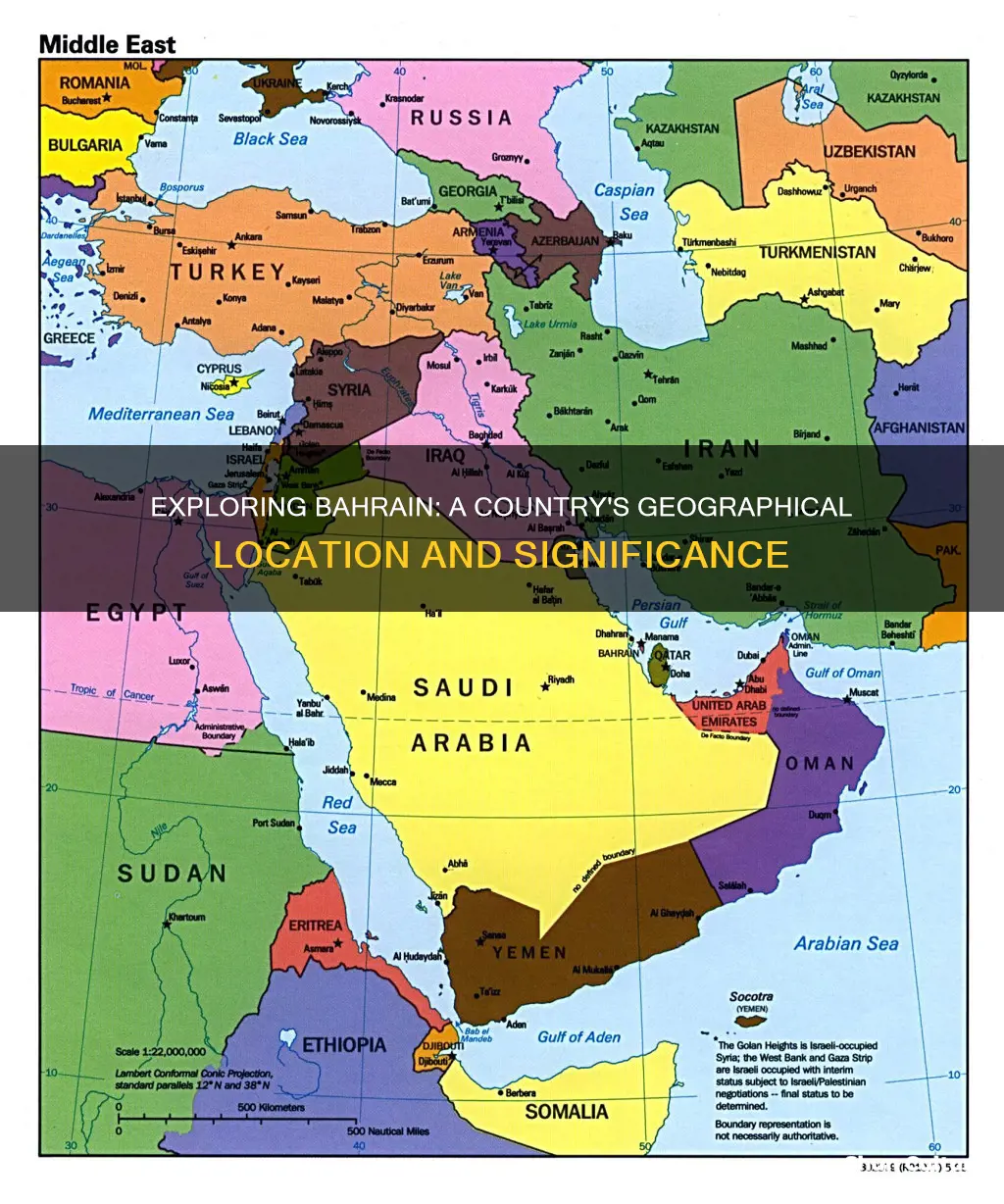
Bahrain is a small island country in the Middle East, officially known as the Kingdom of Bahrain. It is situated in the Persian Gulf and consists of around 50 natural islands and 33 artificial islands, with Bahrain Island making up around 83% of the country's landmass. The country is located between Qatar and Saudi Arabia, with a causeway connecting it to the latter. Bahrain has a population of over 1.5 million people and its capital and largest city is Manama.
Bahrain has a rich history, with archaeologist Geoffrey Bibby claiming that it is the site of the ancient Dilmun civilisation. It has long been famed for its pearl fisheries and was one of the earliest areas to be influenced by Islam. The country has been ruled by various groups throughout its history, including the Portuguese Empire in the 16th century and the Al Khalifa royal family since 1783.
Bahrain has a constitutional monarchy with a parliament consisting of two bodies. While oil still brings in around 80% of the country's revenues, Bahrain has been focusing on diversifying its economy by developing its tourism, financial, and agricultural sectors.
What You'll Learn

Bahrain is an island country in West Asia
Bahrain is officially known as the Kingdom of Bahrain and has a population of 1,501,635 as of May 14, 2023, with 712,362 of those being Bahraini nationals. The capital and largest city is Manama.
Bahrain is believed to be the site of the ancient kingdom of Dilmun, a commercial centre that traded with ancient Sumer. It has been ruled by various groups throughout its history, including the native Arab dynasty, the Khalīfah family (Āl Khalīfah), who have been in power since the late 18th century.
The country's economy has traditionally relied on processing crude oil from neighbouring countries, but in recent years, the financial, commercial services, and communications sectors have grown significantly. Tourism is also a growing industry, with many visitors from neighbouring Saudi Arabia.
Bahrain has a constitutional monarchy with a parliament consisting of two bodies: the Shura Council and the Council of Representatives. The country gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1971.
Sunset Times in Bahrain: When Does the Sun Go Down?
You may want to see also

It is situated on the Persian Gulf
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated on the Persian Gulf. The Persian Gulf is a mediterranean sea in West Asia, an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula. It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz, with its northwestern shoreline formed by the Shatt al-Arab river delta. The Persian Gulf is bordered by Iran, Oman's Musandam exclave, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, and Iraq.
Bahrain is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands, with a total land area slightly greater than that of Singapore. It is joined by causeways to its two main neighbouring islands, Al-Muharraq and Sitrah, and is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway. The country's capital, Manama, is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island.
The Persian Gulf is home to many islands, with Bahrain being the only island nation within it. The Gulf has historically been a major trade route and is now a critical maritime path, with the Allies using it during World War II to transport equipment to the Soviet Union. It is also the world's largest single source of petroleum, with the region producing nearly a third of the world's oil and holding over half of its crude oil reserves.
The Gulf's climate is notoriously unpleasant, with high temperatures and high humidity from May to September. Winters are cooler, with temperatures dipping to around 70 °F (21 °C) from December to March. Rainfall is rare, confined mainly to the winter months and averaging only around 3 inches per year.
The Gulf's waters are very shallow, with a maximum depth of 90 metres (295 feet) and an average depth of 50 metres (164 feet). The water is also very salty, with high evaporation rates leading to salinities ranging from 37 to 41 parts per thousand. The tidal range is around 4 to 5 feet, increasing to 9 to 11 feet in the northwest and southeast.
Eid in Bahrain: When Does the Festival Begin?
You may want to see also

Bahrain is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated on the Persian Gulf. It is officially known as the Kingdom of Bahrain and is recognised as the third-smallest nation in Asia. The country is made up of a small archipelago, consisting of 50 natural islands and 33 artificial islands, with Bahrain Island being the largest and constituting around 83% of the country's landmass.
Bahrain is located between Qatar and the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia and is connected to the latter by the King Fahd Causeway. The causeway is a 25km-long series of bridges and causeways that link Khobar in Saudi Arabia to Al Jasra in Bahrain. The project to build the King Fahd Causeway began in 1954 when King Saud of Saudi Arabia expressed his wish to nurture and solidify the bonds between the two countries. The causeway was officially inaugurated in November 1986 and was named after King Fahd of Saudi Arabia.
The King Fahd Causeway is made up of five bridges that rest on 536 concrete pylons, with seven embankments in the Gulf's shallower waters. One of the embankments, known as Middle Island, has been converted into an artificial island with customs and immigration facilities, a mosque, gardens, and fast-food restaurants. The causeway spans long stretches of sea and reclaimed land and is built using 350,000m3 of concrete and 147,000 metric tonnes of reinforced steel. The four-lane road has two 11.6m-wide roadways and was constructed in three segments, starting from Saudi Arabia.
The causeway is a significant link between Bahrain and Saudi Arabia, with an estimated 25,104 vehicles using it daily. The causeway also serves as a popular tourist attraction, offering vast and thought-provoking views of the surrounding waters.
Understanding Bahrain's Personal Number System: Your Unique Identity
You may want to see also

The country's capital and largest city is Manama
Manama is the capital and largest city of Bahrain, with a population of around 297,502 as of 2012. It is located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island, in the Persian Gulf. Manama has long been an important trading centre, and its economy has traditionally been based on pearling, fishing, boatbuilding, and import trade.
Manama has a rich history, dating back to the Bronze Age. It was first mentioned in Islamic chronicles around 1345 CE and was taken by the Portuguese in 1521, followed by the Persians in 1602. Since 1783, it has been held by the ruling Al Khalifah dynasty, with brief interruptions.
Manama's economy has diversified in recent decades, with significant growth in the banking, tourism, and financial sectors. It is now a major financial hub in the Middle East, with numerous banks and financial institutions. The city is also known for its nightlife, with clubs and bars that attract visitors from all over the world.
Manama is the focal point of Bahrain's road network, and its urban development has led to the expansion of roads and highways connecting it to other parts of the country. The discovery of oil in the early 1930s further accelerated the creation of modern infrastructure in the city and the surrounding areas.
Today, Manama is a cosmopolitan city, known for its diverse population and tolerance towards different faiths. It offers a mix of modern and traditional attractions, including shopping malls, historical sites, and cultural festivals.
Fishing in Bahrain: Best Spots to Cast Your Line
You may want to see also

Bahrain is renowned for its large growth of date palms
Bahrain is a small Arab state situated in a bay on the southwestern coast of the Persian Gulf. It is renowned for its verdant groves of date palms, which have been a source of natural resources for the surrounding area since ancient times. The country's name, Bahrain, is derived from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'.
Bahrain Island is widely believed to be the site of the ancient kingdom of Dilmun, a commercial centre that traded with ancient Sumer. It has been colonised by various groups, including the Khalīfah family (Āl Khalīfah), a native Arab dynasty that has ruled Bahrain since the late 18th century. Recognising the islands' strategic importance, the Khalīfah have opened Bahrain's port facilities to the naval fleets of foreign countries, including the United States.
Bahrain's total land area is slightly larger than that of Singapore. It consists of Bahrain Island and about 30 smaller islands, with the former constituting seven-eighths of the country's total land area. The main island is more varied in appearance, with a rocky and barren central region and a sandy, bleak southern and western lowlands. In contrast, the northern and northwestern coasts feature a narrow belt of date palms and vegetable gardens, irrigated by prolific springs and wells that tap artesian water.
Date palms have played a crucial role in Bahrain's economy and social life. Almost every part of the tree has a practical use, from timber and fuel to food and medicine. However, the discovery of oil has led to revolutionary changes, reducing interest in date palm cultivation. Other factors such as socioeconomic changes, climatic conditions, limited freshwater, and the spread of pests have also contributed to the decline in date palms. Despite these challenges, Bahrain is striving to care for date palms as a state symbol and national treasure. Efforts include the establishment of gene banks, in vitro facilities, and quarantine regulations to protect the trees.
Bahrain's annual date yield does not exceed 16,000 metric tonnes, and the country imports dates from other producing countries to meet market demands. Experts advocate for a radical shift in cultivation, harvesting, and post-harvesting methods to improve the sector.
Unique Hotels in Bahrain: An Unforgettable Experience
You may want to see also







