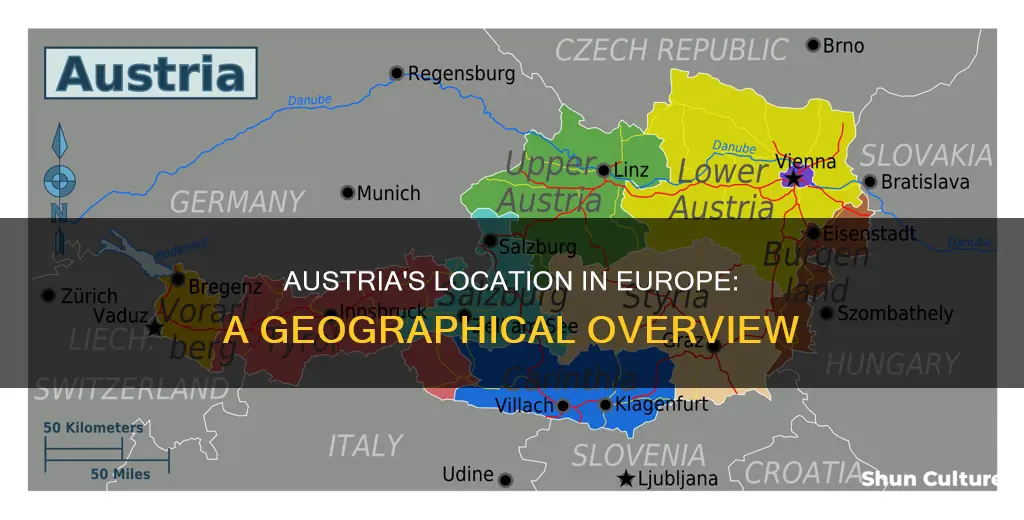
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country is largely mountainous, with mountains and forests giving the Austrian landscape its character. Austria's population is around 9 million, and it has a high standard of living, ranking fifth in the European Union in terms of GDP per capita.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Continent | Europe |
| Geographical Size | 83,882 km2 |
| Population | 9,158,750 |
| Official Language | German |
| Currency | Euro |
| EU Member State | Yes |
| Schengen Member | Yes |
| Type of Government | Federal Parliamentary Republic |
| Head of Government | Chancellor Karl Nehammer |
| Head of State | President Alexander Van der Bellen |
| Number of States | 9 |
| GDP per Capita | €46,200 |
What You'll Learn
- Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe
- It is bordered by Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein
- The country is divided into nine federal states
- Austria is a member of the European Union
- It is a federal parliamentary republic with a chancellor as the head of government and a president as the head of state

Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe
Landlocked in the heart of Europe, Austria shares borders with eight other countries: Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. This strategic location has had a profound impact on the country's history, as it has often served as a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. Throughout the centuries, Austria has been a pivotal point for the movement of people, goods, and ideas across the continent.
The Alps are a dominant geographical feature of Austria, covering more than half of the country's territory. This majestic mountain range not only provides a stunning backdrop to many Austrian cities and towns but also offers a wealth of outdoor activities, including skiing, hiking, and mountaineering. The Alps have shaped the country's identity, with many Austrians taking great pride in their mountainous heritage.
Located in the Danube Basin, Austria is also characterized by its many rivers and lakes, which provide opportunities for water sports and leisure activities. The Danube River, one of Europe's major waterways, flows through the country, connecting Austria to the Black Sea and providing a vital trade route. The river is also a source of hydroelectric power and a popular destination for river cruises.
Austria's central location has had a significant impact on its culture and architecture. The country has a rich history, with many castles, palaces, and historic buildings that showcase a range of architectural styles. Vienna, the nation's capital, is renowned for its grand Habsburg-era architecture, including the iconic Schönbrunn Palace. The city's cultural offerings, from opera to art, have been influenced by its central European location, blending traditions from neighboring countries.
In conclusion, Austria's position as a landlocked country in Central Europe has shaped many aspects of its character. From its diverse geography to its cultural offerings, Austria embodies the essence of Central Europe. Its history as a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange continues to influence its modern identity, making it a fascinating destination that combines the traditions of its neighboring countries with its unique Alpine heritage.
Obtaining Austrian Citizenship: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

It is bordered by Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein
Austria is bordered by eight other European countries: Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein.
Germany
Austria shares its longest border with Germany, at 815km (507 miles). The border runs from east to west in its western part, and in a northeastward direction from a point south of Salzburg to its eastern end. The border passes through the Austrian states of Vorarlberg, Tyrol, Salzburg, and Upper Austria, and the German state of Bavaria.
The Czech Republic
Austria and the Czech Republic have a long shared history. They were united under the rule of Ottokar II of Bohemia in the 13th century and later joined to form a major European power under the Habsburg dynasty. The two countries established diplomatic relations in 1920. Today, the border between them is 487km (302 miles) long.
Slovakia
The border between Austria and Slovakia is the second shortest in Europe, at 91km (56 miles). It runs from the tripoint formed by the Czech, Slovak, and Austrian borders near the towns of Hohenau an der March and Borský Svätý Jur, southwards, and then eastwards along the Morava River.
Hungary
Austria's border with Hungary is part of the former Austro-Hungarian Empire, which was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe from 1867 to 1918. The Empire was a military and diplomatic alliance consisting of two sovereign states with a single monarch.
Slovenia
Slovenia is bordered by Austria to the north. The two countries were once part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and Slovenia gained independence in 1991.
Italy
The Austrian-Italian border is a 404km (251-mile) land border along the Alps. The border has existed since 1861 but was formalised by a peace treaty in 1920.
Switzerland
The border between Austria and Switzerland is divided into two parts, separated by the Principality of Liechtenstein, with a total length of 180km (110 miles). The longer, southern stretch runs across the Grison Alps, and the shorter one follows the Alpine Rhine.
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein is bordered by Switzerland in the south and west and Austria in the east and north. The total length of its borders is 47 miles.
Exploring Innsbruck: Activities and Attractions in Austria's Alpine Gem
You may want to see also

The country is divided into nine federal states
The Republic of Austria is a federal state composed of nine autonomous federal provinces. These are known as federal states or 'Bundesländer' in Austrian German. The European Commission refers to them as provinces.
Each Austrian federal state has an elected legislature, the federal state parliament, and a federal state government (Landesregierung) headed by a governor (Landeshauptmann or Landeshauptfrau).
The nine federal states of Austria are:
- Carinthia (Kärnten)
- Lower Austria (Niederösterreich)
- Upper Austria (Oberösterreich)
- Vienna
- Burgenland
- Styria
- Salzburg
- Tyrol
- Vorarlberg
Vienna, the capital of Austria, is unique in that it is both a city and a federal state. The mayor has the rank of a federal state governor, while the city council also functions as a federal state parliament.
The federal states of Austria have a degree of autonomy. They can pass laws that stay within the limits of the constitution, and each federal state has representatives in the main Austrian parliament. They also have their own legislative bodies and executive organs, and their own systems of financial management.
The federal principle provides for the sharing of tasks – legislative, executive and financial – between the nine Austrian Provinces and the federal government.
The federal states are sub-divided into districts (Bezirke) and statutory cities (Statutarstädte). Districts are subdivided into municipalities (Gemeinden). Statutory Cities have the competencies otherwise granted to both districts and municipalities.
Austria's EU Membership: A Clear Yes or No?
You may want to see also

Austria is a member of the European Union
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a member of the European Union, having joined in 1995. Austria's membership in the EU has had a significant impact on its foreign and European policy, allowing it to advocate for its interests and concerns within the EU's decision-making structures.
Austria has a population of around 9 million people and covers an area of 83,879 square kilometres. It is a federal parliamentary republic with a chancellor as the head of government and a president as the head of state. The country consists of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna.
Austria's economy has benefited significantly from its membership in the EU, particularly due to its involvement in the growing single market. About 70% of Austria's foreign trade is with other EU member states, and since joining the EU, Austrian exports have tripled, and 18,500 new jobs have been created annually. Austria ranks fifth in the EU in terms of GDP per capita, contributing about 2.8% to the EU's total GDP.
Austria actively participates in the decision-making process within the EU. It has representatives in the European Council, the Council, and its preparatory bodies. Additionally, there are directly elected Austrian members of the European Parliament, as well as Austrian representatives in other EU institutions. Austria has held the rotating presidency of the Council of the EU three times: in 1998, 2006, and 2018.
Austria's membership in the EU provides its citizens with numerous advantages, such as the freedom to travel, study, and settle in any other EU member state. It also benefits from being part of the single market, a shared approach to common challenges like migration and climate change, and concrete gains like improved infrastructure and digitalised public services.
Austria-Hungary's Expansion: Bosnia and Herzegovina Annexation Explained
You may want to see also

It is a federal parliamentary republic with a chancellor as the head of government and a president as the head of state
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, bordering eight countries: Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is characterized by a diverse landscape, ranging from the Alpine mountains to the northern plains and the Danube River, which flows through the country's eastern border. Geographically, Austria is strategically located at the heart of Europe.
Regarding its political system, Austria is a federal parliamentary republic. This means that it functions as a representative democracy with a federal structure, dividing powers between a central government and nine states, or "Bundesländer." The Austrian constitution establishes a clear separation of powers between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government, ensuring a system of checks and balances.
The head of state in Austria is the Federal President, who is directly elected by universal suffrage for a term of six years, with the possibility of re-election once. The role of the Federal President is largely ceremonial and representative, but they do have some important duties and reserve powers. These include appointing the Chancellor, who is the head of government, and the members of the federal government, as well as signing laws and international treaties. The President also serves as the commander-in-chief of the country's armed forces.
The head of government and the country's chief executive is the Federal Chancellor. This position is usually held by the leader of the largest party in the National Council, the lower house of Austria's bicameral parliament. The Chancellor is responsible for proposing ministers to the President for appointment and leading the government's activities, including formulating and implementing policies and representing Austria in the European Union (EU).
The Austrian parliament consists of two chambers: the National Council and the Federal Council. The National Council is the primary legislative body, with 183 seats, and its members are elected for a term of five years through a system of proportional representation. The Federal Council, on the other hand, represents the nine states and has 61 members, with each state sending a varying number of representatives depending on its population. While the Federal Council's powers are more limited, it plays a role in reviewing and approving legislation passed by the National Council.
In summary, Austria's political system as a federal parliamentary republic ensures a democratic representation of its citizens, with a clear division of powers between the branches of government and a federal structure that takes into account the interests of its nine states. The interplay between the roles of the Federal President and the Federal Chancellor, along with the legislative functions of parliament, contributes to a balanced and effective governance structure.
Travel Guide: Switzerland to Austria
You may want to see also







