south. Belize City, the country's commercial and cultural centre, is located on the Caribbean Sea coast, which boasts 386 km of coastline.
The country's landscape is characterised by mountains, swamps, and tropical jungle. The northern half of Belize consists of flat wetlands and coastal plains, with diverse flora and fauna. The south of the country contains the Maya Mountains, a plateau of igneous rock cut by erosion into hills and valleys. The lowlands are drained by several major rivers, including the Belize River, the New River, and the Hondo River, which forms the northern border with Mexico. The Belize Barrier Reef, the second-largest barrier reef in the world, flanks much of the coastline.
Belize has a total area of 22,966 square kilometres, twice the size of Jamaica and slightly larger than El Salvador or Massachusetts. The country's land area extends about 280 kilometres north-south and 100 kilometres east-west, with a total land boundary length of 516 kilometres. The country's highest point is Doyle's Delight, at 1,124 metres, while its lowest point is at sea level.
Belize has a tropical climate with a rainy season from June to November and a dry season from January to May. The country experiences hurricanes, mainly during the Atlantic hurricane season from September to December, and is also prone to coastal flooding, especially in the south. The temperature and rainfall vary across the country, with the southern highland plateaus being noticeably cooler than the coastal regions.
Clothing Essentials for ATM Cave
You may want to see also

Belize's history
Belize, located on the northeast coast of Central America, has a rich and complex history that dates back thousands of years. Here is an overview of the country's history, focusing on four key periods: the Maya civilization, colonial rule, the path to independence, and post-independence developments.
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization flourished in the region of Belize between 1500 BC and 1200 BC, with advanced societies and a dense population. Several Maya ruin sites, such as Cahal Pech, Caracol, and Altun Ha, bear witness to their advanced architecture and cultural achievements. The Maya population began to decline around 1000 AD, and their society suffered a severe breakdown in the 10th century. However, the Maya left a lasting impact on the region, and many aspects of their culture persisted even after European colonization.
Colonial Rule
The first recorded European incursions into Belize were made by Spanish conquistadors and missionaries in the 16th century. The Spanish tried to convert the remaining Maya population to Christianity but met with little success. During this period, British buccaneers and logwood cutters also began settling on the coast. Tensions arose between Spain and Britain over territorial claims, with Spain considering the British as interlopers. Treaties signed in 1763 and 1783 granted British subjects the right to exploit logwood and mahogany within specified territories, but Spain retained sovereignty. The Spanish prohibited the British settlers from establishing a formal government, leading to a unique system of public meetings and elected magistrates.
Path to Independence
In the 19th century, Belize became caught between competing colonial powers. It was formally termed the Colony of British Honduras in 1862 and became a crown colony in 1871. Several constitutional changes were enacted to expand representative government, and internal self-government was granted in 1964. The official name was changed to Belize in 1973, reflecting the growing desire for independence. However, the path to independence was complicated by Guatemala's long-standing claim to the entire territory. Belize took its case for self-determination to the international community and gained support from various organizations.
Post-Independence Developments
Belize finally achieved full independence on September 21, 1981, with a British defense guarantee. The British military presence was gradually withdrawn, and border security became the responsibility of the Belize Defence Force. In the post-independence era, Belize has faced challenges such as economic stagnation, political unrest, and ongoing border disputes with Guatemala. The country has also struggled to develop its economy and reduce its dependence on foreign powers. Despite these challenges, Belize has maintained a relatively stable and democratic political system, with successive governments working towards improving the lives of its citizens.
Belize Beach Style: San Pedro Edition
You may want to see also

Costa Rica's location and geography
Costa Rica is a country located in Central America, connecting North and South America. It is bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. The country has a land area of 51,100 square kilometres (19,730 square miles) and a coastline of 1,290 kilometres.
Costa Rica's geography is incredibly diverse and rugged, with a variety of landscapes and climates. The country is home to several mountain ranges, including the Cordillera Volcánica in the north and the Cordillera de Talamanca in the south. These mountain ranges feature numerous volcanoes, including the active Irazú, Poás, Turrialba, and Barva Volcanoes. The country's highest point, Cerro Chirripó, stands at 3,819 metres (12,530 feet) above sea level.
The Caribbean lowlands, which make up about a quarter of the country's total area, are hot and humid and are a major region for banana exports. In contrast, the Guanacaste Plains in the northwest have the lowest annual rainfall and the longest dry season. The Pacific Coastline, which makes up about 80% of the coastal land, is more mountainous than the Caribbean coast, which features long stretches of sandy beaches.
Costa Rica's geography and geology are largely responsible for its incredible biodiversity. The country has a wide variety of ecosystems, including rainforests, dry forests, mangroves, swamps, wetlands, rivers, lakes, and waterfalls. It is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species, including monkeys, anteaters, sloths, deer, wildcats, and numerous bird and reptile species.
The country's capital, San José, is located in the Central Valley region, which is the economic, political, and cultural heart of the country. San José has a population of over one million people and is known for its moderate temperatures and ample rainfall.
Belize's Currency: The Belize Dollar
You may want to see also

Costa Rica's history
Costa Rica has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Here is a brief overview of some key moments and events that have shaped the country's past.
Pre-Columbian Times to Spanish Colonization
In 1503, Columbus incorporated Costa Rica into the Captaincy General of Guatemala as a province of New Spain, beginning over 300 years of Spanish colonization. During this period, Costa Rica remained sparsely populated and impoverished due to its isolation from the Spanish colonial centres. The indigenous population suffered greatly due to infectious diseases and mistreatment, leading to a lack of forced labour for the Spaniards. As a result, most Costa Ricans worked their own land, contributing to the development of an autonomous and individualistic agrarian society.
Independence and Democratic Reforms
In the early 19th century, Napoleon's occupation of Spain led to revolts across Spanish America. Costa Rica joined the other Central American intendancies in declaring independence from Spain in 1821. However, it briefly became part of the Mexican Empire before gaining full independence in 1828. Costa Rica struggled economically due to a lack of trade connections with European suppliers.
In the mid-19th century, Costa Rica resisted attempts by American settlers to take over the government. The country established a democratic government after 1869 and has since enjoyed a relatively stable and peaceful political environment compared to its Central American neighbours.
20th Century and Beyond
Costa Rica's economy, once heavily dependent on agriculture, particularly bananas and coffee, underwent a transformation in the late 20th century. The country now relies on technology, services, and eco-tourism as its major sources of income. Despite facing economic challenges and social issues, Costa Rica continues to be known for its stable democracy, commitment to human rights, and strong environmental protection efforts.
Belize Diving: What to Wear
You may want to see also

Costa Rica's culture
Costa Rica is a cultural melting pot, with indigenous origins, Spanish colonial influence, and a mix of other immigrant cultures, including Jamaican and Chinese. The country's official language is Spanish, but other languages, such as BriBri, Creole Mekatelyu, and English, are also spoken in certain areas. Costa Rica is known for its progressive social and environmental policies, and its people are proud of their values, including their commitment to education, healthcare, democracy, and sustainability.
The people of Costa Rica, affectionately known as Ticos, are renowned for their friendly, peaceful, and proud nature. They place great importance on family, friendship, and loyalty, and have a strong sense of national pride, often describing things as "muy Tico" or "very Costa Rican". The phrase "Pura Vida", which translates to "pure life", is commonly used by Ticos in their everyday speech as a greeting, a way to show appreciation, or to express that things are going well. This phrase embodies the carefree, laid-back, and optimistic spirit of Costa Rican culture.
Catholicism is the official religion of Costa Rica, and it plays a significant role in the country's culture and traditions. Religious holidays, such as Easter Week, Christmas Week, and August 2nd, are important to Ticos, who are predominantly Catholic. During these holidays, there is a mix of religious processions and festive celebrations.
Costa Rican cuisine is influenced by Spanish, South American, Caribbean, and American culinary traditions. The national dish, Gallo Pinto, is a combination of black beans and white rice, spiced with cilantro, onions, garlic, salt, and Salsa Lizano, typically served with eggs and sour cream. Another popular dish is Casado, which consists of rice, beans, meat, fried plantains, and side dishes such as salad or pasta.
Music and dance are also integral parts of Costa Rican culture, with each village having its variation of native music and dance. The province of Guanacaste is particularly known for its musical and dance traditions.
In terms of the arts, Costa Rica has produced renowned painters and sculptors, including Gonzalo Morales Sáurez, Rafa Fernandez, and Ibo Bonilla. The country also has a rich literary history, with notable authors such as Carmen Lyra, Jose Leon Sanchez, and Joaquin Gutierrez.
Belize's Water Hole Mystery
You may want to see also







