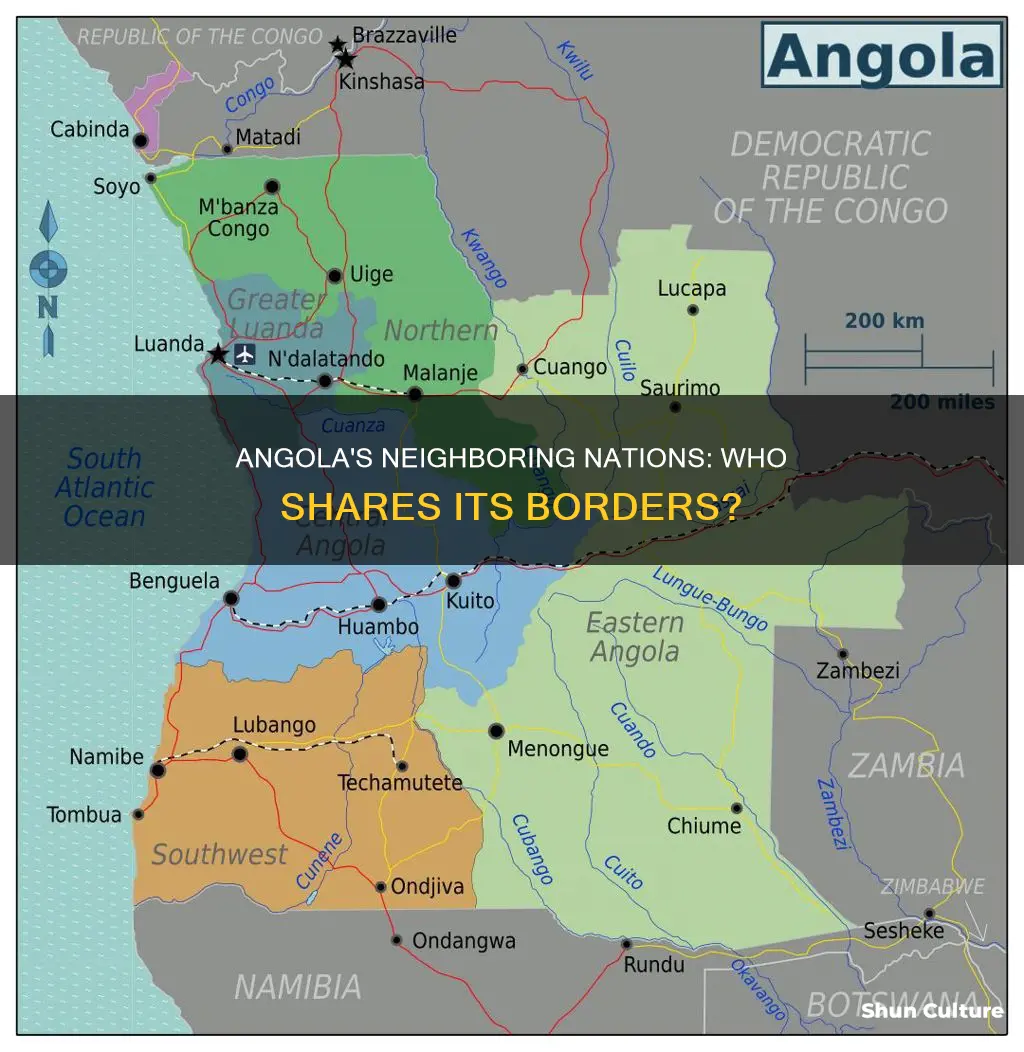
Angola is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, the Democratic Republic of Congo to the north-east, the Republic of Congo to the north, and the South Atlantic Ocean to the west. The country's land border stretches 3,336 miles in total. The border between Angola and the Democratic Republic of Congo is the longest, spanning 1,644 miles in length.
What You'll Learn

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) borders Angola to the north
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north-east, the Republic of the Congo to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is the largest of Angola's bordering nations and is situated north of Angola. The international border delimiting the two African nations is the longest of Angola's borders, spanning 1,644 miles in length. The border starts at the tripoint connecting the two countries and Zambia, from where it extends west until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean.
The DRC was recognised as a Belgian colony during the 19th-century demarcation of the border, while Angola was a Portuguese colony. The two nations recognise the demarcation of the border, and so there have been no territorial conflicts over it. However, the border experiences illegal crossings, which pose a security threat to both countries. Despite having official border crossings and being patrolled by security agencies from both countries, the border is still porous, with thousands of illegal movements made each year.
Smuggling is a significant problem on the border, with cheap products from Angola finding their way into the DRC. While DRC residents celebrate the availability of cheap Angolan products, the smuggling is a direct threat to the economic well-being of the DRC, as its locally manufactured products struggle to compete with the smuggled goods. In 2016, Angola temporarily closed the border when the DRC experienced an outbreak of Ebola, stating that the decision was necessary to contain the spread of the disease.
Angola's province of Cabinda, an exclave sandwiched by the DRC and the Republic of the Congo, also shares a relatively short land border with the DRC.
Angola's Speedy Highway: How Long Does It Take?
You may want to see also

Namibia borders Angola to the south
The border witnessed a surge in cross-border movement at the turn of the 21st century when Angola was engaged in a bloody civil war known as the Angolan Civil War. During the war, thousands of Angolans crossed the border into Namibia between 1999 and 2002, causing a serious humanitarian problem in the bordering region. A significant number of Angolan refugees settled in the Osire camp near the international border. Many of the refugees were later repatriated to their home country after the civil war ended in 2002.
Some of the border crossings found on the Namibia-Angola international border include the Katitwe, Omahenene, Rundu, Ruacana, and Oshikango border crossings. Despite the presence of these border crossings, the border is quite porous and witnesses a high number of border crossings. The security agencies on opposite sides of the border frequently make arrests of people who have made illegal crossings.
Exploring Angola's Distance from New Orleans
You may want to see also

Zambia borders Angola to the east
Angola is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north-east, the Republic of the Congo, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The country is located on the west-central coast of Southern Africa and is the seventh-largest country in Africa.
The Zambia-Angola border is porous, but it has numerous border crossings where officials monitor cross-border movement. One of these border crossings is the Caripande-Chavuma border post, which connects the Zambian town of Chavuma to the town of Caripande in Angola. The border post is popular among tourists who use it to access the picturesque Chavuma Falls near the border post.
The land boundary between Zambia and Angola spans 1,263 kilometers (785 miles) from the tripoint with Namibia in the south to the tripoint with the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the north. The frontier follows a variety of rivers and straight-line features between boundary markers. Relations between the two countries have improved since Angola's civil war in the 1990s.
Angola to Fremont: How Far in Indiana?
You may want to see also

Cabinda is an Angolan exclave bordering the DRC and the Republic of the Congo
Angola is bordered by Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and the Republic of the Congo. In addition, Angola has an exclave province, Cabinda, which is separated from the rest of the country by a narrow strip of territory belonging to the DRC.
Cabinda is an exclave and province of Angola, located on the west (Atlantic) coast of Africa, north of the Congo River estuary. It is bordered by the Republic of the Congo to the north and the DRC to the south and east. Cabinda has a coastline of 56 miles (90 km) and a width of 70 miles (113 km). The capital of the territory is the town of Cabinda, an oil port on the right bank of the Bele (Lulondo) River.
Cabinda was historically known as the Portuguese Congo and was a Portuguese protectorate until Angola gained independence from Portugal in 1975. The Treaty of Simulambuco, signed in 1885, designated Cabinda as a Portuguese protectorate separate from Portuguese West Africa (Angola). However, in the 20th century, Portugal integrated Cabinda as a district within the "overseas province" of Angola. Despite this, Cabinda has continued to be a focus of separatist movements, with groups such as the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda (FLEC) advocating for self-rule and independence from Angola.
Cabinda has a diverse economy, producing hardwoods, coffee, cocoa, crude rubber, and palm oil. However, it is best known for its oil production, with considerable offshore oil reserves contributing to more than half of Angola's oil output. The discovery and exploitation of these oil fields have made Cabinda a critical economic region for Angola.
Angola's Soyo: Is it a Safe Haven?
You may want to see also

The Atlantic Ocean forms Angola's western border
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north-east. To the west, Angola's border is formed by the Atlantic Ocean, with a coastline stretching 1,650 kilometres long.
The western border of Angola is washed by the Atlantic Ocean, marking the boundary between the country and the ocean. The coastline is approximately 1,650 kilometres long, providing Angola with a favourable position for maritime trade and offering four natural harbours: Luanda, Lobito, Moçâmedes, and Porto Alexandre. The presence of these natural harbours has contributed to the development of maritime trade and economic growth in the region.
The Atlantic Ocean serves as a natural boundary, separating Angola from the neighbouring countries and the rest of the world. It provides a vast expanse of water, offering opportunities for navigation, trade, and exploration. The ocean also plays a significant role in shaping the climate and weather patterns of the region, influencing the lives of those residing along the coast.
The western border, defined by the Atlantic Ocean, has played a crucial role in Angola's history, particularly in the establishment of the Atlantic slave trade during the 15th century. The Portuguese Empire, in collaboration with local kingdoms, built coastal settlements and trading posts, leveraging the country's strategic position along the ocean. This dark chapter in history had a profound impact on Angola, with an estimated loss of up to 4 million people due to the slave trade.
Today, the Atlantic Ocean continues to be of significant importance to Angola's economy and international relations. The country has vast mineral and petroleum reserves located offshore, contributing to its status as one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. The ocean also presents opportunities for tourism and recreational activities, attracting visitors to Angola's western coast.
In conclusion, the Atlantic Ocean forms a vital component of Angola's geography, history, and economy. It serves as a natural border, influencing the country's trade, climate, and economic development. The western coastline, with its natural harbours, has been integral to Angola's growth and continues to shape its future prospects.
Angola China Kitchen: Delivery Delights
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Angola is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north-east, and the Republic of the Congo to the north-west.
Angola's border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the longest at 2,646 km, while its border with the Republic of the Congo is the shortest at 231 km.
Angola's borders were established during the Scramble for Africa in the late 19th century when European powers divided the African continent into colonies.
No, there have been no territorial disputes over Angola's borders.
Yes, the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo experiences illegal crossings and smuggling, which poses a security threat and economic problem for both countries.