Bahrain is an island country in the Persian Gulf, situated between Qatar and Saudi Arabia. It is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway to the west of the country. The country is technically surrounded by water, but it shares maritime borders with Iran, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia.
What You'll Learn

Bahrain is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway
The idea of building a bridge linking Bahrain and Saudi Arabia had been of great interest to both kingdoms for generations. The project to build the bridge began during an official visit to Bahrain in 1954 by King Saud, who wished to nurture and solidify the bonds between the two countries.
In 1965, plans to construct the causeway began to take form officially when Sheikh Khalifah ibn Sulman Al Khalifah, the Prime Minister of Bahrain, paid a courtesy visit to King Faisal, who again expressed his wish to move forward with the project.
On 8 July 1981, an agreement was signed to start construction on the maritime causeway. On 11 April 1985, Shaikh Khalifa bin Salman Al Khalifa, the Prime Minister of Bahrain, pressed the button to install the final part of the box bridges, officially linking the Saudi mainland with Bahrain. The causeway was inaugurated in November 1986 in the presence of King Fahd and Shaikh Isa bin Salman Al Khalifa, who consented to naming the bridge the King Fahd Causeway.
The King Fahd Causeway is not just a feat of engineering but also a testament to the cultural and social bonds between Saudi Arabia and Bahrain. The causeway has improved travel and trade between the two countries, with an estimated 25,104 vehicles using the route daily as of 2010. The causeway also features several amenities, including restaurants, mosques, and gardens, making the journey more pleasant and communal for commuters.
Lyft in Bahrain: Availability and Accessibility
You may want to see also

The country shares maritime borders with Iran, Qatar and Saudi Arabia
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated in the Persian Gulf. It is officially known as the Kingdom of Bahrain and consists of Bahrain Island and 33 other islands, including some artificial islands. The country does not share any land borders with other nations. However, it is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway to the west of the country.
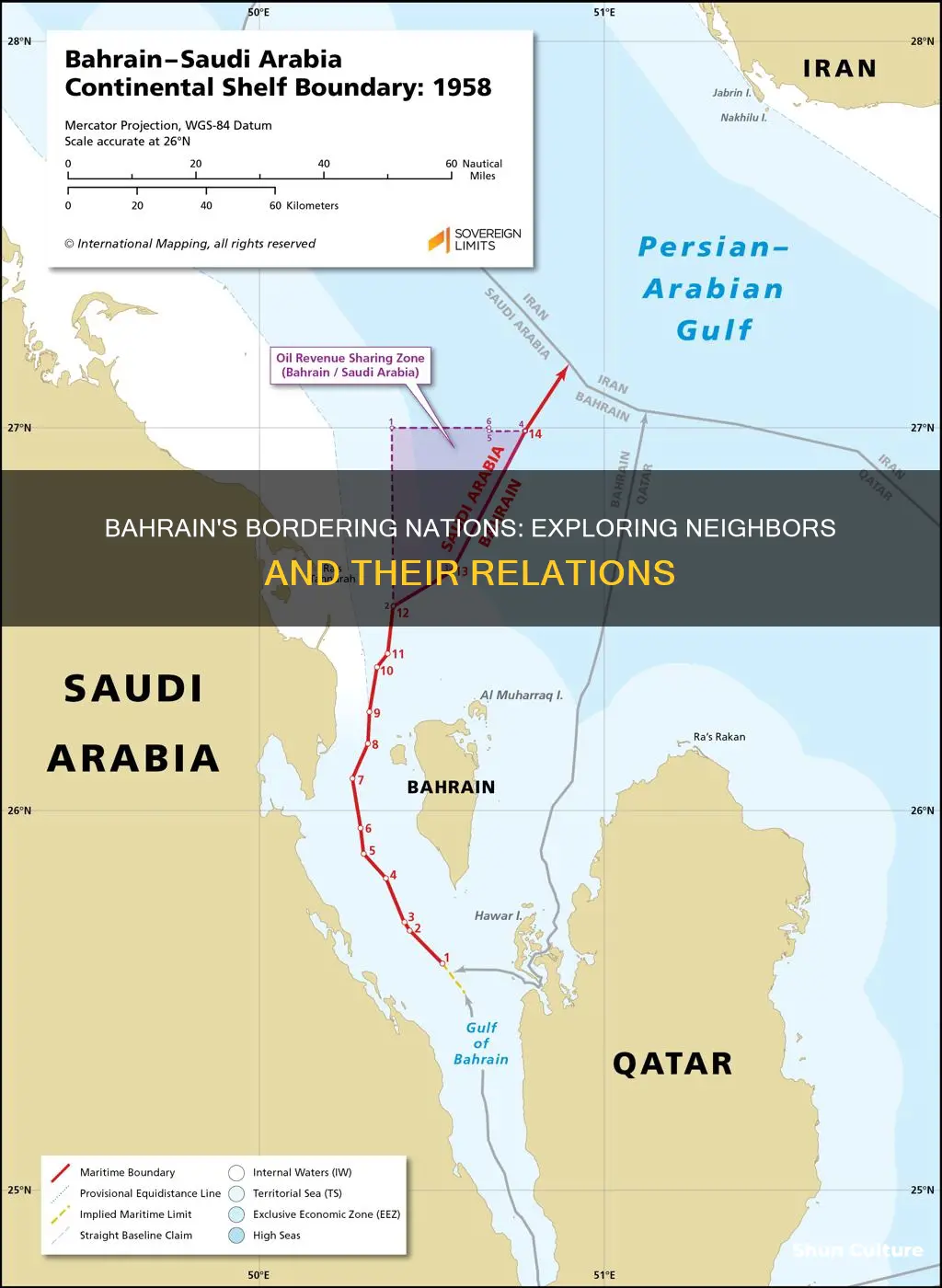
Bahrain shares maritime borders with three countries: Iran, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia. The maritime boundary between Bahrain and Saudi Arabia was established in 1958 and was the first to delimit a continental shelf boundary in the Gulf. It follows a modified equidistance line and the eastern limit of a Saudi Arabian oil field.
The country's territorial waters extend 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from its coast, and its contiguous zone is 24 nautical miles (44.4 km). Bahrain's northern coast is lined with extensive coral reefs, and the seabed adjacent to the islands is rocky. The country's highest point, Jabal ad Dukhan (also known as Jabal al Dukhan or Mountain of Smoke), rises to 134 meters (440 feet) above sea level.
The main island, Al Bahrayn, accounts for about 78% of the country's land area. It is surrounded by some of the Middle East's large petroleum fields and is strategically located amid the Persian Gulf's shipping lanes. The capital and largest city of Bahrain is Manama, located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island.
Safety for Women in Bahrain: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Bahrain is situated in the Persian Gulf
Bahrain is an island country in West Asia, situated in the Persian Gulf. It is an archipelago consisting of Bahrain Island and around 30 smaller islands, with the capital, Manama, located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island. The country's name derives from the Arabic term 'al-baḥrayn', meaning 'two seas'.
Bahrain is bordered by the Gulf of Bahrain, an inlet of the Persian Gulf, and is located off the eastern coast of Saudi Arabia and north of Qatar. The King Fahd Causeway, a series of bridges and causeways, connects Bahrain with Saudi Arabia to the west, and it shares maritime borders with Iran, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia.
The country's terrain is characterised by a low desert plain, with most of the island being low-lying and barren. The interior features an escarpment, Jabal ad Dukhan, which, at 134 metres, is the country's highest point. The northern coast features a fertile strip where date, almond, fig, and pomegranate trees grow. Bahrain is known for its date palms, with the northern and northwestern coasts featuring a narrow belt of date palms and vegetable gardens irrigated by artesian water from springs and wells.
Bahrain has an arid climate with two distinct seasons: an extremely hot summer and a relatively mild winter. The summer months, from April to October, are very hot and humid, with temperatures often exceeding 32°C. Winters are cooler, with temperatures ranging from 21°C to 32°C. Rainfall is minimal and confined to the winter months, with an average annual precipitation of 70-75mm.
Bahrain's economy has traditionally relied on processing crude oil from neighbouring countries, and more recently, the financial, commercial services, and tourism sectors have grown significantly. The country has developed one of the first post-oil economies in the Persian Gulf, with many of the world's largest financial institutions having a presence in Manama.
Bahrain's Free Zones: Business Opportunities and Tax Exemptions
You may want to see also

The country is officially known as the Kingdom of Bahrain
Bahrain is ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family, with Shaikh Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa as king. The country is a constitutional hereditary monarchy, with the king as the chief of state and the prime minister as the head of government. The country's legislative assembly consists of the Council of Representatives (the lower house) and the Shura Council (the upper house).
Bahrain has a mixed economy, with the government controlling many basic industries. Petroleum and natural gas are the country's only significant natural resources. Bahrain has developed one of the first post-oil economies in the Persian Gulf, investing heavily in the banking and tourism sectors. The country is also in the aluminium business and practices Islamic banking.
Bahrain is a member of the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the Arab League, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, and the Gulf Cooperation Council. It has established bilateral relations with 190 countries worldwide and maintains a network of embassies, consulates, and permanent missions.
Bahrain Lockdown: What's the Current Situation?
You may want to see also

Bahrain is an island country
Bahrain is bordered by the sea and has no land borders with other nations. However, it is connected to Saudi Arabia by the King Fahd Causeway, a series of bridges and causeways. The country shares maritime borders with Iran, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia.
Bahrain has a subtropical climate and is known for its desert vegetation, date palms, and camels. The country has a diverse population, with about 70% Shia and 30% Sunni Muslims. The capital and largest city is Manama, located on the northeastern tip of Bahrain Island.
Bahrain has a mixed economy, with a focus on petroleum processing and refining, as well as international banking. The country has a rich history, including its ancient past as the site of the Dilmun civilisation, famed for its pearl fisheries.
Bahrain's Sunni Majority: A Complex Religious Landscape
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, Bahrain does not share any land borders with other nations.
The King Fahd Causeway.
The islands of Bahrain are about 24km off the east coast of Saudi Arabia.
Bahrain is situated in the Persian Gulf, to the east of Saudi Arabia and north of Qatar. It shares maritime borders with Iran, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia.
Bahrain has a total territory of around 780 sq. km.







