The unification of Germany under the leadership of Otto von Bismarck was a significant event in European history. One of the key steps in this process was the acquisition of Austrian territory, which played a crucial role in the formation of the German Empire. This territorial expansion occurred during a period of intense political and military maneuvering, and it marked a pivotal moment in the struggle for German unification. The question of when Bismarck took Austrian territory is an important one, as it highlights the strategic decisions and diplomatic maneuvers that shaped the course of German history.
What You'll Learn
- Bismarck's Rise to Power: The unification of Germany and the role of Otto von Bismarck
- Austerian Wars: Bismarck's involvement in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866
- Bauer Revolution: The impact of the 1848 revolution on Bismarck's political career
- German Empire Formation: The establishment of the German Empire and its territories
- Bismarck's Legacy: His influence on German politics and the legacy of his policies

Bismarck's Rise to Power: The unification of Germany and the role of Otto von Bismarck
The unification of Germany in the 19th century was a complex and pivotal moment in European history, largely driven by the ambitions and strategic maneuvers of Otto von Bismarck, a key political figure of the time. Bismarck's rise to power and his role in the unification process are deeply intertwined with his diplomatic skills, strategic thinking, and ability to navigate the political landscape of the German states.
Bismarck's journey began in the small German state of Prussia, where he was born in 1815. He quickly rose through the ranks of the Prussian civil service, demonstrating a keen intellect and a strong sense of national identity. Bismarck's political career took a significant turn in 1862 when he was appointed as the Minister President of Prussia by King Wilhelm I. This position allowed him to exert considerable influence over Prussian politics and lay the groundwork for his future endeavors.
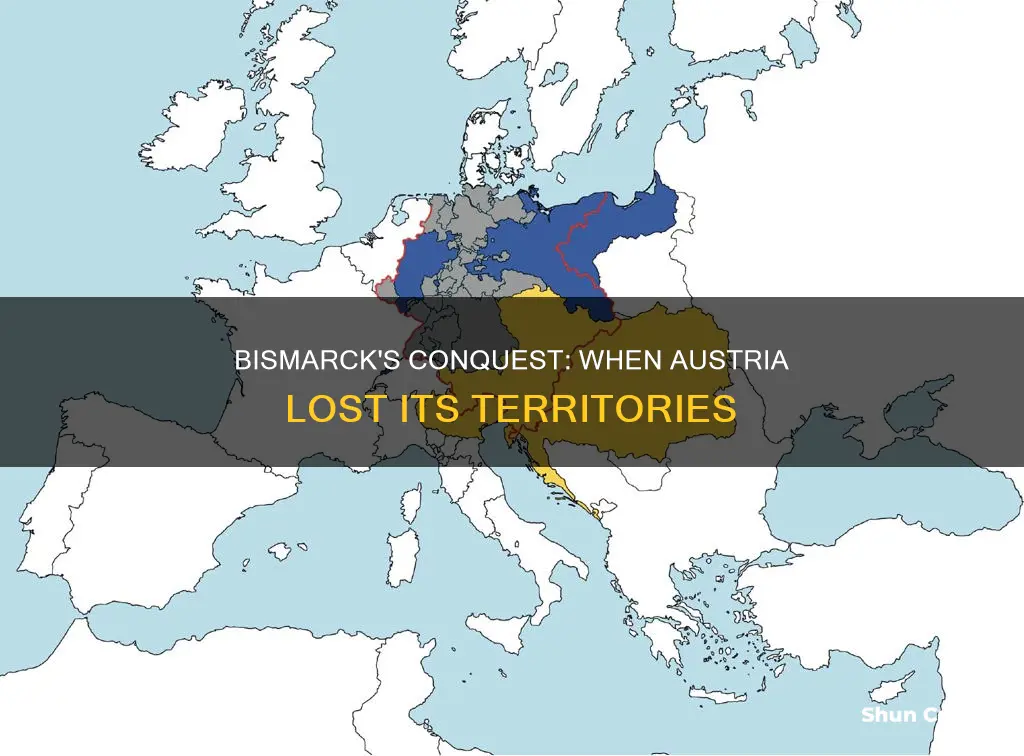
One of Bismarck's most notable achievements was his role in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866. Prussia, under Bismarck's leadership, successfully challenged the Austrian Empire for dominance in the German states. Through a series of strategic military campaigns and diplomatic maneuvers, Bismarck secured a decisive victory, resulting in the dissolution of the Austrian Empire and the acquisition of significant territories, including those previously held by Austria. This war marked a turning point in Bismarck's career, as it showcased his ability to navigate international conflicts and assert Prussia's power.
The aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War set the stage for Bismarck's next major move. He envisioned a unified Germany, free from the influence of other European powers. In 1867, Bismarck played a pivotal role in the establishment of the North German Confederation, which brought together the northern German states under Prussian leadership. This confederation laid the foundation for the eventual unification of Germany. Bismarck's diplomatic skills were instrumental in convincing the various German states to align with Prussia, ensuring a unified front against potential adversaries.
The final piece of the puzzle fell into place with the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-1871. Bismarck's strategic planning and diplomatic prowess led to a decisive Prussian victory over France. This war not only resulted in the unification of Germany but also established Bismarck as a dominant figure in European politics. The Treaty of Frankfurt, signed in 1871, formally unified the German states and recognized the German Empire, with Bismarck as its first Chancellor. His role in the unification process was so significant that he became known as the "Iron Chancellor," a title that highlights his unwavering determination and strategic approach to achieving German unity.
Austria-Hungary's Secret WW1 Goal: Unveiling the True Motive
You may want to see also

Austerian Wars: Bismarck's involvement in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866
The Austro-Prussian War of 1866 was a pivotal conflict that shaped the future of Germany and the balance of power in Europe. While Otto von Bismarck is often credited with the unification of Germany, his role in the war against Austria was significant and complex. Bismarck's involvement in the war was driven by his strategic vision and desire to establish a strong German state.
Bismarck's actions began with a series of diplomatic maneuvers. He skillfully negotiated with other European powers, particularly Russia, to isolate Austria. Bismarck's goal was to weaken Austria's position and create a favorable environment for the Prussian army. Through a series of treaties and alliances, he managed to secure Russian support, which was crucial for the upcoming conflict.
The war itself commenced in June 1866. Bismarck's strategy focused on a quick and decisive victory. He ordered the Prussian army to invade Austrian territory, targeting key cities and military installations. The Prussian forces, under the command of Field Marshal von Roon and General von Blumenthal, achieved remarkable success. They defeated the Austrian army at the Battle of Königgrätz, a decisive victory that effectively ended the war. Bismarck's military strategy was characterized by rapid troop movements and the use of superior Prussian technology and tactics.
Bismarck's involvement extended beyond military affairs. He played a crucial role in shaping the political outcome of the war. After the Prussian victory, Bismarck negotiated the Peace of Prague with the Austrians, which imposed harsh terms on Austria, including territorial losses and the dissolution of the Austrian Empire's alliance with Russia. This marked a significant shift in European politics, as it weakened Austria and solidified Prussia's dominance in the region.
In summary, Bismarck's involvement in the Austro-Prussian War was a demonstration of his strategic brilliance and political acumen. His diplomatic skills, combined with military prowess, led to the defeat of Austria and the establishment of Prussia's dominance in Germany. The war's outcome had long-lasting effects on the region, setting the stage for Bismarck's later efforts to unify Germany and shape its future.
Austria's Economy: Impact of Natural Resources
You may want to see also

Bauer Revolution: The impact of the 1848 revolution on Bismarck's political career
The year 1848 marked a pivotal moment in European history with the outbreak of the 'Bauer Revolution', a series of revolutionary events that swept across the German states, including Prussia. This period of political upheaval had a profound impact on the young Otto von Bismarck, who would later become a key figure in the unification of Germany and the architect of its empire.
Bismarck, at the time, was a 28-year-old Prussian officer and civil servant. The revolution presented him with a unique opportunity to engage with the political landscape and assert his influence. He was an early supporter of the revolutionary cause, advocating for democratic reforms and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy in Prussia. As the revolution unfolded, Bismarck's involvement grew, and he played a crucial role in the formation of the Frankfurt Parliament, a revolutionary assembly aimed at creating a unified German state.
The impact of the Bauer Revolution on Bismarck's political career was significant. It provided him with a platform to voice his political ideals and gain recognition. Bismarck's involvement in the revolution allowed him to network with influential figures, including liberal politicians and intellectuals, which would later prove valuable for his political ambitions. He became a prominent figure in the liberal movement, advocating for a strong, centralized government while also pushing for democratic reforms.
During this period, Bismarck's political career took off. He was appointed as a government official and later became a member of the Prussian Assembly, where he actively participated in debates and proposed reforms. His ability to navigate the complex political landscape of the time, coupled with his strategic thinking, positioned him as a rising star within the liberal faction. The revolution's legacy would continue to shape Bismarck's political ideology and his approach to governance.
In the years following the Bauer Revolution, Bismarck's political career flourished. He became a key advisor to Prussian Prime Minister Otto von Bismarck, and his influence grew exponentially. The revolutionary experiences of 1848 left an indelible mark on his political philosophy, shaping his views on the role of the state, the importance of national unity, and the need for a strong, centralized government. These experiences laid the foundation for his future leadership and his significant impact on the unification of Germany.
The Fate of the Austrian Monarchy: A Royal Legacy Unravels
You may want to see also

German Empire Formation: The establishment of the German Empire and its territories
The formation of the German Empire was a pivotal moment in European history, largely shaped by the ambitious leadership of Otto von Bismarck. His strategic maneuvers and diplomatic skills played a crucial role in unifying the various German states into a powerful empire. One of the key steps in this process was the acquisition of Austrian territories, which significantly expanded the Empire's reach and influence.
Bismarck's strategy involved a series of calculated wars and political alliances. The first significant conflict was the Austro-Prussian War of 1866. Prussia, under Bismarck's leadership, successfully challenged Austria and its allies, leading to the Treaty of Prague. This treaty resulted in the dissolution of the Austrian Empire's influence over several German states, including those that would later become part of the German Empire. The war effectively ended the influence of the Austrian Empire in the German-speaking world, allowing Bismarck to centralize power and begin the unification process.
Following the Austro-Prussian War, Bismarck's attention turned to the southern German states, which were still under the influence of the Kingdom of Bavaria and other smaller principalities. In 1867, the North German Confederation was established, with Prussia as its dominant power. This confederation included most of the northern German states and laid the groundwork for further unification. Bismarck's influence was instrumental in this process, as he negotiated and secured the support of these states, gradually bringing them under Prussian control.
The final step in the formation of the German Empire was the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-1871. This conflict, sparked by the French Empire's attempt to capture Alsace-Lorraine, resulted in a decisive Prussian victory. The Treaty of Frankfurt, signed in 1871, not only ended the war but also finalized the unification of Germany. The treaty recognized the German Empire, with Bismarck as its chancellor, and included the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine, which had been a point of contention between France and Prussia.
The acquisition of Austrian territories and the subsequent unification of German states under Prussian leadership were significant achievements in Bismarck's diplomatic and political career. These actions not only created a powerful German Empire but also reshaped the political landscape of Europe, leaving a lasting impact on the continent's history.
Buying Property in Austria: Rights for US Citizens
You may want to see also

Bismarck's Legacy: His influence on German politics and the legacy of his policies
The unification of Germany under the leadership of Otto von Bismarck is a pivotal moment in European history, and his legacy continues to shape the country's political landscape. Bismarck's strategic maneuvers and diplomatic skills played a crucial role in the formation of the German Empire, which had a profound impact on the region's political and social structures.
One of Bismarck's most significant contributions was his ability to navigate complex political alliances and rivalries. He skillfully utilized the Franco-Prussian War (1870-1871) to unite the German states under Prussian leadership, ultimately leading to the establishment of the German Empire with Wilhelm I as its emperor. This unification process was not merely a military conquest but a diplomatic achievement, as Bismarck employed a series of strategic treaties and agreements to bring the various German states together.
Bismarck's policies had a lasting impact on German politics. He advocated for a strong, centralized state and implemented a conservative, nationalist agenda. His government introduced a range of social welfare reforms, including health insurance and workers' compensation, which were groundbreaking at the time. These policies aimed to improve the lives of the working class and gain their support for the state, marking a shift towards a more welfare-oriented state. Additionally, Bismarck's foreign policy, known as the 'Bismarckian System', focused on maintaining peace in Europe by forming alliances and promoting a balance of power. This policy helped Germany avoid major conflicts for several decades, allowing for economic growth and the consolidation of power.
The legacy of Bismarck's actions can be seen in the long-term stability and prosperity of the German Empire. His unification efforts created a sense of national identity and pride among the German people, which had a profound impact on their cultural and political development. Bismarck's conservative policies also contributed to a more socially conservative and nationalist atmosphere in Germany, influencing the country's political discourse for generations.
Furthermore, Bismarck's influence extended beyond German borders. His diplomatic skills and strategic thinking inspired other European leaders, and his policies served as a model for the balance of power in Europe. The establishment of the German Empire under Bismarck's leadership marked a significant shift in the continent's political dynamics, leaving a lasting impact on the development of modern European states.
Austria's Majestic Alps: Unveiling the Ultimate Mountain Range
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Bismarck did not take Austrian territory. The unification of Germany was a complex process that involved multiple stages and the efforts of various political leaders and movements. Otto von Bismarck played a crucial role in the unification process, but he did not directly acquire Austrian territory. The unification of Germany was primarily achieved through diplomatic and military strategies, including the Franco-Prussian War and the formation of the German Empire in 1871.
The Austrian Empire, under Emperor Franz Joseph, was a significant obstacle to German unification. Bismarck's strategy involved isolating Austria by forming alliances with other German states, such as Prussia and the German Confederation. The Austrian Empire's involvement in the Austro-Prussian War (1866) was a turning point, as Prussia's victory led to the establishment of the North German Confederation, which Bismarck then used as a platform for further unification.
Bismarck's actions did not directly result in the loss of Austrian territories. The territories that became part of the German Empire were primarily from the Kingdom of Prussia and other German states, not from the Austrian Empire. The annexation of Austrian territories was a result of the Austro-Prussian War, which was a conflict between Prussia and Austria, not a direct action by Bismarck. The unification process involved complex political and military developments, and the territories of the German Empire were acquired through various means, including treaties and the establishment of new political entities.







