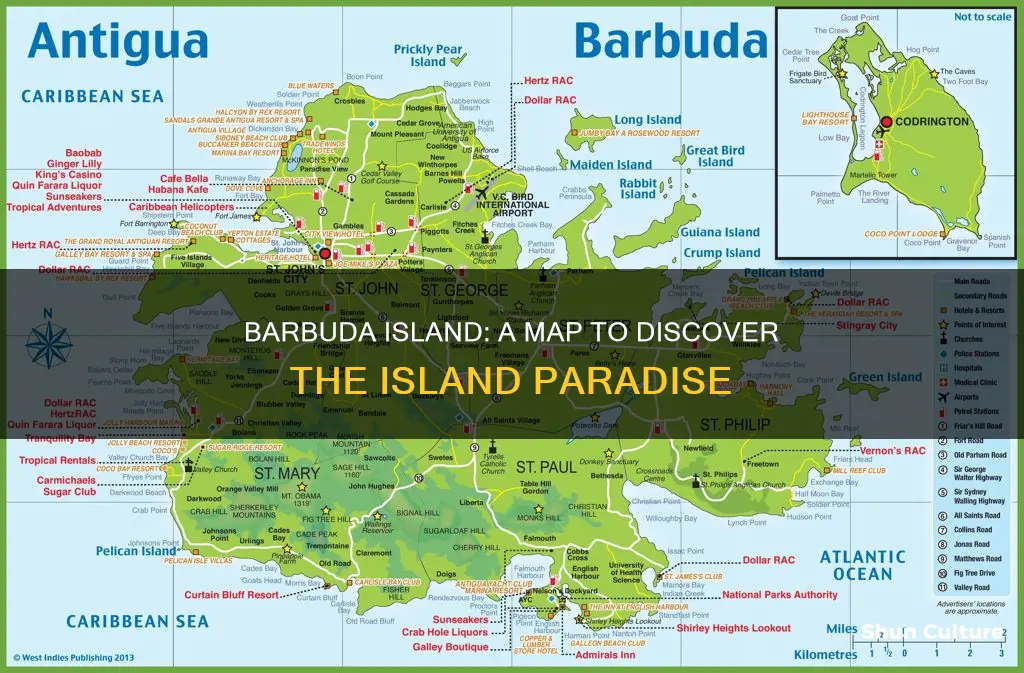
Barbuda is an island in the Caribbean that forms an independent state with Antigua, known as Antigua and Barbuda. It is located in the Leeward Islands chain, which is part of the Lesser Antilles, and is situated about 40km (25 miles) north of its sister island, Antigua. Barbuda is known for its secluded pink and white sand beaches and pristine landscape, which have made it a popular tourist destination. The island has a unique history, land tenure, and geography, setting it apart from other Caribbean islands. With a population of approximately 1,500, the Barbudan community resides in the only village of Codrington, which is also the island's largest town.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Country | Antigua and Barbuda |
| Island Group | Leeward Islands |
| Location | 17°5’N 61°48’W |
| Capital | St. John's |
| Population | 1,634 |
| Area | 62 sq mi (160 km2) |
| Highest Point | 143 ft (44 m) at Lindsay Hill |
| Climate | Tropical Marine |
| Main Industries | Tourism, Fishing, Lobster Catching |
What You'll Learn

Barbuda's location in the Caribbean
Barbuda is a small island in the Caribbean, forming part of the twin-island state of Antigua and Barbuda. It is located in the eastern Caribbean, in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles, at the conjunction of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
Barbuda is a dependency of Antigua, lying approximately 30 miles (48 km) north of its larger sister island. It is one of the most sparsely populated islands in the Caribbean, with a population of around 1,634 and an area of 62 square miles (160 km2). The island is flat, with a western portion dominated by the Codrington Lagoon and an eastern portion dominated by an elevated plateau, with salty ponds and scrubland throughout.
The only settlement on the island is Codrington, with a population of around 1,300 people. The island is known for its secluded pink and white sand beaches, as well as its natural beauty and peaceful way of life. Barbuda has a semi-arid climate, with less rainfall than Antigua, and is known for its fresh to slightly brackish aquifer system.
The majority of the population of Barbuda is of African descent, with English being the most commonly spoken language on the island. The economy of Barbuda is largely based on tourism, fisheries, and government, with the central and local governments being the largest employers.
Barbuda's Hurricane Irma Death Toll and Devastation
You may want to see also

The island's geography and topography
Barbuda is a flat island with an area of 62 square miles (160 km2) and a population of 1,634, making it one of the most sparsely populated islands in the Caribbean. The island is divided into two portions: the western and the eastern. The western portion is dominated by the Codrington Lagoon, while the eastern portion is dominated by an elevated plateau, with salty ponds and scrubland spread throughout the island. The island's topography is characterised by its lack of diversity, with coral limestone making up the majority of it. The highest point on the island is Lindsay Hill in the northeast, which rises to 143 feet (44 metres). The Barbuda Highlands on the eastern side of the island is home to hills that can reach heights of up to 38 meters (125 feet), but the majority of Barbuda is quite flat, and the northwest corner is home to many lagoons.
The island's climate is classified as tropical marine, with little seasonal temperature variation. The average daily high temperature in the coolest months of January and February is 27 °C (81 °F), while in the warmest months of July and August, it is 30 °C (86 °F). The island is susceptible to hurricanes during the late summer and early autumn months, and in September 2017, it was devastated by Hurricane Irma, which destroyed over 90% of its buildings and infrastructure.
Barbuda is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including several rare and endemic species such as the Barbuda warbler, the Antiguan racer (one of the rarest snakes in the world), and Griswold's ameiva, a species of lizard. The island also hosts several near-threatened bird species, including the West Indian whistling duck and the White-crowned pigeon. The Magnificent Frigate Bird Sanctuary, located in the Codrington Lagoon, is one of the primary tourist destinations on the island.
Antigua and Barbuda's Uber Availability: What's the Situation?
You may want to see also

The history of Barbuda
Early History (c. 3000-4000 BCE – 1666 CE
The first inhabitants of Barbuda were hunter-gatherers who arrived by canoe around 3,000-4,000 years ago. These early settlers were followed by the Arawak and Kalinago peoples, who made the island their home. The Spanish were the first Europeans to establish settlements on Barbuda, with the French and English later forming a colony in 1666.
Colonial Era (1666-1834)
In 1685, Barbuda was leased to brothers John and Christopher Codrington, who established the primary residential area, the village of Codrington. The island became a colony in 1678 and was used for provisioning their plantations in other islands. During this period, slavery was common in Barbuda, and the island was a source of slaves for other colonies in the Caribbean and the southern US. The Codrington family owned the island from 1685 to 1870 and were absentee landlords. They profited from the slave trade and attempted to transfer slaves to Antigua to increase their profits. This led to several slave rebellions, including Beach's Rebellion in 1741, which resulted in the killing of animals, property damage, and the escape of slaves.
Post-Slavery and Independence (1834-Present)
Slavery was abolished in Barbuda in 1834, and the island became a dependency of Antigua in 1859, subject to the laws of the Antigua colony. In 1976, Barbuda gained autonomy with the passing of the Barbuda Local Government Act, which established the Barbuda Council. The island gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1981 as part of the twin-island state of Antigua and Barbuda, becoming a constitutional monarchy.
Barbuda has a rich and complex history, shaped by its geographical location, natural resources, and the diverse cultures of its inhabitants. The island's economy has traditionally been based on tourism, fishing, and government, with a significant lobster-catching industry. In recent years, the island has faced the challenges of hurricane devastation and the threat of environmental damage from construction projects. Despite these challenges, Barbuda remains a strong and independent community, welcoming visitors to its pristine beaches and natural attractions.
Barbuda and Buck Island: Caribbean Neighbors?
You may want to see also

Population and demographics
Barbuda is an island located in the eastern Caribbean, approximately 30 miles (48 km) north of Antigua. It is one of the two main islands of the twin-island state of Antigua and Barbuda, with a population of 1,634 and an area of 62 square miles (160 km2). Barbuda is one of the most sparsely populated islands in the Caribbean, with a population density significantly lower than that of Antigua. The only settlements on the island are Codrington and its surrounding localities, with an estimated population of 1,300 people as of 2011.
According to the 2011 census, 95.11% of Barbuda's population is of African descent, followed by 2.88% Mixed Black/White, 1.00% other Mixed, 0.44% Hispanic, 0.13% White, 0.13% Indian, 0.13% Syrian/Lebanese, and 0.13% other. The population of Barbuda is quite homogeneous, with 89.28% born in Antigua and Barbuda, while the remaining 10.5% are foreign-born, representing over 18 different countries. The top five countries of birth outside of Barbuda are Guyana, Dominica, Jamaica, the United States, and the United States Virgin Islands.
In terms of age distribution, 33.92% of Barbuda's population is aged 0-17, with the largest segment of the population being 18-59 years old. The population of Barbuda has a relatively low level of educational attainment, with 67.46% lacking any form of educational examination. However, the majority of the population is employed, with 75.55% actively working, and only 9.99% attending school.
Health-wise, Barbuda has a low prevalence of certain conditions, with no reported cases of AIDS, a low cancer rate of 0.32%, and a diabetes rate of 6.45%. Allergies are relatively common, affecting 10.75% of the population, while 6.58% have asthma.
When it comes to housing, 73.59% of Barbudans live in owner-occupied homes, 20.95% in privately rented accommodation, and 10.47% in overcrowded housing. Internet access is available to 36.46% of the population, and 31.89% of households have internet. Cable TV is present in 77.46% of households, while 50.36% have fixed-line telephones.
Crime rates in Barbuda are relatively low, with 3.87% of the population being victims of any crime. The sex ratio is 110.42, with more males than females in the population.
Barbuda's Size Compared to US States: A Quick Guide
You may want to see also

The impact of tourism
Barbuda is part of a three-island state with Antigua and uninhabited Redonda in the northeastern Caribbean. The island is approximately 30 miles (48 km) north of Antigua and is one of the most sparsely populated islands in the Caribbean, with a population of around 1,634 and an area of 62 square miles (160 km2). Barbuda's economy is largely based on tourism and government, with the central and local governments being the largest employers on the island.
Tourism has brought economic benefits to Barbuda, contributing significantly to the island's GDP and providing employment opportunities. However, there is a concern that the increase in tourism and construction work, especially on the south coast, may negatively impact the environment and the rural way of life on the island. The natural beaches and peaceful way of life that attract tourists to Barbuda are at risk of being lost due to the relentless construction.
Additionally, Barbuda is vulnerable to the effects of climate change, such as sea level rise and more intense hurricanes, which can cause significant damage to the island's infrastructure and economy. In 2017, Hurricane Irma devastated Barbuda, destroying over 90% of the island's buildings and leading to the evacuation of the entire population to Antigua. The impact of this hurricane highlighted the fragility of the island's infrastructure and the challenges it faces in the face of extreme weather events.
Overall, tourism has had a significant impact on Barbuda, contributing to its economy and employment while also raising concerns about environmental preservation and the potential loss of the island's natural attractions due to increased development.
Is Barbuda Island a US Territory?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Barbuda is an island in the Caribbean Sea, part of the twin-island state of Antigua and Barbuda, located 40km north of Antigua.
Barbuda is a flat coral island with a land area of 161 sq km. The western portion of the island is dominated by the Codrington Lagoon, while the eastern portion features an elevated plateau with salty ponds and scrubland.
The population of Barbuda is approximately 1,634 people, making it one of the most sparsely populated islands in the Caribbean.
Barbuda is known for its natural, pristine beaches, including the famous Pink Sands Beach. It offers various outdoor activities such as swimming, snorkelling, fishing, and caving. The Frigate Bird Sanctuary in the Codrington Lagoon is a popular tourist destination.







