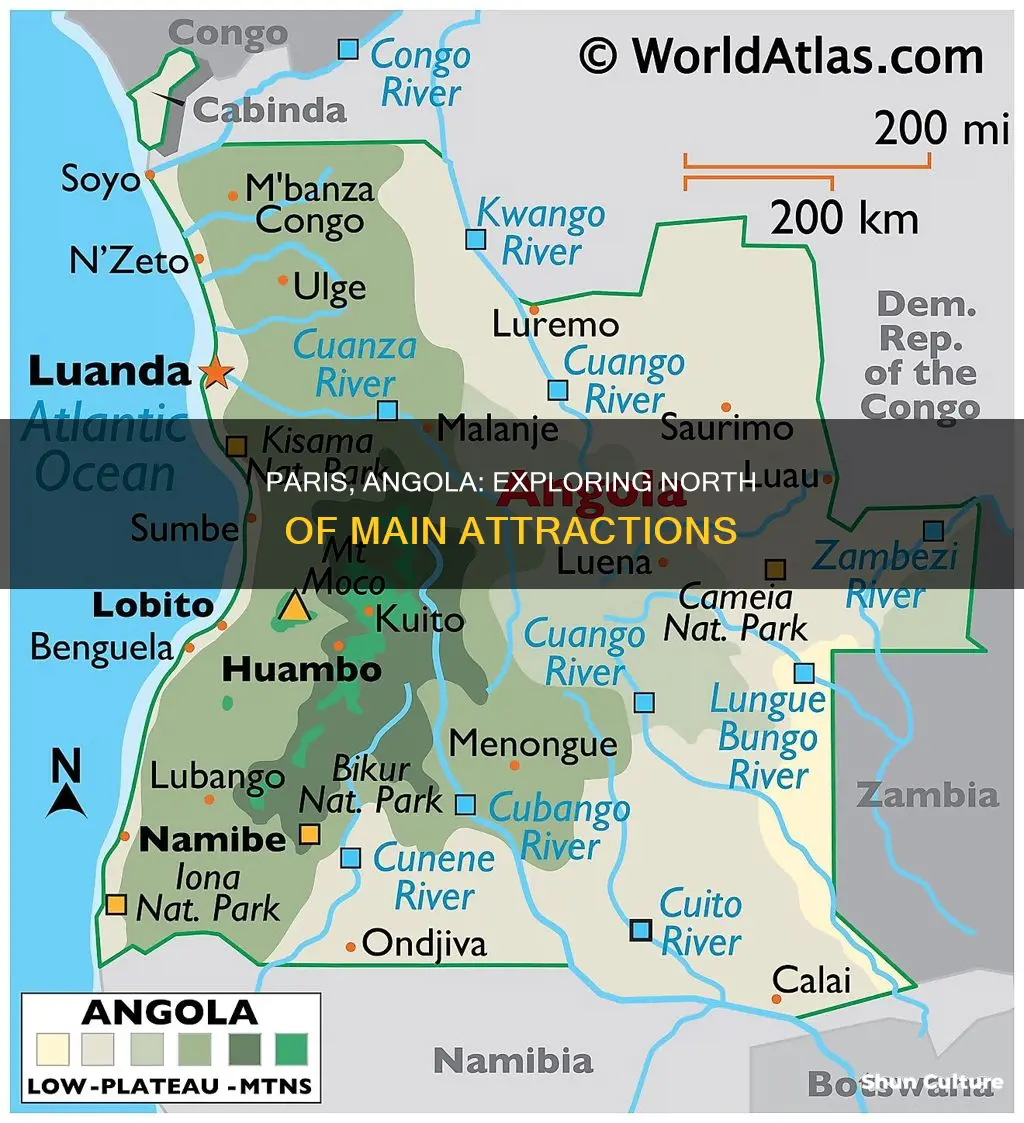
Angola is a country in southwestern Africa with a landscape that includes a semidesert Atlantic littoral, a rainforest interior, rugged highlands, and a densely populated north coast. The capital and largest city is Luanda, located on the northern coast. North of Luanda, Angola is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo. The province of Cabinda, an exclave of Angola, is also located north of Luanda, bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south and east, and the Republic of the Congo to the north.
What You'll Learn
- The capital of Angola, Luanda, is north of Paris
- Angola is a country in west-central Africa
- Angola is bordered by Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Atlantic Ocean
- Angola is rich in natural resources, including precious gems, metals and petroleum
- Luanda is the largest city in Angola

The capital of Angola, Luanda, is north of Paris
Luanda, the capital of Angola, is north of Paris. Paris is a city located in France, whereas Luanda is in Angola, a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. Paris is crossed by the Seine River, which divides it into the Left and Right Bank. On the other hand, Luanda is located on the northern Atlantic coast of Angola.
Luanda is the largest city in Angola and one of its busiest seaports. It was founded in 1576 by Paulo Dias de Novais and was initially settled by the Portuguese. The city became the administrative centre of the Portuguese colony of Angola in 1627 and was a major outlet for the slave trade to Brazil. Luanda is considered the capital of the Mbundu peoples, who have their roots in the surrounding area.
The city has a warm and equable climate, and the surrounding region consists of a tropical coastal plain that gives way to a tableland dissected and drained by the Cuanza River and other coastal streams. The Cambambe Dam, located on the Cuanza River, provides power to Luanda. Luanda has a modern appearance, with skyscrapers and wide avenues. The higher part of the city, consisting of the outlying districts, is generally poverty-ridden, while the lower part is commercial and industrial.
Luanda is an important economic centre for Angola, with industries such as the processing of agricultural products, beverage production, textiles, and oil. It is also the country's primary port and major industrial, cultural, and urban centre. The city has undergone significant reconstruction in the 21st century, with many new developments transforming its landscape.
Gas Prices in Angola: A Costly Affair
You may want to see also

Angola is a country in west-central Africa
The country has a diverse landscape, including a semi-desert Atlantic littoral bordering Namibia's "Skeleton Coast", a sparsely populated rainforest interior, rugged highlands in the south, and the densely populated northern coast and river valleys. The coastal plain, where most of the population resides, rises abruptly to the east, forming a series of escarpments that lead to the rugged interior highlands.
Angola has a tropical climate with two distinct seasons: a hot and rainy season from September to May, and a semi-arid season from May to September. The climate varies across the country, with the northern region experiencing a longer rainy season and higher rainfall than the south.
Angola has a rich history, dating back to the Paleolithic Age. The Kingdom of Kongo, which flourished from the 14th century, played a significant role in the country's formation. The kingdom established the Atlantic slave trade with the Portuguese Empire, and Portuguese explorers first arrived in the region in 1483. Angola gained independence from Portugal in 1975 after a protracted anti-colonial struggle and subsequently endured a devastating civil war.
Today, Angola is a relatively stable constitutional republic with a fast-growing economy, driven primarily by its vast mineral and petroleum reserves. The country is culturally diverse, with influences from both indigenous customs and traditions and centuries of Portuguese colonisation.
Angola is a member of various international organisations, including the United Nations, the African Union, and the Community of Portuguese Language Countries. The country has one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, but most of the nation's wealth is concentrated in a small portion of the population, resulting in a low standard of living for most Angolans.
Angola's Weather: Cold or Comfortable?
You may want to see also

Angola is bordered by Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Atlantic Ocean
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, the Democratic Republic of Congo to the north and northeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The country is roughly square-shaped and is the seventh-largest in Africa. It is the second-largest Lusophone (Portuguese-speaking) country in both total area and population.
The northern part of Angola includes the Cabinda exclave, which borders the Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republic of Congo. The border between the two countries is 2,646 km (1,644 mi) long and consists of two non-contiguous sections. The western section runs along the coast and the eastern section runs through the Congo River and the tripoint with Zambia.
Angola's capital and largest city is Luanda, located on the northern Atlantic coast. It is the country's administrative centre, chief seaport, and economic hub. The city is known for its Portuguese colonial architecture and is undergoing major reconstruction.
Angola has a tropical climate with a dry season. The climate is influenced by the seasonal movements of the intertropical convergence zone and the cold Benguela Current. Rainfall varies across the country, with the northern Maiombe forest receiving the highest rainfall of about 70 inches (1,800 mm) per year. Luanda, on the dry coast, receives approximately 13 inches (330 mm) of rainfall annually.
Angola's Air Conditioning: A Comfortable Climate Control Solution
You may want to see also

Angola is rich in natural resources, including precious gems, metals and petroleum
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is the third-largest producer of diamonds in Africa and has vast mineral and petroleum reserves.
Angola's natural resources include:
- Petroleum: Angola has large reserves of petroleum and natural gas, concentrated in the maritime zones off the Cabinda exclave and the Congo River estuary. Angola has become one of the largest exporters of petroleum in sub-Saharan Africa, and production has nearly tripled since independence.
- Diamonds: Diamonds are the second-largest export for Angola and the country is the third-largest producer in Africa. Diamonds are found in the northeastern quarter of the country, with a high proportion of gem-quality stones.
- Iron Ore: There are large reserves of iron ore in the southwestern part of the country, although the grade is low.
- Other Minerals: Angola is also rich in copper, manganese, gold, phosphates, uranium, feldspar, platinum, granite, marble, and other minerals.
- Hydroelectric Power: Angola's hydroelectric potential is one of the largest in Africa, with most electricity coming from dams on the Cuanza, Cunene, Catumbela, and Dande rivers.
The exploitation of these natural resources has led to economic growth in Angola, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. However, economic growth is uneven, with wealth concentrated in a small part of the population. Efforts to diversify the economy and reduce corruption are ongoing.
Exploring Angola, Indiana: Your Travel Guide
You may want to see also

Luanda is the largest city in Angola
Luanda is the capital and largest city of Angola. It is located on the country's northern Atlantic coast and serves as its primary port and administrative centre. Luanda is also the capital of the Luanda Province and is divided into two parts: the Baixa de Luanda (the old city) and the Cidade Alta (the new part).
Luanda was founded in 1576 by Portuguese explorer Paulo Dias de Novais and was initially settled by the Portuguese. It became the administrative centre of the Portuguese colony of Angola in 1627 and was a major hub for the slave trade to Brazil. Today, it is considered the capital of the Mbundu peoples, who are indigenous to the surrounding area.
Luanda is the most populous Portuguese-speaking capital city in the world and the most populous Lusophone city outside of Brazil. In 2020, its population reached more than 8.3 million inhabitants, accounting for about a third of Angola's population. The city has a thriving industrial sector, with industries such as agricultural product processing, beverage production, textiles, and metallurgy. It is also a notable economic centre for oil, with a refinery located within the city.
Luanda has a rich cultural heritage, with a mix of Portuguese and indigenous influences. It is home to several museums, including the National Museum of Anthropology, the National Museum of Natural History, and the National Museum of Slavery. The city also hosts the annual Luanda International Jazz Festival, which has been held since 2009.
Luanda has undergone significant development in the 21st century, with major reconstruction projects aimed at improving its infrastructure. However, the city continues to face challenges such as inadequate water supply and traffic congestion.
Travel Tales: Angola, Indiana to Standard, Virginia
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Luanda is the capital and largest city of Angola. It is located on the northern Atlantic coast of the country.
The city of Luanda is home to many landmarks, including the Agostinho Neto University, the National Library of Angola, the National Historic Archive, and the National Museum of Slavery.
The co-ordinates of Luanda are 8°50′18″S 13°14′04″E.







