Belize's economy is a developing free-market economy, with a mixed economic system that includes a private enterprise system, combined with centralised economic planning and government regulation. The main economic activities in Belize are tourism, agriculture, energy, and services. Belize's economy is small, with a GDP of around US$2.5 billion in 2021 and US$2.95 billion in 2022. The country's primary exports are citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas, and the primary industries are agriculture, tourism, and services.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Economic type | Developing free-market |
| Economic system | Mixed |
| Primary industries | Agriculture, tourism, services |
| GDP (2022) | US$2.95 billion |
| Tourism revenue (2022) | US$242 million |
| % of economy from international tourism | 40% |
| Primary exports | Citrus, sugar, bananas |
| Primary imports | Refined petroleum, rolled tobacco, recreational boats, passenger and cargo ships, ethers |
| Primary import partners | United States, Mexico, China, Guatemala, Japan |
| Primary export partners | United Kingdom, United States |
| Primary sectors | Hotels and restaurants, financial intermediation, trade, transport and communication |
| Secondary sectors | Manufacturing, electricity and water supply, construction |
| Tertiary sectors | Agriculture, forestry, fishing, mining |
What You'll Learn
- Belize's economy is based on tourism, agriculture, and services
- The country's main exports are citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas
- Belize's economy depended on forestry until the 20th century
- The country's main import partners are the US, Mexico, China, Guatemala, and Japan
- Belize's economy is small, with a GDP of US$2.5 billion in 2021

Belize's economy is based on tourism, agriculture, and services
Belize's economy is based on three key sectors: tourism, agriculture, and services.
Tourism
Belize's tourism industry has been a primary driver of its economy, contributing significantly to foreign exchange earnings. The country's natural attractions, including its long Caribbean coastline, small islands, the Belize Barrier Reef, abundant wildlife, and Mayan ruins, have drawn tourists from around the world. In 2011, tourist arrivals totalled 888,191, with revenues reaching $260 million. The industry's impact on the GDP was estimated at 12% in 2011, and it supported 40,000 jobs, accounting for 30.1% of total employment. The tourism sector also includes fishing, boating, swimming, and diving, with the Belize Barrier Reef being a popular destination for these activities.
Agriculture
Agriculture has been a traditional pillar of Belize's economy, with a focus on crops such as citrus fruits, bananas, and sugarcane. In 1999, banana production alone accounted for 16% of total exports. In recent years, Belize has also expanded its production of other crops, such as papaya, rice, and soy. The country has about 8,090 square kilometres of arable land, but only a small fraction is under cultivation. Agriculture contributes about 20% of the country's GDP and employs approximately 20%-to25% of the workforce.
Services
The services sector in Belize has become the dominant economic activity in recent decades, accounting for the largest share of the GDP since the early 1980s. It includes a range of industries such as wholesale and retail trade, finance, telecommunications, and transportation. The Central Bank of Belize oversees the country's banking system and issues the Belize dollar, which is fixed to the US dollar at a rate of 2:1.
Belize Exchange: Exploring the Pros and Cons
You may want to see also

The country's main exports are citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas
Belize's economy is small, with a GDP of around US$2.5 billion in 2021 and US$2.95 billion in 2022. The country's main exports are citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas, with agriculture contributing about 20% of the country's GDP and 25% of the workforce.
Citrus fruits are Belize's second most important agricultural crop and oranges are the most common variety grown. In 2018, Belize produced 100,000 tons of oranges, along with 1,700,000 tons of sugarcane and 80,000 tons of bananas. Citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas are grown on farms or plantations, most of which are smaller than 100 acres (40 hectares). These crops are cultivated for export, with sugar being sent to the United States and the European Union, and citrus fruits and bananas being exported from ports in the Stann Creek and Cayo areas, south and west of Belize City.
The country's agricultural sector has faced challenges due to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, which have destroyed sugarcane fields, and fluctuations in world market prices, especially for sugar and bananas. Despite these challenges, Belize continues to focus on agriculture as a key sector for economic growth and development.
Belize's Biggest District
You may want to see also

Belize's economy depended on forestry until the 20th century
Belize's economy was heavily dependent on forestry until well into the 20th century. The country's initial main export was logwood, which was used to make dye. However, as the supply of logwood outstripped demand, loggers turned to mahogany, which grew abundantly in Belize's forests. Mahogany was prized for its use in building cabinets, ships, and railroad carriers.
The mahogany industry brought wealth to many merchants and traders, but the market was volatile, and the industry was vulnerable due to the slow growth rate of mahogany trees. As the 19th century progressed, loggers had to venture deeper into the forests to find trees, increasing labour costs. While improvements in hauling methods helped satisfy rising demands for mahogany, the industry was still susceptible to fluctuations in supply.
By the 20th century, logging had become unprofitable, and the country's economy shifted to new sectors. Sugarcane became the principal export, followed by expanded production of citrus fruits, bananas, seafood, and apparel. This shift was also influenced by the destruction of forests and price fluctuations of traditional export products.
Belize's small domestic market, high labour costs, and expensive energy have constrained its domestic industry. However, the country has attracted significant foreign investment in sectors such as energy, telecommunications, and agriculture.
Hopkins, Belize: Beach Paradise
You may want to see also

The country's main import partners are the US, Mexico, China, Guatemala, and Japan
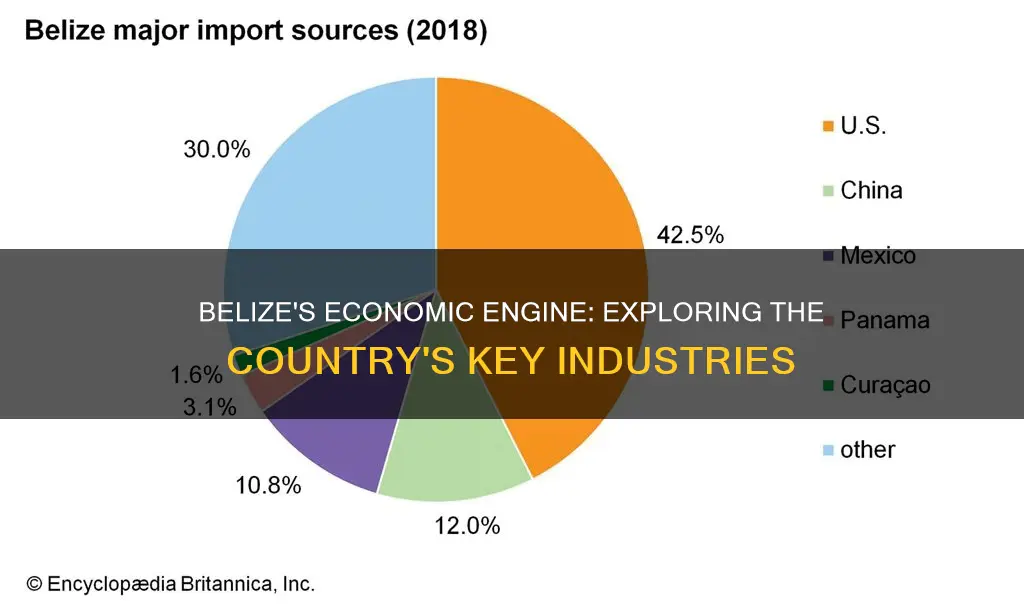
Belize's economy is a small, private enterprise economy based on agriculture, tourism, and services. The country's main import partners are the US, Mexico, China, Guatemala, and Japan. In 2022, Belize imported goods worth $1.68 billion, with its top imports being refined petroleum, passenger and cargo ships, rolled tobacco, petroleum gas, and computers. The US was the largest exporter to Belize, with $560 million worth of goods, accounting for 42% of overall imports. China was the second-largest importer to Belize, with $379 million worth of goods, a significant increase from previous years. Mexico, Guatemala, and Canada were also major import partners, with imports of $130 million, $156 million, and $58.2 million, respectively.
The US has consistently been Belize's largest trading partner and import source. In 2018, the US accounted for 42.5% of Belize's overall imports, and in 2000, it accounted for 49.7%. The proximity to the US and the shared language make it an attractive market for US exports. Belize's economy is highly dependent on imports, and its trade deficit has been growing due to low export prices for commodities such as sugar and bananas.
In recent years, Belize has been taking steps to diversify its economy and reduce its dependence on traditional exports. The discovery of oil in Spanish Lookout presents new opportunities and challenges for the country. Additionally, the government has been promoting commercial agriculture through CARICOM and providing duty-free access to the US market through the Caribbean Basin Initiative. Despite these efforts, Belize's domestic industry remains limited due to high-cost labour and energy, and a small domestic market.
Belize's main import partners play a crucial role in the country's economy, with the US being the largest and most consistent source of imports. The country's import-dependent economy and trade deficit present ongoing challenges for Belize's economic stability and growth.
San Pedro's Best Party Spots
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is small, with a GDP of US$2.5 billion in 2021
Agriculture has been a key industry in Belize since the 20th century, with the country's arable land used for the production of citrus fruits, bananas, and sugar. In addition, Belize has expanded its production of agricultural goods such as papayas, maize, rice, and soy. Agriculture is a priority for Belize's economic growth, contributing about 20% of the country's GDP and employing about one-fifth of the population. Most farms are smaller than 100 acres, and many are temporary forest clearings.
Tourism is another vital sector, contributing 12.1% to the GDP in 2022, with international tourism accounting for approximately 40% of the country's economy. The Belize Barrier Reef, Mayan ruins, and ecotourism opportunities attract many visitors, with the number of tourists increasing fivefold from the late 1990s to the mid-2000s.
The services sector, including wholesale and retail trade, has also been significant, accounting for the largest share of the GNP since the early 1980s. It sustains nearly half of the labour force and the GNP.
Belize's economy faces challenges such as a small domestic market, high-cost labour and energy, and a growing trade deficit due to low export prices for sugar and bananas. However, the country has made progress despite the negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global trade. Belize's government is committed to supporting economic growth while maintaining its business-friendly environment and promoting investment opportunities.
Belize's Spring Break Buzz: Navigating the Crowds
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Belize's economy is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and services.
Sugar, citrus fruits, bananas, and seafood are the main agricultural products grown and exported by Belize.
International tourism accounts for approximately 40% of Belize's economy, with the country's many Mayan ruins, the Belize Barrier Reef, and its jungle flora and fauna being popular attractions.
Belize also has a manufacturing industry, which includes food products, fertilisers, and textiles. Additionally, the discovery of oil in Spanish Lookout has presented new opportunities and challenges for the country's economy.
Belize's economy is small, with a GDP of around US$2.5 billion to US$2.95 billion. It is considered a developing free-market economy with a mix of private enterprise and centralised economic planning.







