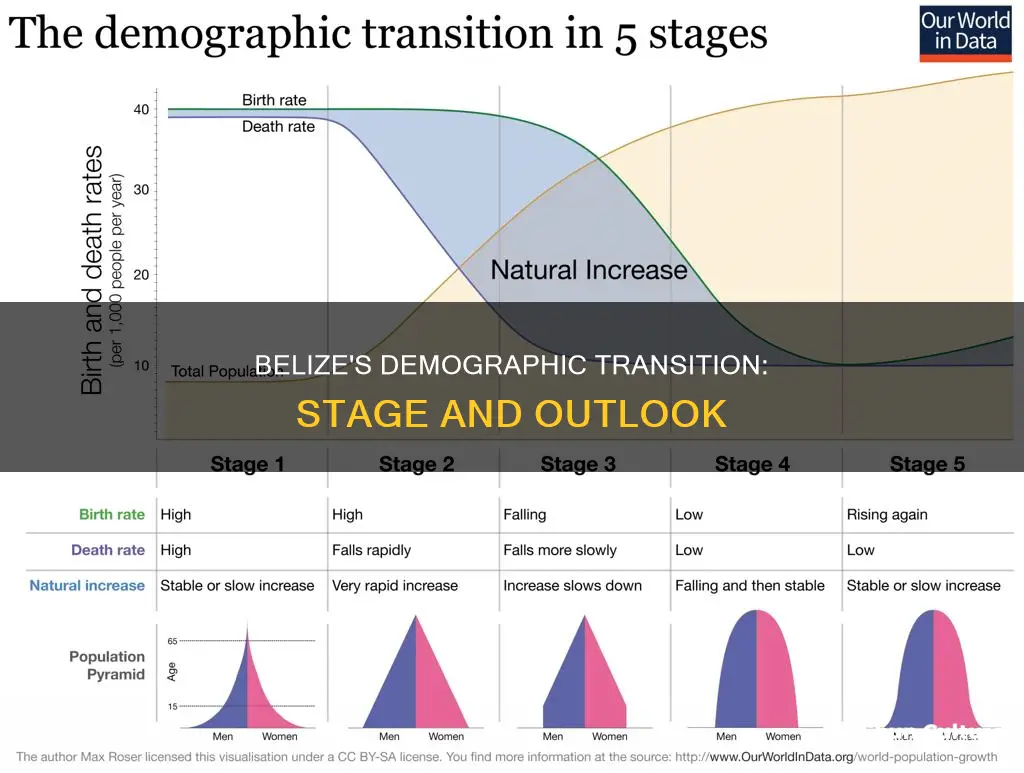
Belize is currently in stage 2 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM). This is characterised by a high birth rate and a decreasing death rate due to advances in healthcare, family planning, and technology. Belize's population is growing, and the country is poorer relative to other nations. As a result of the National Women's Commission of Belize, women's rights have improved, and in 1990, a bill was signed giving women equal rights to men.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Stage of the Demographic Transition Model | 1 |
| Population | 441,471 |
| Population Density | 35 people per square mile |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.64% (2022) |
| Birth Rate | 21.28 births/1,000 population (2022) |
| Death Rate | 3.94 deaths/1,000 population (2022) |
| Total Fertility Rate | 2.62 children born/woman (2022) |
| Infant Mortality Rate | 12.0 (2009) |
| Life Expectancy | 75.82 years (2022) |
| Literacy Rate | 80% |
| Urban Population | 46.4% (2022) |
What You'll Learn
- Belize is in stage 1 of the DTM due to a high birth rate and high death rate
- Belize is the most sparsely populated nation in Central America
- Belize has the lowest population density in Central America
- Belize's population is growing due to improved water sanitation and urbanisation
- Belize's population is multiracial, with Mestizo and Creole being the largest ethnic groups

Belize is in stage 1 of the DTM due to a high birth rate and high death rate
Belize is currently in stage one of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM) due to a high birth rate and high death rate. The birth rate in Belize is 19.292 births per 1000 people as of 2024, a decline of 1.7% from 2023. The death rate in Belize, however, increased by 1.1 deaths per 1,000 inhabitants in 2021, reaching 6.35 deaths per 1,000 inhabitants, the highest value in the observed period. This combination of a high birth rate and a high death rate places Belize in stage one of the DTM.
Stage one of the DTM is characterised by high birth and death rates, and it typically occurs in pre-industrial societies. During this stage, countries often experience high infant mortality rates and low life expectancy. In Belize, infant mortality rates have been declining, and life expectancy is on the rise. Despite this, Belize still has a relatively high infant mortality rate and a lower life expectancy compared to other countries. For example, the life expectancy in Belize is 75.82 years, which is lower than the global average of 79 years.
The high birth rate in Belize can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, Belize has a relatively young population, with 32.57% of the population under 14 years old. This results in a larger proportion of women of childbearing age, leading to a higher number of births. Additionally, Belize has a significant population of religious groups that encourage large families and oppose family planning and contraception. According to the 2010 census, 40.1% of the population is Roman Catholic, and 31.5% is Protestant, with groups such as Pentecostals and Adventists showing slight growth in recent years.
The high death rate in Belize is influenced by various factors, including the leading causes of death in the country. In 2019, ischemic heart disease was the leading cause of death, accounting for 49.2 deaths per 100,000 people. Interpersonal violence and diabetes mellitus were the second and third most significant causes of death, with mortality rates of 37.3 and 36 deaths per 100,000 people, respectively. Furthermore, Belize has a high AIDS-related mortality rate compared to other countries in the region.
Belize Airport Ocean Resorts
You may want to see also

Belize is the most sparsely populated nation in Central America
The population of Belize is predominantly multiracial, with approximately 52.9% of the population being of mixed Indigenous (mainly Maya) and European descent, known as Mestizo. Additionally, about 24.9% are Kriols, 10.6% are Maya, and 6.1% are Afro-Amerindian (Garifuna). The remaining population includes people of European, East Indian, Chinese, Middle Eastern, and North American descent. The country's largest cities include Belize City, San Ignacio, Belmopan, and Orange Walk Town.
Belize's population is distributed across rural and urban areas, with slightly more than half living in rural regions. Belize City, the principal port, commercial centre, and former capital, is home to about one-fourth of the population. The country's capital, Belmopan, is located in the Cayo District and has a population of approximately 19,931.
In terms of demographics, Belize is currently in Stage 1 of the Demographic Transition Model. This characterisation is due to its low population growth rate, high birth rate, and high death rate. In Stage 1, the total population flux is inconsistent from year to year. Typically, a high birth rate is a response to a high death rate as a country seeks to maintain its replacement level.
Belize's population growth rate of 1.87% per year (as of 2018) is the second-highest in the Central American region and one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere. This growth rate, combined with the country's land area, contributes to its sparse population distribution.
Belize's diverse population reflects its history as a melting pot of cultures. The country has a rich multicultural heritage, influenced by its past as a British Colony and its proximity to the Caribbean and Central America. English is the official language, and Belize is the only Central American country where this is the case. However, Belizean Creole is the most widely spoken dialect, and Spanish is also commonly spoken, particularly in the northern districts.
Belize's Wildlife: A Tropical Haven
You may want to see also

Belize has the lowest population density in Central America
Belize is the least densely populated country in Central America, with a population density of 18 people per square kilometre. It has a total land area of 22,810 square kilometres and a population of around 410,000-440,000 people.
Belize is currently in stage 1 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM), characterised by a high birth rate and a high death rate. This results in inconsistent total population growth from year to year. In stage 1, countries tend to have a low population growth rate, which is the case for Belize.
Belize's population is largely rural, with slightly more than half of the population living outside of urban areas. The population is also quite diverse, with most Belizeans being of multiracial descent. The official language of Belize is English, but many Belizeans are multilingual, speaking a variety of languages including Spanish, Mayan dialects, and Belizean Creole.
Belize's population growth rate is one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere, at 1.87% per year (2018 estimate). This growth rate, combined with Belize's large land area, contributes to its low population density.
In summary, Belize's low population density can be attributed to its stage 1 placement in the DTM, its diverse and multilingual population, and its high population growth rate in relation to its land area.
Belize's Postal Code System
You may want to see also

Belize's population is growing due to improved water sanitation and urbanisation
Belize is currently in the early stages of the demographic transition model, with a growing population and increasing life expectancy. The country's population is expected to continue growing due to improved water sanitation and urbanisation.
Belize has made significant strides in improving water sanitation and access to clean drinking water. According to the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), Belize's water supply exceeds that of other Central American and Caribbean nations. The country has an abundant natural water supply from groundwater, rivers, and the sea. By 2009, residents enjoyed improved water connections, and the government has since continued its efforts to enhance sanitation and access to potable water. Companies like Belize Water Services Limited (BWS) have invested in infrastructure, doubling the water supply to the communities they serve. As a result, sanitation in Belize has improved, and the gap between poor sanitation and sound infrastructure is narrowing.
However, challenges remain, especially in rural areas and the south side of Belize City. UNICEF's Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) programme highlights that over 20% of schools in Belize report an unreliable water supply, and 25% have untreated water. Basic cleaning materials like toilet paper and soap are also lacking in many schools. There is a pressing need for improved latrines and better menstrual hygiene management for girls and women, especially in rural communities.
Despite these challenges, the country's urban population is growing. In 2022, Belize's urban population was 188,030, a 1.74% increase from 2021. As of 2023, 47.8% of the population is urban, with Belize City being the principal port, commercial centre, and home to about one-fourth of the country's population. The urban population growth can be attributed to the country's urbanisation and the continued improvement of sanitation and infrastructure.
Belize's population growth is also influenced by its position as a popular tourist destination. The country's vast natural ecosystems and welcoming locals attract both celebrities and non-famous individuals looking to purchase property or vacation. Between 2017 and 2018, tourist visits to Belize increased by nearly 25%, indicating a demand for improved quality of life for both citizens and visitors.
In summary, Belize's population is growing due to improved water sanitation, urbanisation, and its appeal as a tourist destination. The country has made significant progress in enhancing water sanitation and infrastructure, which, along with urbanisation, contributes to its growing population. However, challenges remain, particularly in rural areas, where basic sanitation infrastructure is lacking, and in schools, where reliable water supply and adequate sanitation facilities are needed.
Royal Caribbean's Belize City Port
You may want to see also

Belize's population is multiracial, with Mestizo and Creole being the largest ethnic groups
Belize is a country with a multiracial population, with Mestizo and Creole being the largest ethnic groups. Belize is considered the most culturally diverse nation in Central America. It is a melting pot of cultures, languages, and religions. The country's population primarily consists of people of mixed ethnic origins, including English Creoles and Spanish Mestizos.
Mestizos, who make up about 52.9% of Belize's population, are people of mixed Indigenous (mostly Maya) and European (mainly Spanish) descent. They are the descendants of the original Maya inhabitants of the Yucatán peninsula and early Spanish colonizers. The Mestizo population in Belize has grown over time due to the influx of refugees, economic migrants, and seasonal farm workers from neighbouring Central American countries. Mestizos are found throughout Belize but are predominantly located in the northern lowlands of Corozal and Orange Walk and in the western district of Cayo. They introduced agriculture to Belize, which was previously a society heavily reliant on timber extraction for British buyers. Mestizo culture is a blend of Spanish and Mayan influences, evident in their food, language, and belief systems. They predominantly speak Spanish and practise Catholicism, incorporating Mayan food and cultural elements into their religious traditions.
Creoles, also known as Kriols, constitute around 25% of Belize's population and are primarily the mixed-race descendants of enslaved West and Central Africans and European colonizers, mainly English and Scottish log cutters. Over time, they have intermarried with other ethnic groups in Belize, including Miskito, Jamaicans, Caribbean people, Mestizos, Europeans, Garifunas, Mayas, Chinese, and Indians. Creoles are predominantly found in urban areas such as Belize City and most coastal towns and villages. They were the majority group in Belize until the 1980s and played a pivotal role in shaping Belizean national identity. The Creole language, known as Kriol, is now recognised as an official language in Belize, showcasing the significant influence of this ethnic group.
Belize's population distribution also includes other ethnic groups such as indigenous Maya (11.3%), Garifuna (6.1%), East Indian (3.9%), Mennonite (3.6%), Caucasian/White (1.2%), and Asian (1%) communities. Each of these groups contributes to the rich cultural tapestry of Belize, bringing their unique traditions, languages, and customs.
In terms of the demographic transition model, Belize is currently in Stage 1. This characterisation is due to its low population growth rate, high birth rate, and high death rate. In Stage 1, total population flux is inconsistent from year to year. Typically, a high birth rate accompanies a high death rate as a country seeks to reach or maintain its replacement level.
Belize's Diverse Settlers
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) illustrates the growth and decline of a country's population and its level of development.
Stage 1 of the DTM is characterised by high birth and death rates, low sanitation, limited healthcare, and little to no family planning or technology. Stage 2 sees a rapid decrease in death rates due to advances in healthcare, family planning, and technology, but birth rates remain high. In Stage 3, birth and death rates continue to decrease rapidly, and Stage 4 countries have very low birth and death rates, high levels of education, and advanced technology and healthcare.
Belize is considered to be in Stage 2 of the DTM. This is due to its high birth rates, declining death rates, and ongoing development in healthcare, family planning, and technology.
As a Stage 2 country, Belize has a high proportion of children, and most of the population is dependent on others for resources like food, water, and shelter. The country is also facing challenges in providing safe drinking water and managing the impact of rural living on the cost of resources.







