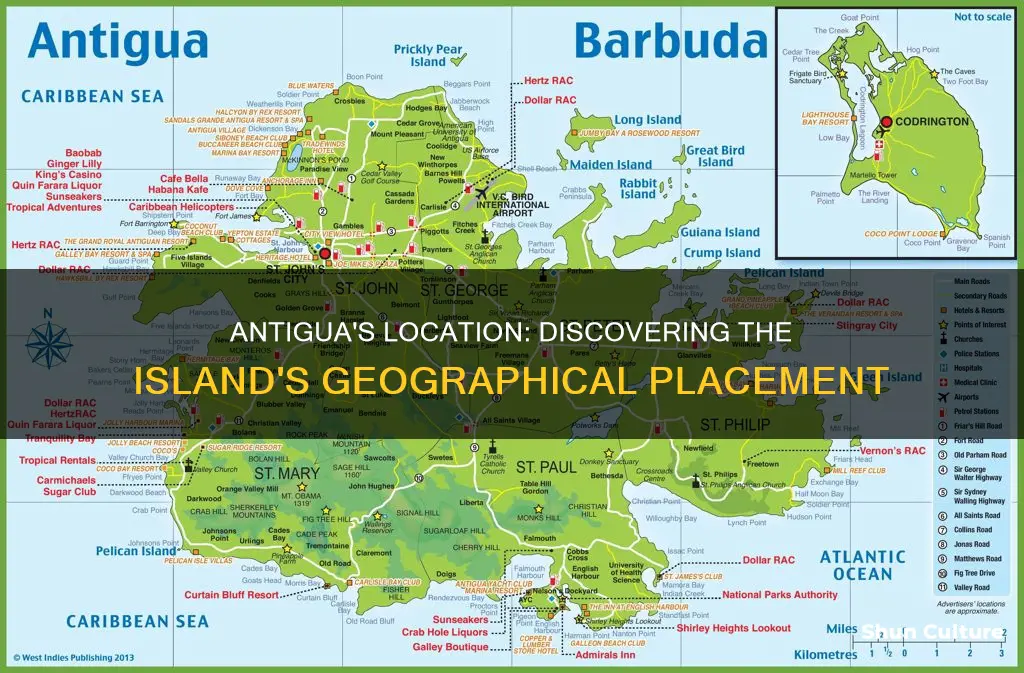
Antigua, also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the local population, is an island in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands and the most populous island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. The country is a dual-island nation, with the islands of Antigua and Barbuda positioned in the Caribbean Sea, acting as a natural border that separates it from the Atlantic Ocean. The closest nation to Antigua is St. Kitts and Nevis. The capital of Antigua and Barbuda, St. John's, is located on the northwestern coast of Antigua. The island's intricate coastline is fringed with reefs and boasts numerous natural harbours, including English Harbour, a protected deep-water harbour and the site of the UNESCO World Heritage Site, Nelson's Dockyard.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Country | Antigua and Barbuda |
| Type of Location | Island |
| Location | Caribbean Sea, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean |
| Hemisphere | Northern and Western |
| Area | 440 sq. km |
| Population | 83,191 (2011 Census) |
| Capital | St. John's |
| Highest Point | Mount Obama (405m) |
| Economy | Tourism, agriculture |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar |
| Airports | VC Bird Airport |
What You'll Learn

Antigua's capital, St. John's
Antigua and Barbuda is a dual-island nation in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles. The islands are a natural border that separates the Atlantic Ocean from the Caribbean Sea. The nation is part of the Leeward Islands chain, located southeast of Puerto Rico and north of Guadeloupe.
St. John's is the capital of Antigua and Barbuda and is located on the island of Antigua's northwestern coast. It is the largest city in the nation, with a population of around 22,000-25,000 people. St. John's has been the administrative centre of the nation since the islands were colonised in 1632, and it became the official seat of government when the nation gained independence in 1981.
As the main commercial centre of the island, St. John's is a hub for shopping, dining, and galleries. The city is known for its shopping malls and boutiques, selling designer jewellery and haute-couture clothing. The city also attracts tourists with its cruise ship port and commercial centre located around the waterfront at Redcliffe Quay.
Some of the main attractions in St. John's include the St. John's Cathedral, built in 1845 after being destroyed twice by earthquakes in 1683 and 1745. The Museum of Antigua and Barbuda, located in the colonial Court House, features the early history of the island, including the Arawak and colonial periods. The local market, held every Friday and Saturday morning, is also a popular attraction, as well as the Antigua Rum Distillery, located at the Citadel.
St. John's is served by the V. C. Bird International Airport and is home to two medical schools, secondary schools, and private grade schools. The city has a tropical savanna climate with summer-like weather year-round, and rainfall is highest during the months of September to November due to hurricane activity.
Barbuda's Best Accommodation Options for Your Vacation
You may want to see also

Antigua's highest point, Mount Obama
Antigua is a small island in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles, which acts as a natural border between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. The island is known for its white sand and clear blue waters, making it a popular tourist destination for those looking to escape harsh winters. Antigua's highest point is Mount Obama, formerly known as Boggy Peak. This peak rises to a height of around 400 metres (approximately 1,300 feet) and is located in the hilly southwestern region of the island. It is a remnant of a volcanic crater and is surrounded by lush green vegetation, giving the impression of a tropical rainforest.
Mount Obama is the highest point of the Shekerley Mountains and was renamed in 2009 after United States President Barack Obama. The name change was short-lived, however, as the original name, Boggy Peak, was restored in 2016. The peak holds significant cultural heritage as the surrounding area was once used for sugarcane plantations during slavery times. The name Boggy Peak itself has an interesting history, stemming from stories told by slave masters about the dangers of the Boogie Man, who lived in the mountains, to discourage slaves from escaping.
Reaching the summit of Mount Obama can be challenging due to a barbed-wire fence surrounding it. The official summit is owned by a cell phone company, requiring visitors to obtain permission for access. The mountain is often included in Caribbean country high-point traverses, and while it does not present technical difficulties, the logistics of gaining access can be tricky. The peak is occupied by various telecom-related structures, and the summit's highest point is within a large private fenced compound. While there are no guided trips to the summit, those lucky enough to gain access are rewarded with impressive views across most of the island.
The area surrounding Mount Obama, including the steep hills of the Shekerley Mountains, is being transformed into a national park and nature reserve to protect the natural environment. The hills here are ancient volcanic formations with steep-sided valleys that hold fast-flowing streams during heavy rain. Despite this, there are no permanent rivers or streams on the island, and rainfall is quite light. Antigua's warm weather and low rainfall make it an ideal destination for outdoor activities all year round.
Exploring Antigua and Barbuda: Travel Options and Adventures
You may want to see also

Antigua's neighbouring islands
Antigua, part of the dual-island nation of Antigua and Barbuda, is located in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the most populous island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda.
Antigua and Barbuda is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. The closest nation to the islands is St. Kitts and Nevis. The islands are also nearby to the British overseas territory of Montserrat and the French overseas territory of Guadeloupe.
The country consists of two major islands, Antigua and Barbuda, and several smaller islands, including Great Bird, Green, Guiana, Long, Maiden, Prickly Pear, York, and Redonda. The permanent population is approximately 97,120 (2019 estimates), with 97% residing in Antigua. St. John's, Antigua, is the country's capital, major city, and largest port. Codrington is Barbuda's largest town.
Antigua's coastline is intricate, with bays and headlands fringed with reefs and shoals. Several inlets, including Parham and English Harbour, afford anchorage for shipping, and St. John's has a deepwater harbour. The island has an area of 108 square miles (280 square km). It is mostly low and undulating, but in the west, there are volcanic rocks that rise to 1,330 feet (405 meters) at Mount Obama (formerly Boggy Peak).
Exploring Antigua and Barbuda: Time Zones and More
You may want to see also

Antigua's beaches
Antigua is a Caribbean island located in the northeastern Caribbean Sea. It is part of a dual-island nation, with its sister island, Barbuda, located to the north. The island is known for its beautiful beaches and Caribbean resorts.
Antigua has over 365 beaches, all with pristine white sand and surrounded by turquoise waters. The beaches offer a range of activities, from water sports to snorkelling and scuba diving. The calm, shallow waters at some beaches, like Dickenson Bay, are perfect for children and those new to swimming in the sea.
Dickenson Bay
Located in the northwestern part of Antigua, in the parish of St. John, Dickenson Bay is one of the most beautiful and pristine beaches on the island. It offers a range of water sports activities, including jet skiing, wakeboarding, parasailing, tubing, kayaking, snorkelling, and scuba diving. The beach is about a mile long, providing ample space for a peaceful and tranquil experience. It is also just a 9-minute drive from St. John's, with luxury beach resorts, restaurants, and shopping options nearby.
Ffryes Beach
Ffryes Beach is situated on the western shore of the island, towards the southern end. It is about a 30-minute drive from St. John's and is known for its secluded and tranquil atmosphere. Beach chairs and umbrellas are available for rent, and there are restaurants and parking facilities nearby. The water at Ffryes Beach is deeper than at other beaches, and the waves can sometimes be strong.
Carlisle Bay
Carlisle Bay is a crescent-shaped beach on the south coast of Antigua, about 40 minutes by car from St. John's. It is surrounded by palm trees and offers views of luxury yachts and catamarans. The beach is clean and tranquil, with calm waters, making it an ideal spot for relaxation. There is a resort at one end and palm trees at the other, providing options for both types of experiences.
Half Moon Bay
Half Moon Bay is a quiet and isolated beach located on the Atlantic coast of Antigua, in Saint Philip Parish. The crescent-shaped beach gets its name from its shape, and it is known for its strong waves, making it ideal for bodysurfing and boogie boarding. The left side of the bay is sheltered by rocks, providing calmer waters for those who prefer a more relaxed swim or snorkelling.
Jolly Beach
Jolly Beach is considered one of the best beaches in Antigua and is located in Jolly Harbour on the western side of the island. It is a mile-long spacious beach, perfect for romantic walks and livelier water sports activities like jet skiing and snorkelling. The beach is conveniently located, with restaurants, bars, and shopping within walking distance.
Pigeon Point Beach
Pigeon Point Beach is a popular spot located in English Harbour on the southern tip of Antigua, about a 40-minute drive from St. John's. It is known for its calm, clear waters, making it ideal for snorkelling. The beach offers plenty of shade from the surrounding trees, and nearby hiking trails lead to Nelson's Dockyard, a marina, and cultural site.
Turner's Beach
Turner's Beach is a beautiful stretch of powdery white sand located along the west coast of Antigua, in the Caribbean Sea. It is a spacious, clean, and undeveloped beach with several restaurants and beach bars within walking distance. It is also an excellent spot for snorkelling, with the opportunity to see tropical fish and stingrays.
Galleon Beach
Galleon Beach is a pristine and uncrowded beach located in English Harbour, about a 40-minute drive from St. John's. It is popular for snorkelling, with the left side of the beach offering the best experience. The calm and transparent waters make it ideal for spotting aquatic life, including turtles, stingrays, tropical fish, and coral. The beach is surrounded by hills and offers beautiful scenery, with the option to explore nearby sections via rock scrambling.
Long Bay Beach
Long Bay Beach is located on the Atlantic side of the island and is protected by a reef, resulting in calm waters ideal for swimming and snorkelling. The beach is rarely crowded, and beach chair and umbrella rentals are available for $10-$20 USD.
Hawksbill Bay Beaches
The Hawksbill Bay Beaches are located on the western shore of Antigua, about a 20-minute drive from St. John's. These beaches are accessible through the Hawksbill Resort and include Royal Palm Beach, Sea Grape Beach, Honeymoon Cove, and Eden Beach, the only clothing-optional beach in Antigua. The beaches in this area are generally quiet and secluded, offering a peaceful atmosphere.
Fort James Beach
Fort James Beach is located on the western shore of Antigua and is known for its natural beauty and serene atmosphere. It is just a 6-minute drive from St. John's and offers a mix of eateries and bars, along with parking, public showers, and beach chair and umbrella rentals. However, the water can be turbulent at times, so it may not be suitable for children or weak swimmers.

Antigua's history
Antigua and Barbuda is a dual-island nation in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles, acting as a natural border between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. The islands were inhabited by three successive Amerindian societies thousands of years before European colonisation. Christopher Columbus surveyed the islands in 1493, naming the larger one Santa Maria de la Antigua.
England succeeded in colonising the islands in 1632, with Thomas Warner as the first governor. Settlers raised tobacco, indigo, ginger, and sugarcane as cash crops. Under English/British control, the islands witnessed an influx of both Britons and African slaves. In 1674, Sir Christopher Codrington established the first large sugar estate in Antigua, and Barbuda became a leasehold where he could raise provisions for his plantations. In the 50 years after Codrington established his initial plantation, the sugar industry became so profitable that many farmers replaced other crops with sugar, making it the economic backbone of the islands.
Slavery was common in Barbuda in the 1700s and until 1834, and the island was a source of slaves for other locations. Several slave rebellions took place on the island, with the most serious in 1834–5. Britain emancipated slaves in most of its colonies in 1834, but that did not include Barbuda, so the island then freed its own slaves.
During the 18th century, Antigua was used as the headquarters of the British Royal Navy Caribbean fleet. English Harbour Dockyard, as it came to be called, was the main base, and facilities there were greatly expanded during the later 18th century. Admiral Horatio Nelson commanded the British fleet for much of this time, and made himself unpopular with local merchants by enforcing the Navigation Act, a British ruling that only British-registered ships could trade with British colonies.
In the 20th century, as the main cash crops changed over the years, the economy of Antigua and Barbuda began to decline as other nations were able to sell goods at a price no longer feasible to sustain in the Antiguan economy. In more recent times, however, Antigua has developed a primarily service-based economy relying on tourism as their leading source of income.
The islands gained full independence from the United Kingdom on 1 November 1981, becoming the nation of Antigua and Barbuda. However, it remains part of the Commonwealth of Nations, and remains a constitutional monarchy, with the first Queen of Antigua and Barbuda Elizabeth II.
Frequently asked questions
Antigua is an island in the Caribbean's Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands and is the most populous island in the country of Antigua and Barbuda.
Antigua is a fairly big island with an intricate coastline. It has a land area of 281 square kilometres (108 square miles) and a perimeter of 87 kilometres (54 miles). The island is mostly low-lying and undulating, with volcanic rocks in the west that rise to a height of 405 metres (1,330 feet) at Mount Obama (formerly known as Boggy Peak). Antigua is distinct from the other Leeward Islands due to the absence of mountains and forests.
The capital of Antigua and Barbuda is St. John's, located on the north-western coast of Antigua. Over 22,000 people live in the capital, which has a deep harbour that can accommodate large cruise ships.
Antigua is known for its magnificent views and beaches. It is said to have 365 beaches, one for every day of the year! The island also has a rich history, including sites like English Harbour, a UNESCO World Heritage Site that was once a British colonial naval station.







