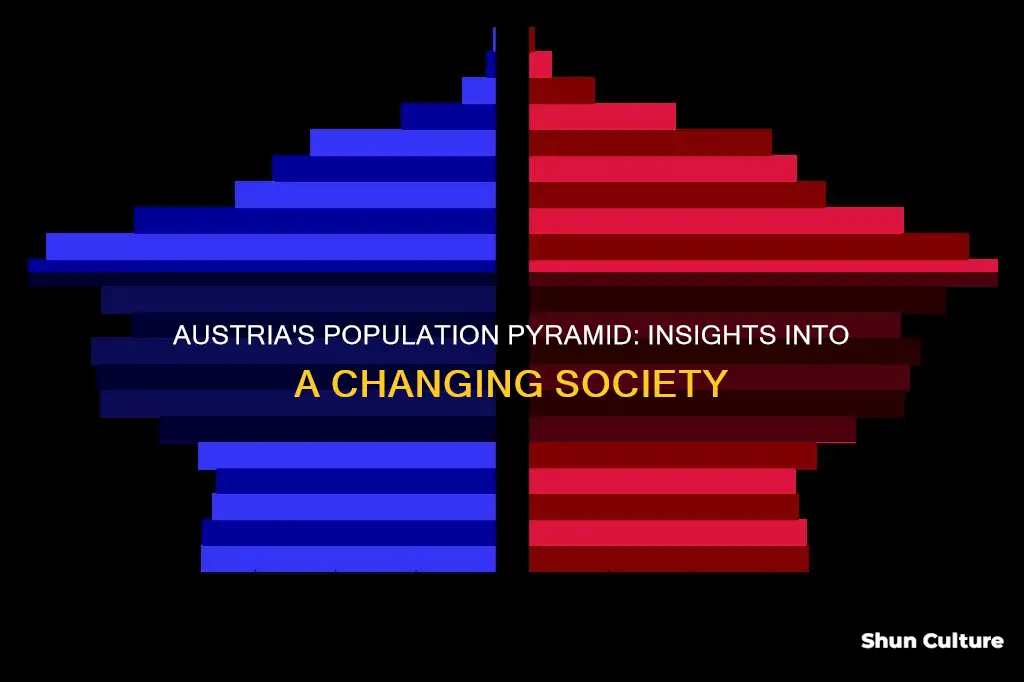
The population pyramid of Austria provides a visual representation of the country's demographic structure, offering valuable insights into its population's age and gender distribution. This pyramid-shaped diagram categorizes the population into distinct age groups, typically from 0 to 80 years and above, with males on the left and females on the right. By examining the shape and characteristics of the pyramid, we can identify trends and patterns that reflect Austria's historical and current demographic trends. The pyramid's structure can indicate the country's population growth, aging, or decline, as well as potential imbalances in gender ratios, which are crucial for understanding social, economic, and healthcare needs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Total Population | 9,023,761 (as of 2023) |
| Median Age | 44.5 years |
| Life Expectancy at Birth | 81.5 years (2021) |
| Fertility Rate | 1.42 children per woman (2022) |
| Dependency Ratio | 42.5% (2022) |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.1% (2022) |
| Age Structure | A significant portion of the population is in the older age groups, with a large elderly population. |
| Gender Ratio | 48.4% male / 51.6% female (2022) |
| Urbanization | 68.2% of the population lives in urban areas (2022) |
| Population Density | 113.6 inhabitants per square kilometer (2022) |
| Population Pyramid Shape | The pyramid is skewed to the left, indicating a lower birth rate and an aging population. |
| Migration Patterns | Austria has experienced a net migration loss in recent years, with more people leaving than arriving. |
| Ethnic Diversity | The population is predominantly of Austrian ethnicity, with a small minority of foreign-born residents. |
| Education Level | High literacy rate and a significant proportion of the population with tertiary education. |
| Economic Activity | A large working-age population, with a focus on services and industry. |
What You'll Learn
- Age Structure: The pyramid reveals the distribution of ages, indicating a youthful or aging population
- Gender Balance: It shows if there's an imbalance, suggesting migration or health issues
- Fertility Rate: High fertility rates are evident, impacting future population growth
- Life Expectancy: The shape hints at longevity, with older generations living longer
- Migration Patterns: The pyramid can indicate net migration, affecting population distribution

Age Structure: The pyramid reveals the distribution of ages, indicating a youthful or aging population
The population pyramid of Austria provides valuable insights into the country's demographic landscape, particularly regarding age distribution. This visual representation, often resembling a pyramid, categorizes the population by age groups, offering a clear picture of the population's structure. The base of the pyramid represents the youngest age groups, while the top represents the oldest.
In the context of Austria, the age structure within the pyramid can indicate whether the country has a youthful or aging population. A broad base suggests a large youth population, indicating a high birth rate and potentially a growing workforce in the future. This could be beneficial for the economy, as a large working-age population can drive productivity and innovation. However, it also means that the country may face challenges in providing adequate education and employment opportunities for its young citizens.
On the other hand, a narrowing pyramid shape at the top, with a smaller number of older individuals, suggests an aging population. This demographic shift can have significant implications for social and economic policies. As the population ages, there may be an increased demand for healthcare services, pension systems, and age-friendly infrastructure. The country might need to adapt its policies to support a growing elderly population, ensuring their well-being and addressing potential healthcare and social care challenges.
The age structure within the pyramid can also influence migration patterns and labor force participation. A youthful population might attract international students and workers, contributing to cultural diversity and economic growth. Conversely, an aging population could lead to labor shortages, impacting industries that rely on a younger workforce. Understanding these age-related trends is crucial for policymakers to make informed decisions regarding education, healthcare, and economic development.
In summary, the population pyramid of Austria serves as a powerful tool to understand the country's demographic trends, especially the age structure. It highlights the balance between youth and aging populations, which has far-reaching consequences for various aspects of society and the economy. By analyzing this pyramid, policymakers and researchers can develop strategies to address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by Austria's demographic composition.
Austrian Elections: Truly Free or Far From It?
You may want to see also

Gender Balance: It shows if there's an imbalance, suggesting migration or health issues
The population pyramid of Austria provides valuable insights into the country's demographic structure, particularly regarding gender balance. This visual representation categorizes the population by age and gender, offering a comprehensive overview of the population's distribution. One of the key aspects to consider is the balance between male and female populations at various age groups.
An imbalanced gender distribution within the population pyramid can indicate significant demographic trends. For instance, if there is a higher number of males in the younger age groups, it may suggest a recent influx of male immigrants, possibly due to migration patterns or economic opportunities. Conversely, a higher number of females in the younger age groups could indicate a potential gender imbalance in birth rates or a result of migration, where more females are moving to Austria compared to males.
The population pyramid can also reveal long-term health and social issues. A significant gender imbalance, especially if it persists over several generations, might suggest underlying health problems or societal factors affecting one gender more than the other. For example, if there is a consistent higher number of females in the older age groups, it could be indicative of higher female life expectancy or potentially higher female mortality rates in certain age groups.
Furthermore, the analysis of gender balance in the population pyramid can help policymakers and researchers understand the potential impact on social services, education, and healthcare. An imbalanced gender distribution may influence the allocation of resources and the development of policies to address specific needs, ensuring that the population's requirements are met effectively.
In summary, the population pyramid of Austria serves as a powerful tool to assess the country's demographic health and stability. By examining the gender balance, demographers and policymakers can identify potential migration patterns, health disparities, and social issues, enabling them to make informed decisions to support the well-being of the population. This analysis is crucial for understanding the complex dynamics of a country's population structure and its implications for various sectors.
Austria's Population: Is It Sustainable?
You may want to see also

Fertility Rate: High fertility rates are evident, impacting future population growth
The population pyramid of Austria reveals a significant aspect of its demographic landscape: a high fertility rate. This rate, which indicates the average number of children born to a woman during her reproductive years, has been a consistent and notable feature of the country's population dynamics. The data suggests that Austrian women, on average, have more children than those in many other European countries, which has implications for the nation's future population growth and structure.
This high fertility rate is particularly interesting when viewed through the lens of Austria's historical context. In the past few decades, Austria has experienced a gradual increase in fertility rates, moving away from the low levels seen during the post-World War II baby boom. This shift could be attributed to various factors, including changing social and economic conditions, improved access to healthcare, and a more favorable environment for raising children. The country's population pyramid, therefore, provides a visual representation of this trend, showing a broader base, which signifies a larger youth population and, consequently, a larger working-age population in the future.
The impact of this high fertility rate is far-reaching. Firstly, it contributes to a rapid population growth rate, which can put pressure on the country's infrastructure, resources, and social services. As the number of children increases, there is a higher demand for education, healthcare, and other essential services, requiring the government to invest in and expand these sectors. Moreover, a growing youth population can lead to a larger workforce, which could potentially boost the economy. However, it also means that the country will need to address the challenges associated with an aging population, such as an increased demand for pension systems and healthcare for the elderly.
The population pyramid also highlights the potential long-term effects of high fertility rates. As the current generation of children reaches adulthood, they will contribute to the country's future workforce and social fabric. This could result in a more diverse and vibrant society, but it also requires careful planning to ensure that the necessary resources and opportunities are available to support this growing population. Additionally, the pyramid suggests that Austria may experience a demographic dividend, where a large working-age population can drive economic growth, provided that the necessary conditions for productivity and innovation are in place.
In summary, the high fertility rate evident in Austria's population pyramid has significant implications for the country's future. It influences population growth, puts pressure on social and economic infrastructure, and shapes the demographic landscape for generations to come. Understanding these trends is crucial for policymakers and planners to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, social welfare, and economic development strategies. This analysis also underscores the importance of considering demographic factors in shaping a country's overall development trajectory.
Royals in Austria: What Are Their Titles and Roles?
You may want to see also

Life Expectancy: The shape hints at longevity, with older generations living longer
The population pyramid of Austria reveals intriguing insights into the country's demographic trends, particularly regarding life expectancy. The shape of the pyramid, with a broader base and a narrower top, suggests a fascinating pattern. This structure indicates that the older generations in Austria have experienced significantly higher life expectancy compared to younger age groups.
The broader base of the pyramid signifies a larger proportion of the population in younger age brackets, which is typical for many countries. However, the unique feature lies in the subsequent narrowing, which is more pronounced in Austria. This narrowing indicates a higher concentration of individuals in the older age categories, implying that older Austrians are living longer than their counterparts in other regions.
This longevity trend is a positive indicator of the country's overall health and well-being. It suggests that Austria has made significant strides in healthcare, nutrition, and living standards, all of which contribute to increased life expectancy. The data also highlights the potential for a growing elderly population, which may present both challenges and opportunities for the country's social and economic structures.
The population pyramid's shape provides a visual representation of the demographic transition, showing how Austria has evolved from a stage with a high birth rate and a relatively small elderly population to a more mature society with an aging population. This transition is a common trend in developed nations, and Austria's pyramid offers a clear illustration of this process.
Understanding these demographic patterns is crucial for policymakers and researchers. It enables them to make informed decisions regarding healthcare infrastructure, pension systems, and social services, ensuring that the country is prepared for the changing needs of its aging population. Moreover, it underscores the importance of continued efforts to maintain and improve the quality of life for all Austrians, especially the elderly.
Bosnia-Austria-Hungary: The Spark that Ignited WWI
You may want to see also

Migration Patterns: The pyramid can indicate net migration, affecting population distribution
The population pyramid of Austria provides valuable insights into the country's demographic trends, including migration patterns. This visual representation of the age and sex distribution of a population can reveal much about the country's past and future migration trends.
One key aspect is the shape of the pyramid. A typical pyramid shape with a broad base and a narrow top indicates a young population, often associated with high birth rates and low death rates. However, when analyzing migration, the shape can also indicate the net migration rate. If the pyramid has a more elongated shape, it suggests a significant number of young people migrating into the country, potentially due to economic opportunities or better education prospects. This influx of young migrants can contribute to population growth and potentially impact the country's social and economic landscape.
The pyramid can also highlight areas of concern or potential issues related to migration. For instance, if the pyramid shows a significant number of young adults leaving the country, it may indicate a 'brain drain,' where skilled and educated individuals migrate abroad for better career prospects. This could have long-term consequences for the country's development and innovation capacity. On the other hand, a pyramid with a more balanced distribution of ages might suggest a stable migration pattern, with a steady influx and outflow of migrants, which could be beneficial for population replacement and maintaining a diverse workforce.
Furthermore, the population pyramid can help identify regions or cities within Austria that are experiencing migration trends. For example, if the pyramid for a specific region shows a rapid increase in the younger age groups, it could indicate a popular destination for international students or young professionals, attracting migrants from various countries. This information is crucial for local governments and policymakers to plan for infrastructure, housing, and social services accordingly.
In summary, Austria's population pyramid serves as a powerful tool to understand migration patterns and their impact on the country's population distribution. By analyzing the shape and structure of the pyramid, demographers and policymakers can make informed decisions regarding immigration policies, urban development, and social welfare programs to accommodate and support the changing demographics of the country.
A Guide to Navigating Austrian Healthcare: Tips for a Smooth Doctor Visit
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Austria's population pyramid provides valuable insights into the country's demographic structure. It shows that the country has a relatively small and aging population, with a higher proportion of older adults compared to younger individuals. This indicates a potential decline in the working-age population, which could have implications for the labor market and social security systems.
The pyramid's shape suggests a post-baby boom era, with a significant baby boom generation in the past decades. This is reflected in the broad base of the pyramid, indicating a large youth population. However, as these individuals age, the pyramid may transform into a more compact shape, suggesting a potential aging and shrinking population in the future.
Yes, the pyramid can provide context for understanding immigration trends. Austria's population pyramid might indicate a need for immigration to sustain its population and workforce. The country could implement policies to attract skilled workers or encourage family reunification to address potential labor shortages and demographic imbalances.