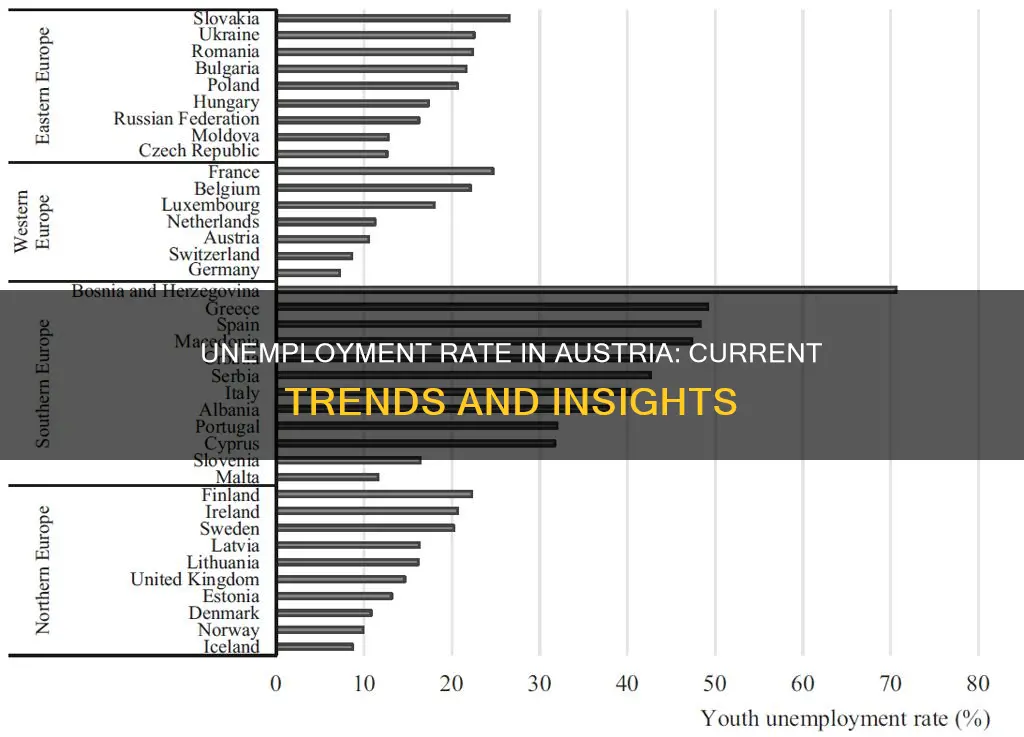
The unemployment rate in Austria, a country known for its strong economy and low unemployment, has historically been one of the lowest in the European Union. As of the latest data, the unemployment rate in Austria stands at approximately 4.5%, which is significantly lower than the EU average. This rate reflects the country's robust job market and the government's commitment to supporting employment through various initiatives. Understanding these figures is crucial for assessing the economic health of Austria and its ability to provide job opportunities for its citizens.
What You'll Learn
- Demographics: Age, gender, and education levels of the unemployed in Austria
- Regional Disparities: Unemployment rates vary across regions, with some areas more affected than others
- Industry Impact: Sectors like tourism and manufacturing have seen significant job losses
- Government Policies: Impact of government initiatives on reducing unemployment
- Economic Recovery: How the economy's recovery affects unemployment rates and job creation

Demographics: Age, gender, and education levels of the unemployed in Austria
The unemployment rate in Austria, as of the latest data, stands at approximately 4.5%, which is relatively low compared to many other European countries. This rate, however, masks some interesting demographic trends among the unemployed population.
Age-wise, the majority of the unemployed in Austria fall into the 25-34 age group. This demographic is often considered the prime working age and is crucial for the labor market. Younger individuals, aged 15-24, also constitute a significant portion of the unemployed, which is a concern as it indicates a potential skills gap or a lack of opportunities for this age group. On the other hand, older individuals, particularly those aged 55 and above, experience higher unemployment rates, which could be attributed to age-related discrimination or a mismatch between their skills and the current job market demands.
Gender distribution among the unemployed is also noteworthy. Women in Austria have a slightly higher unemployment rate than men, with a difference of about 1-2 percentage points. This disparity can be attributed to various factors, including occupational segregation, where women are often concentrated in sectors with higher unemployment rates, and the gender pay gap, which can lead to financial instability and higher unemployment rates.
Education levels play a crucial role in the unemployment landscape. Interestingly, the data reveals that individuals with higher education qualifications, such as university degrees, often face higher unemployment rates compared to those with lower educational attainment. This paradox can be explained by the mismatch between the skills demanded by the job market and the skills possessed by these highly educated individuals. For instance, certain technical or vocational skills might be in higher demand, and those with lower educational levels might be more adaptable to these roles.
Furthermore, the region within Austria can also influence unemployment demographics. Urban areas, particularly Vienna, tend to have higher unemployment rates, often due to a more diverse and competitive job market, which can lead to a more selective hiring process. In contrast, rural areas might offer fewer job opportunities, resulting in lower unemployment rates but also a more limited job market.
Customs Fees for Electronics: Austria's Import Costs Explained
You may want to see also

Regional Disparities: Unemployment rates vary across regions, with some areas more affected than others
The unemployment rate in Austria, as of the latest data, stands at around 4.5%, which is relatively low compared to many other European countries. However, this figure masks significant regional disparities, with certain areas experiencing much higher unemployment rates. These variations are primarily due to the diverse economic landscape and the varying levels of industrialization and development across regions.
In the western regions of Austria, particularly in the states of Vorarlberg and Tyrol, the unemployment rate is notably lower, often below the national average. These areas have a strong tourism industry, with many resorts and ski destinations, which provide seasonal employment opportunities. Additionally, the presence of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in these regions contributes to a more robust local economy, offering a variety of job prospects.
In contrast, the eastern regions, including the states of Burgenland, Carinthia, and Styria, face higher unemployment rates. These areas have traditionally relied on heavy industry, such as metal production and manufacturing, which have been in decline in recent years. The shift towards a more service-oriented economy has not yet fully materialized, leaving these regions with a higher proportion of low-skilled jobs and a more limited job market.
The capital city, Vienna, also exhibits a unique pattern. While it has a lower unemployment rate than the eastern states, it still faces challenges due to its high cost of living and a competitive job market. Vienna's strong service sector and presence of international organizations provide a steady stream of jobs, but the city also attracts a large number of immigrants seeking employment, which can put pressure on the local job market.
Addressing these regional disparities is a key challenge for the Austrian government. Strategies may include investing in infrastructure and education in the less-developed regions to attract new industries and create more job opportunities. Additionally, providing incentives for businesses to establish themselves in these areas could help reduce the unemployment gap between the east and the west. Understanding and tackling these regional variations are essential for ensuring a more balanced and sustainable economic growth across Austria.
Austrian Crystals: Are They Worth the Investment?
You may want to see also

Industry Impact: Sectors like tourism and manufacturing have seen significant job losses
The tourism industry in Austria has been significantly impacted by the global economic downturn, particularly due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The country's reliance on tourism as a major economic sector has led to a sharp decline in visitor numbers, resulting in widespread job losses. Many hotels, restaurants, and travel agencies have had to lay off staff or reduce their workforce, as the industry grapples with a sharp drop in demand. This has had a cascading effect on related sectors, such as hospitality and entertainment, which have also seen a decline in business. The impact is particularly severe in regions that heavily depend on tourism, such as the Alps and Vienna, where the closure of ski resorts and the cancellation of cultural events have further exacerbated the situation.
Similarly, the manufacturing sector in Austria has also faced significant challenges. The global supply chain disruptions and the economic slowdown have led to a decline in production and, consequently, a reduction in the workforce. Many manufacturing companies have had to cut jobs or implement cost-saving measures, including temporary layoffs and reduced working hours. This sector's impact is felt across the country, with regions known for their automotive and machinery industries experiencing a particularly hard hit. The automotive industry, in particular, has seen a decline in sales and production, leading to job cuts and a shift towards more sustainable and innovative practices.
The effects of these job losses are far-reaching, impacting not only the individuals directly affected but also their families and the wider community. Many employees in these sectors have been long-term workers, and the sudden loss of employment can lead to financial strain and uncertainty about the future. The government has implemented various support programs, including unemployment benefits and retraining initiatives, to assist those affected. However, the road to recovery for these industries is expected to be long, requiring significant investment and strategic planning to regain their former glory.
The tourism and manufacturing sectors' struggles have contributed to a broader economic challenge in Austria, with the unemployment rate reflecting the overall economic downturn. As these industries continue to navigate the post-pandemic landscape, the government and industry leaders must work together to develop sustainable solutions. This includes investing in infrastructure, promoting domestic tourism, and fostering innovation in manufacturing to create new job opportunities and ensure the long-term viability of these sectors.
In summary, the significant job losses in the tourism and manufacturing industries in Austria have had a profound impact on the country's economy and its workforce. The pandemic's effects have exposed vulnerabilities in these sectors, highlighting the need for strategic interventions to support recovery and create a more resilient economic future.
Austria's Student Population: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Government Policies: Impact of government initiatives on reducing unemployment
The Austrian government has implemented various initiatives to combat unemployment, which has historically been a significant economic challenge. One of the key strategies is the promotion of vocational training and apprenticeships, recognizing that a skilled workforce is essential for economic growth. The government encourages businesses to offer apprenticeships, providing financial incentives and subsidies to companies that take on young people for training programs. This approach aims to bridge the gap between education and employment, ensuring that graduates and young adults have the necessary skills and experience to enter the job market.
In addition to vocational training, the Austrian government has focused on improving the overall business environment to attract investments and create jobs. They have introduced measures to simplify business registration, reduce administrative burdens, and offer tax incentives for new businesses and startups. These initiatives aim to foster entrepreneurship and encourage the creation of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which are known to be significant job creators. By making it easier for businesses to operate, the government hopes to stimulate economic activity and reduce unemployment.
Another critical aspect of the government's strategy is the support for long-term unemployment benefits and reintegration programs. Austria offers extended unemployment benefits to those who have been out of work for an extended period, providing a safety net while they seek employment. Additionally, the government has established reintegration programs that offer personalized support, including job-seeking assistance, career counseling, and training opportunities. These programs aim to help individuals overcome barriers to employment and re-enter the job market successfully.
The impact of these government initiatives has been positive, with a noticeable decline in unemployment rates over the years. The focus on vocational training and apprenticeships has led to a more skilled workforce, making Austria an attractive destination for businesses seeking qualified talent. The improved business environment has also resulted in increased foreign investments, further boosting job creation. As a result, the country has experienced a steady reduction in unemployment, particularly among young people, who often face significant challenges in finding their first job.
Furthermore, the government's commitment to supporting the long-term unemployed has been crucial in addressing structural issues in the labor market. By providing financial and career support, the reintegration programs have helped individuals gain the necessary skills and confidence to re-enter the workforce. This approach not only reduces unemployment but also contributes to a more resilient and adaptable economy. The success of these initiatives is evident in the decreasing unemployment rate, which has fallen below the European Union average, indicating that Austria's economic policies are on the right track.
Exploring Salzburg: Best Areas for Accommodation
You may want to see also

Economic Recovery: How the economy's recovery affects unemployment rates and job creation
The economic recovery in Austria has had a significant impact on unemployment rates and job creation, offering valuable insights into the relationship between economic growth and labor market dynamics. As the country emerged from the global financial crisis, it embarked on a path of recovery, and the labor market responded with a gradual improvement in unemployment figures. The initial stages of the recovery were characterized by a focus on stimulus measures and support for businesses, which helped stabilize the economy and prevent further job losses. This period saw a slight decrease in unemployment, but the rate remained relatively high, indicating a challenging job market.
As the economy continued to strengthen, the recovery gained momentum, and the labor market began to show more positive signs. The Austrian government's strategic investments in infrastructure and green initiatives played a crucial role in this phase. These investments created a surge in demand for skilled workers, particularly in sectors like renewable energy and construction. As a result, unemployment rates dropped more significantly, and the job market became more competitive. The recovery's impact on job creation was evident, with businesses expanding their operations and hiring new employees to meet the growing demand.
The economic recovery's influence on unemployment rates can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the government's proactive approach to stimulating the economy provided a much-needed boost to businesses, allowing them to retain and hire workers. Secondly, the focus on specific industries, such as technology and innovation, created a skilled workforce demand, encouraging companies to invest in training and development. This, in turn, led to a more dynamic job market, where employers sought to attract talent by offering competitive packages.
Moreover, the recovery's effect on job creation extended beyond traditional employment sectors. The rise in entrepreneurship and small business formation contributed to the overall job market. Many individuals seized the opportunity to start their ventures, creating new job opportunities and fostering a culture of innovation. This shift towards a more diverse and dynamic economy played a vital role in reducing unemployment, especially among younger workers.
In summary, Austria's economic recovery has been instrumental in addressing the unemployment challenge. The strategic approach to recovery, combined with targeted investments, has resulted in a more robust job market. As the economy continues to grow, the labor market's resilience and adaptability become essential factors in sustaining this positive trend. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike, as they navigate the path towards a more prosperous and inclusive economy.
The Age-Old Mystery: Unveiling Victoria's Blue Vase
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of the latest data, the unemployment rate in Austria stands at around 4.5% (as of 2023). This rate has been steadily decreasing over the past few years, indicating a positive trend in the country's labor market.
Austria's unemployment rate is relatively low compared to many other European nations. For instance, it is lower than the EU average, which was 6.2% in 2022. Austria's strong economy and social welfare system have contributed to this favorable position.
Yes, there can be regional differences. Some areas in Austria, particularly those with a strong tourism industry, may experience lower unemployment rates during peak seasons. Conversely, regions with a more diversified economy might have a slightly higher unemployment rate.
Several factors play a role. These include economic growth, industry-specific trends, government policies, and the overall health of the labor market. For instance, sectors like technology, healthcare, and renewable energy have been creating jobs, potentially impacting the unemployment rate.
The pandemic had a significant impact on Austria's economy, leading to a temporary increase in unemployment. However, the government's swift response, including financial support measures, helped mitigate the effects. As the economy recovered, the unemployment rate started to decline, and it is expected to continue improving.







