Bolivia's external debt has fluctuated over the years. In 2022, the country's external debt was nearly 30% of its GDP, a significant decrease from 2000 when it stood at 41.2%. In 2021, Bolivia's external debt was 39.5% of its GDP, compared to 24.7% a decade earlier. Bolivia's external debt reached an all-time high of 15.8 billion USD in December 2023 and a record low of 5.1 billion USD in March 2007. The country's economy is driven largely by its natural resources, and it has become a regional leader in economic growth, fiscal stability, and foreign reserves. However, Bolivia still faces challenges such as political instability, difficult topography, and a history of rampant inflation and corruption.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| External debt as % of GDP in 2023 | 35.0% |
| External debt as % of GDP in 2022 | 35.3% |
| External debt as % of GDP in 2021 | 39.5% |
| External debt as % of GDP in 2013 | 26.1% |
| External debt as % of GDP in 2006 | 69.3% |
| External debt in USD bn in Mar 2024 | 15.4 |
| External debt in USD bn in Dec 2023 | 15.8 |
| External debt in USD bn in 2004 | 5.7 |
| External debt as % of GDP in 2000 | 41.2% |
What You'll Learn

Bolivia's external debt as a percentage of GDP
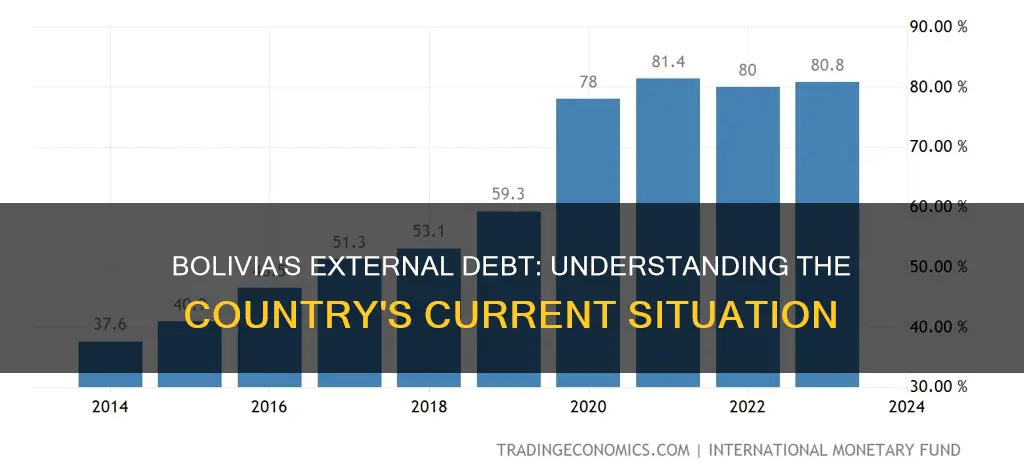
Bolivia's external debt as a percentage of its GDP has fluctuated between 26.1% and 69.3% from 2006 to 2023. In 2023, Bolivia's external debt accounted for 35% of the country's nominal GDP, compared to 35.3% in 2022. This is a significant decrease since 2000, when the external debt was 41.2% of the country's GDP.
The external debt of Bolivia reached an all-time high of 69.3% in 2006. It then decreased to 26.1% in 2013, the lowest it has been in the period under review. The World Bank provides external debt figures in USD, while the Nominal GDP is based on the local currency, with the Central Bank of Bolivia's average market exchange rate used for conversions.
Bolivia's external debt reached 15.8 billion USD in December 2023, which was the highest figure recorded during this period. The following quarter, in March 2024, the external debt decreased to 15.4 billion USD. The Nominal GDP of Bolivia was reported at 12.0 billion USD in December 2022.
Swimming in Laguna Verde, Bolivia: Is It Safe?
You may want to see also

The World Bank's role in Bolivia's external debt
Bolivia's external debt is currently estimated to be around 15.4 billion USD as of March 2024. This figure represents a decrease from the previous quarter's high of 15.8 billion USD. Bolivia's external debt as a percentage of its nominal GDP was 35.0% in 2023, down from 35.3% the previous year.
Now, let's discuss the World Bank's role in Bolivia's external debt:
The World Bank, through its Country Partnership Framework (CPF) for the fiscal period 2023-2026, plays a significant role in guiding Bolivia's economic development and addressing external debt challenges. The CPF aims to advance three key development priorities:
- Increased climate and economic resilience: The World Bank supports projects that enhance Bolivia's resilience to climate risks, such as the Urban Resilience Project and the Resilient Water Management for Household and Community Irrigation Project.
- Increased income earnings for vulnerable households: Initiatives like the Rural Alliances Project aim to improve the livelihoods of rural producers, increase their income, and reduce vulnerability to food insecurity.
- Expanded access to quality public services: The Improving Sustainable Access to Electricity Project aims to provide new or improved access to electricity for domestic and productive use, benefiting over 141,000 people.
Additionally, the World Bank focuses on promoting private sector development and attracting foreign investment. The International Finance Corporation (IFC) plays a crucial role in this regard, fostering climate finance, financial inclusion, and foreign trade operations. The World Bank also provides advisory services and technical analysis to inform investment project design and implementation.
The World Bank's interventions in Bolivia have had a transformative impact, particularly in agriculture and rural development. By addressing structural challenges, promoting macroeconomic stability, and encouraging private investment, the World Bank's programs contribute to Bolivia's efforts to manage its external debt and achieve sustainable economic growth.
USAID's Bolivian Legacy: Is the Agency Still Active?
You may want to see also

Bolivia's external debt in USD
Bolivia's external debt has fluctuated over the years, with the country's total external debt being the sum of public, publicly guaranteed, and private nonguaranteed long-term debt, use of IMF credit, and short-term debt. As of March 2024, Bolivia's external debt reached 15.4 billion USD, a slight decrease from the previous quarter's high of 15.8 billion USD.
In 2022, Bolivia's external debt was approximately 15.93 billion USD, a decline of 0.59% from 2021. This decline followed a pattern of increases in the preceding years, with the external debt in 2021 being 3.93% higher than in 2020 and 7.82% higher than in 2019.
Bolivia's external debt as a percentage of its GDP has also varied. In 2023, it accounted for 35% of the country's nominal GDP, compared to 35.3% in the previous year. In 2021, the external debt was 39.5% of GDP, a significant increase from 24.7% a decade earlier in 2011. The highest percentage in the last two decades was 69.3% in 2006, while the lowest was 26.1% in 2013.
The external debt of Bolivia, as a percentage of its GDP, has generally decreased since 2000 when it stood at 41.2%. This reduction is reflected in the 2022 figure, where the external debt was reported to be nearly 30% of the country's GDP.
Public Education in Bolivia: Availability and Access
You may want to see also

Bolivia's external debt compared to Latin America
Bolivia's external debt has fluctuated over the years, reaching an all-time high of 15.8 billion USD in December 2023 and a record low of 5.1 billion USD in March 2007. As of March 2024, Bolivia's external debt stood at 15.4 billion USD. When considered as a percentage of the country's GDP, external debt in Bolivia was 39.5% in 2021, compared to the Latin American average of 34.0%. This was a decrease from 41.2% in 2000.
Bolivia's external debt as a percentage of GDP has generally shown a downward trend over the last decade, with an average of 32.5% from 2011 to 2021. In 2022, the public debt owed by Bolivia's central government to foreign creditors was nearly 30% of the country's GDP. This places Bolivia below the Latin American average in terms of external debt relative to the size of its economy.
Comparatively, other countries in Latin America have also experienced varying levels of external debt. For example, the external debt of Brazil, one of the largest economies in the region, reached 346.1 billion USD in 2021. Mexico, another economic powerhouse in Latin America, had an external debt of 467.4 billion USD in 2021.
It is important to note that the impact of external debt can vary across countries due to differences in economic structures, income levels, and debt management strategies. While Bolivia's external debt as a percentage of GDP is lower than the Latin American average, it still represents a significant portion of the country's economic output. Effective management of external debt is crucial for maintaining economic stability and ensuring long-term growth.
In summary, Bolivia's external debt has fluctuated but generally decreased as a percentage of GDP over the last decade, placing it below the Latin American average. However, with an external debt of over 15 billion USD as of March 2024, the country still faces challenges in managing its debt obligations.
Healthcare for Elderly Bolivians: Free or Fee-Based?
You may want to see also

Bolivia's external debt and foreign assistance
Bolivia's external debt has fluctuated since 2006, reaching an all-time high of 15.8 billion USD in December 2023 and a record low of 5.1 billion USD in March 2007. As of March 2024, Bolivia's external debt stood at 15.4 billion USD, a slight decrease from the previous quarter. This external debt amounts to 35.0% of the country's nominal GDP in 2023, a decrease from 35.3% in 2022.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) in Bolivia has been increasing, with a rise of 72.1 USD million in March 2024 compared to the previous quarter. Additionally, Bolivia's direct investment abroad has expanded, with a 7.6 USD million increase in the same period. The country's foreign portfolio investment also increased by 2.0 USD million in March 2024.
Bolivia's current account recorded a deficit of 612.9 USD million in March 2024, and the nominal GDP was reported at 12.0 USD billion in December 2022.
Exploring Bolivia: Discovering Unique Culture and Nature
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Bolivia's external debt reached 15.4 billion USD in March 2024.
Bolivia's external debt has decreased significantly since 2000, when it stood at 41.2% of the country's GDP. In 2022, the public debt that Bolivia's central government owed to foreign creditors was nearly 30% of the country's GDP.
Bolivia's external debt averaged 32.5% of GDP over the last decade, which was below the Latin America average of 34%.
Bolivia's economy is driven largely by its natural resources, and the country has become a regional leader in measures of economic growth, fiscal stability, and foreign reserves. However, the country has faced challenges such as political instability, difficult topography, low population growth, and inflation, which have impacted its external debt.







