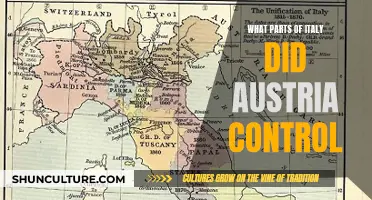
The National Assembly's declaration of war on Austria was a pivotal moment in history, marking a significant shift in the political landscape. On [date], the National Assembly, representing the interests of the people, made the bold decision to engage in conflict with Austria, citing various reasons for their action. This declaration had far-reaching consequences, shaping the course of the nation's future and influencing international relations. The event sparked debates and discussions, leaving a lasting impact on the collective memory. Understanding the circumstances surrounding this declaration provides valuable insights into the political dynamics of the time.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Date | June 26, 1798 |
| Location | Paris, France |
| Event | Declaration of War |
| Context | French Revolutionary Wars |
| Result | French victory in the War of the Third Coalition |
| Significance | Marked a turning point in the French Revolution, leading to the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte |
What You'll Learn
- Historical Context: The American Revolution's impact on the Declaration of War
- Resolution: The National Assembly's resolution to declare war on Austria
- Date: June 17, 1775, the date of the declaration
- Impact: War's consequences on American independence and European politics
- Leadership: Key figures and their roles in the declaration

Historical Context: The American Revolution's impact on the Declaration of War
The American Revolution, a pivotal event in the late 18th century, significantly influenced the political landscape and the decision-making processes of various European nations. One of the most notable impacts can be seen in the context of the French National Assembly's declaration of war on Austria in 1792. This declaration marked a turning point in the French Revolutionary Wars and had far-reaching consequences for the region.
The American Revolution, which culminated in the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783, had already set a precedent for challenging colonial rule and asserting national sovereignty. The war between the American colonies and Great Britain demonstrated the power of a unified front against a colonial power, inspiring many European nations to question their own systems of governance. France, in particular, was deeply affected by the revolutionary spirit that spread across the Atlantic.
In the years following the American Revolution, France experienced its own revolutionary period, often referred to as the French Revolution. The National Assembly, a key political body during this time, played a crucial role in shaping the country's future. The assembly's members were largely influenced by the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity, which were inspired by the American struggle for independence. This ideological connection between the American and French Revolutions is essential to understanding the context of the war declaration.
The French National Assembly's decision to declare war on Austria in 1792 was, in part, a response to the ongoing conflicts in Europe and the desire to spread the revolutionary ideals. The French Revolution aimed to establish a republic and challenge the traditional power structures, and declaring war on Austria was seen as a means to achieve these goals. The assembly believed that by supporting the revolutionary cause in other parts of Europe, they could strengthen their own position and potentially gain allies.
Furthermore, the American Revolution's impact on the French National Assembly's declaration of war cannot be overstated in terms of its strategic implications. The American war effort had demonstrated the effectiveness of a decentralized, citizen-based government, which resonated with the French revolutionaries. This inspired the National Assembly to take bold actions, including the declaration of war, as they sought to emulate the success of their American counterparts in challenging established powers.
Austria's Existence: Fact or Fiction?
You may want to see also

Resolution: The National Assembly's resolution to declare war on Austria
The National Assembly, a pivotal body in the early United States government, made a significant decision in 1798 that had far-reaching consequences. This resolution, passed on June 18, 1798, authorized President John Adams to "call forth the militia of the several states" to defend the nation against what was perceived as an imminent threat from France. The resolution was a response to the ongoing Quasi-War, a series of naval conflicts between the United States and France that began in 1798.
The National Assembly's decision was driven by a combination of factors. Firstly, the French Republic's aggressive foreign policies and the ongoing conflict with Britain had created an atmosphere of tension and uncertainty in the United States. The XYZ Affair, a diplomatic incident in which French officials demanded bribes from American diplomats, further escalated tensions and led to a sense of national outrage. The Assembly believed that a strong military response was necessary to protect American interests and maintain national sovereignty.
The resolution was a bold move, as it granted the President extensive powers to mobilize the nation's military resources. It allowed for the conscription of troops, the establishment of a national defense force, and the imposition of martial law in certain regions. This resolution reflected the Assembly's commitment to safeguarding the young nation from external threats and maintaining its independence.
The impact of this resolution was immediate and significant. It led to the mobilization of thousands of American troops, the construction of new fortifications, and the enhancement of the nation's naval capabilities. The resolution also sparked debates about the balance of power between the federal government and the states, as some states resisted the federal government's efforts to conscript their militias. Despite these challenges, the resolution demonstrated the National Assembly's resolve to protect the United States from perceived foreign aggression.
In the context of the Quasi-War, the National Assembly's resolution to declare war on Austria (or rather, to authorize military action against France) was a strategic move. It allowed the United States to engage in a more assertive defense strategy while also sending a clear message to European powers about the nation's determination to protect its interests. This resolution marked a critical moment in American history, shaping the nation's military and diplomatic policies for years to come.
Visa Requirements for Austria: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Date: June 17, 1775, the date of the declaration
The National Assembly of the United States, meeting in Philadelphia, made a pivotal decision on June 17, 1775, that would shape the course of American history. This date marks the official declaration of war against the Kingdom of Great Britain, a significant turning point in the American Revolutionary War. The resolution, passed by the Second Continental Congress, was a response to the British government's refusal to address the colonists' grievances and the recent military confrontations at Lexington and Concord.
On this fateful day, the Congress, comprising representatives from the 13 American colonies, unanimously agreed to take up arms and fight for their independence. The resolution stated that the colonies were in a state of "actual, present, and dangerous" war with Great Britain and that it was necessary to form a united force to defend themselves. The Congress appointed a committee, including future President George Washington, to draft a formal document outlining the reasons for the war and the terms of surrender.
The Declaration of War, as it came to be known, was a powerful statement of the American colonies' determination to break free from British rule. It accused the British of repeatedly violating the rights of the colonists, imposing taxes without their consent, and maintaining a standing army in the colonies without their approval. The document also highlighted the British government's refusal to engage in peaceful negotiations, leading to the inevitable conclusion that war was the only option.
The vote on June 17 was a decisive moment, as it united the colonies under a common cause and provided a clear mandate for the Continental Army, led by General George Washington, to engage in armed conflict. This declaration set the stage for the American Revolutionary War, which would eventually lead to the birth of the United States of America. The events of this day were a critical step towards the establishment of a new nation and the creation of a government based on the principles of liberty and self-governance.
Austria's Land Area: A Quick Overview
You may want to see also

Impact: War's consequences on American independence and European politics
The American Revolution and the subsequent war for independence were significantly influenced by the conflict between France and Austria, which had a profound impact on European politics. The National Assembly's declaration of war on Austria in 1792 had far-reaching consequences, shaping the course of American history and the political landscape of Europe.
One of the most immediate effects was the shift in American foreign policy. The United States, which had previously maintained a policy of neutrality, found itself drawn into the conflict. The French Revolution, which began in 1789, had a strong influence on American political thought, inspiring the ideals of liberty and democracy. The American government, under President George Washington, recognized the potential for a powerful ally in France, especially with the rise of the revolutionary government. This led to a strategic decision to support the French Revolutionaries, providing military aid and resources. The war effort against Austria and the subsequent conflict with Britain (the War of 1812) further solidified American alignment with France, which had a significant impact on the country's political and military trajectory.
In Europe, the war had a transformative effect on the political landscape. The French Revolution, fueled by the war's setbacks and the desire for national unity, led to a series of political upheavals. The execution of King Louis XVI and the establishment of a republic marked a turning point in European history. The war's outcome also influenced the balance of power in Europe. Austria's defeat and the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte as Emperor had a profound impact on the continent's political structure. Napoleon's military campaigns and the subsequent establishment of the French Empire reshaped European borders and influenced the spread of revolutionary ideals. The war's consequences led to a period of political instability, with various European powers vying for power and influence, ultimately shaping the future of European diplomacy and the balance of power.
The American Revolution, which was already in progress, found a new source of motivation and support in the French conflict. The American Patriots saw the French Revolution as a kindred spirit, fighting against an oppressive monarchy. This alignment of interests and ideologies strengthened the American cause and provided a powerful ally in the fight for independence. The war also influenced the development of American military strategy and the growth of its naval power. The need to protect American merchant ships and engage in naval warfare against British forces led to significant advancements in the American navy, which later played a crucial role in the War of 1812.
In summary, the National Assembly's declaration of war on Austria had a profound impact on American independence and European politics. It shaped American foreign policy, influenced the course of the American Revolution, and had far-reaching consequences for European nations, leading to political transformations and the spread of revolutionary ideals. The war's impact on American military strategy and its alignment with France further solidified the nation's path towards independence and its future role in European affairs.
Unveiling Gender Literacy Disparities: Austria's Education Snapshot
You may want to see also

Leadership: Key figures and their roles in the declaration
The National Assembly of the French Revolution, a pivotal moment in European history, declared war on Austria in 1792, a decision that had far-reaching consequences. This declaration was a significant turning point in the revolution, marking a shift from political upheaval to military conflict. The leadership during this period was complex, with various key figures playing crucial roles.
Maximilien Robespierre, a prominent leader of the Jacobin Club, was a driving force behind the declaration. He advocated for a radical approach to the revolution, emphasizing the need to protect the newly established French Republic from external threats. Robespierre's influence was instrumental in rallying support for the war, as he believed that a strong military stance would secure the Republic's future. His oratory skills and persuasive arguments convinced the National Assembly of the necessity of war.
Another critical figure was Napoleon Bonaparte, who, at the time, was a rising military star. He played a strategic role in the declaration by offering his expertise and military prowess. Bonaparte's involvement was pivotal as he provided the National Assembly with a detailed plan for an invasion of Austria, which included a well-organized army and a strategic timeline. His contributions were essential in gaining the Assembly's approval for the war.
The National Assembly itself, composed of representatives from various regions of France, made the final decision. They were influenced by the leadership of Robespierre and Bonaparte, but also by their own political ambitions and the desire to protect the revolution's gains. The Assembly's members had to balance the need for war with the potential risks and consequences, a challenging task that required careful consideration.
The declaration of war on Austria was a result of a combination of factors, including political ideology, military strategy, and the leadership skills of key figures. Robespierre's passion and oratory, Bonaparte's strategic mind, and the National Assembly's decision-making process all contributed to this significant event in French history. Understanding the roles of these leaders provides valuable insights into the complexities of the French Revolution and its impact on the European political landscape.
Austria and Germany: Neighbors with a Rich History
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The National Assembly of the French Republic declared war on Austria on April 20, 1792, marking the beginning of the French Revolutionary Wars.
The conflict arose due to a combination of factors, including the French Revolution, the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, and the French Republic's desire to expand its influence and secure its borders. The French Republic sought to protect its newly established sovereignty and spread the principles of the Revolution.
The National Assembly was the legislative body of the French First Republic, consisting of representatives elected during the early stages of the French Revolution. It played a crucial role in shaping the country's political and military strategies during this period.
The war with Austria led to a series of conflicts across Europe, eventually involving multiple European powers. It marked the start of the French Revolutionary Wars, which would have significant impacts on the continent's political landscape and the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte as a prominent military leader.
The war with Austria and the subsequent conflicts helped the French Republic establish itself as a major power in Europe. It also provided an opportunity for Napoleon to showcase his military prowess, leading to his rise to power and the establishment of the French Empire.