Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia's republic of Dagestan to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. The country includes the autonomous region of Nakhchivan, which is separated from the rest of Azerbaijan by Armenian territory. Azerbaijan's capital and largest city is Baku, which has the largest and best harbour on the Caspian Sea.
What You'll Learn

Azerbaijan is bordered by Russia, Georgia, Armenia, Iran, and Turkey
Azerbaijan is a landlocked country in eastern Transcaucasia, bordered by Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. The country also has a coastline along the Caspian Sea to the east. The exclave of Nakhchivan, located southwest of Azerbaijan, is bordered by Armenia, Iran, and Turkey.
Russia is Azerbaijan's neighbour to the north. The two countries share a 390km border, and Russia's republic of Dagestan also borders Azerbaijan. Georgia borders Azerbaijan to the northwest, with a border of 480km. Armenia and Turkey both border Azerbaijan to the west, with a border of 1,007km and 15km, respectively. The Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan borders Armenia, Iran, and Turkey, while the country itself shares a border of 756km with Iran to the south.
Azerbaijan's location at the boundary of Eastern Europe and West Asia places it in a unique geographic position, with diverse landscapes and cultural influences from Europe and Asia.
Azerbaijan's Climate: Cold Comforts and Chilly Facts
You may want to see also

The country is located in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
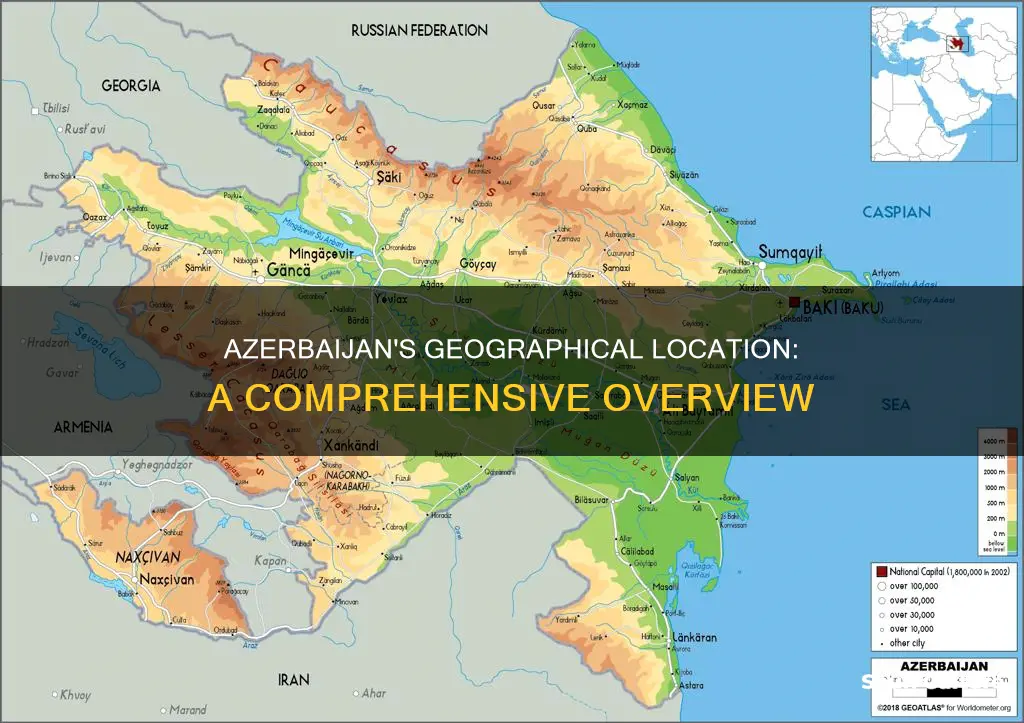
Azerbaijan is a transcontinental country located in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia. It is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia's republic of Dagestan to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. The country is ringed by mountains, except for its eastern Caspian shoreline and some areas bordering Georgia and Iran.
To the northeast, bordering Russia's Dagestan, is the Greater Caucasus range; to the west, bordering Armenia, is the Lesser Caucasus range; and to the extreme southeast, the Talysh Mountains form part of the border with Iran. The highest elevations occur in the Greater Caucasus, where Mount Bazarduzu rises 4,466 metres (14,652 feet) above sea level.
Azerbaijan's landscape is characterised by lowlands, foothills, and mountain regions. The Greater and Lesser Caucasus ranges and the Talysh Mountains cover approximately 40% of the country. The remaining 60% consists of flatlands and extensive central lowlands, through which the Kura River flows. The country's landscape also features eight large rivers, numerous mud volcanoes, and mineral springs.
Azerbaijan's climate is arid, dry, and subtropical, with hot summers and mild winters. The country includes nine of the world's eleven climatic zones, with temperatures and precipitation varying across the different regions. The dry subtropical climate of central and eastern Azerbaijan is characterised by mild winters and very hot summers, with temperatures averaging 27°C and reaching maxima of 43°C. In contrast, the mountain regions experience a dry continental climate, with cold winters and dry, hot summers.
Azerbaijan's flora is rich and diverse, with over 4,500 species of higher plants, including the iron tree, the Lenkoran acacia, the basket oak, the Caucasian persimmon, the evergreen shrub of Ruscus hyrcana, and the box tree.
Azerbaijan Visa: Process for Afghan Travelers
You may want to see also

Azerbaijan is a unitary semi-presidential republic
The president, currently Ilham Aliyev, is elected for a seven-year term and is responsible for drafting and executing the state budget, overseeing the implementation of state economic and social programs, and advising on policy issues. The president also appoints the prime minister and cabinet members, who are then approved by parliament. The executive branch is made up of the president, prime minister, and cabinet.
The legislative branch consists of 125 members, including a speaker, a first deputy speaker, and two other deputy speakers, who are all elected by direct vote. The speaker heads the unicameral National Assembly (Milli Majlis). The legislature is formally independent of the executive and is responsible for making laws and approving some executive decisions, such as the appointment of cabinet members and approval of state budgets.
The judiciary is responsible for interpreting and applying the constitution and arbitrating disputes at various levels. It consists of the Supreme Court, a court of appeal, magistrate courts, district courts, and the constitutional court. The president nominates Supreme Court judges, who are then appointed by parliament to serve ten-year terms.
Azerbaijan holds elections every five years, and all persons above the age of 18 are eligible to participate. Presidential and parliamentary elections are held every five years, but they occur at different times. The government of Azerbaijan has been criticized for human rights violations, corruption, and media oppression.
Azerbaijan's Independence: A Country's Sovereign Journey
You may want to see also

Baku is the capital and largest city
Baku is a very windy city, hence its nickname, the "City of Winds". It is also the world's lowest-lying capital city, at 28 metres (92 ft) below sea level. Baku is renowned for its harsh winds, including the cold northern wind khazri and the warm southern wind gilavar.
Baku has a rich history, with traces of human settlement in the region dating back to the Stone Age. Baku was the realm of the Shirvanshahs during the 8th century AD. The city frequently came under assault from the Khazars and the Rus'. Baku was in the possession of the Shīrvān-Shāhs in the 11th century, who made it their capital in the 12th century. Baku was captured by Peter the Great in 1723, returned to Persia in 1735, and finally captured by Russia in 1806. In 1920, Baku became the capital of the Azerbaijan republic.
Baku's economy is centred on the petroleum industry, with the presence of oil in the region known since antiquity. Baku is a major cultural and educational centre, home to institutions such as Baku State University, Khazar University, and Azerbaijan Technical University. Baku is also a tourist destination, with hotels in the city earning 7 million euros in 2009.
Azerbaijan's Oil Wealth: A Country's Black Gold Fortune
You may want to see also

Azerbaijan is a former Soviet republic
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a former Soviet republic. It was a part of the Soviet Union from 1920 to 1991.
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic (ADR) was the first modern parliamentary republic in the Muslim world. It was also the first secular democratic Muslim-majority state. The ADR was established in 1918, a year after the Russian Empire collapsed, and proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic.
Soviet Rule
In 1920, the country was conquered by the Bolshevik 11th Soviet Red Army and incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (also referred to as the Azerbaijan SSR, Azerbaijani SSR, AzSSR, Soviet Azerbaijan, or simply Azerbaijan).
During its 71 years in the Soviet Union, the Azerbaijan SSR was strictly controlled, especially under the rule of Joseph Stalin and Azerbaijan Communist Party leader Mir Jafar Baghirov. Extensive repressions continued during the 1940s, in parallel with the deportations in the Baltic states, West Ukraine, and Moldova. During this time, the Caucasus suffered from a "cleansing" of Soviet borders and population transfer. In 1949, more than 100,000 people of various ethnic backgrounds were deported from Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Armenia to Kazakhstan and Siberia. Overall, some 120,000 people were deported from Azerbaijan during the first decades of the Soviet era.
Independence
The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Geography
Azerbaijan is a transcontinental country at the boundary of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia's republic of Dagestan to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city.
Politics
Azerbaijan is a unitary semi-presidential republic. It is one of six independent Turkic states and an active member of the Organization of Turkic States and the TÜRKSOY community. Azerbaijan has diplomatic relations with 182 countries and holds membership in 38 international organizations, including the United Nations, the Council of Europe, the Non-Aligned Movement, the OSCE, and the NATO PfP program.
Demographics
Azerbaijan's population is approximately 9.7 million people. The vast majority of the country's population (97%) is nominally Muslim, but the Constitution of Azerbaijan does not declare an official religion, and all major political forces in the country are secular.
Economy
Azerbaijan is a developing country and ranks 91st on the Human Development Index. The country's economy is dominated by industry, and more-diversified pursuits have supplemented the exploitation of oil, of which Azerbaijan was the world's leading producer at the beginning of the 20th century.
Ganja, Azerbaijan: A Devastating Incident and its Aftermath
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Azerbaijan is a transcontinental country found at the boundary of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It is part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia's republic of Dagestan to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south.
The capital of Azerbaijan is Baku.
Azerbaijan has a population of approximately 10 million people.