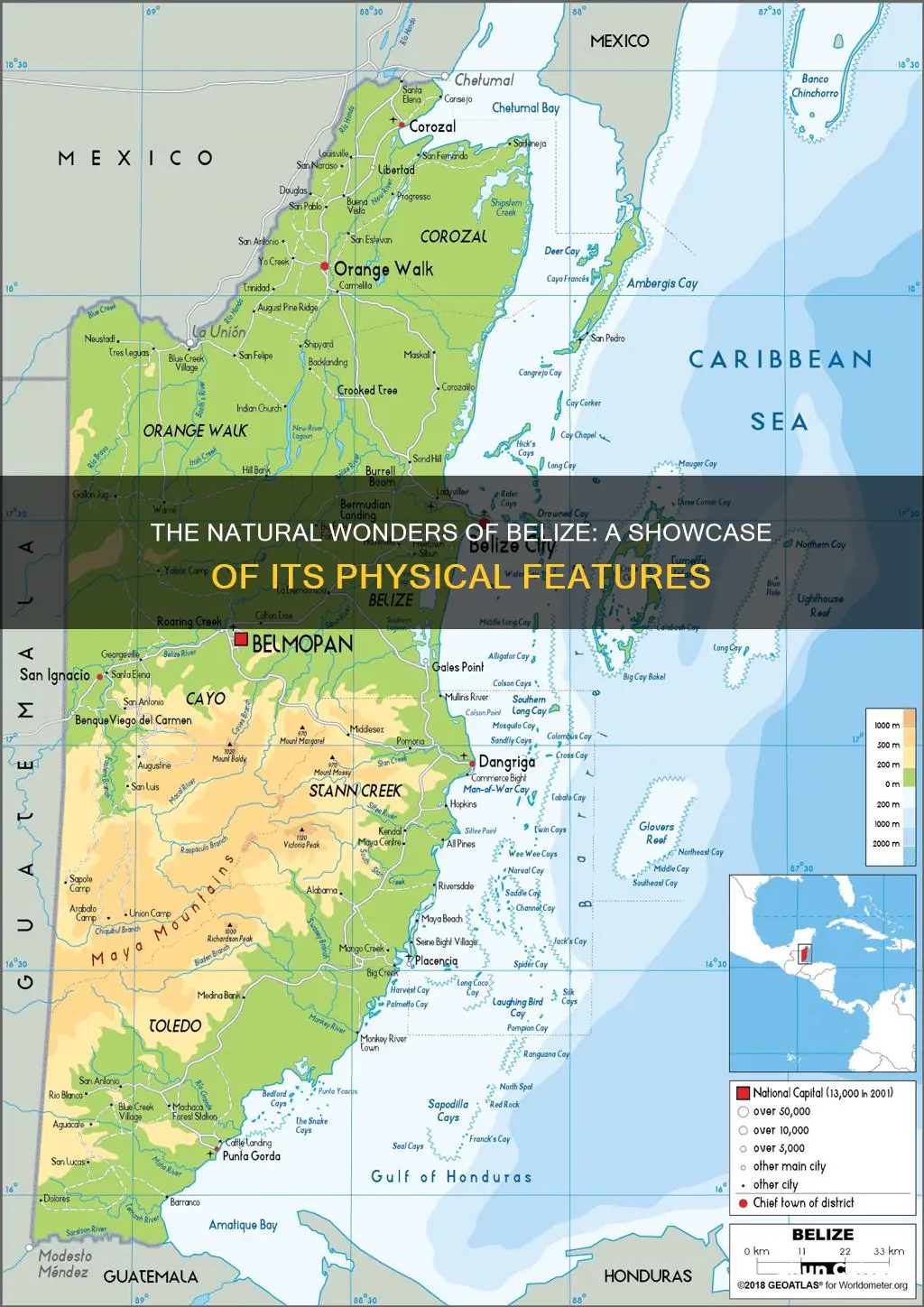
Belize is a small Central American country with a diverse landscape, characterised by mountains, rainforest, a Caribbean coast, and islands. The country is divided into two main regions: the southern region, which is distinguished by the Maya Mountains and the northern lowlands, which include the coastal plain. The Belize River, also known as the Old River, is the country's largest and most important river, serving as a vital source of drinking water for locals and playing a key role in the country's history as a trade route. The country's highest point is Doyle's Delight, at 1,124 metres, located in the Cockscomb Range, a spur of the Maya Mountains. The coastline is flat and swampy, with many lagoons, and the country is home to the second-largest barrier reef system in the world.
What You'll Learn
- Belize's landscape is divided into four regions: mountains, rainforest, the Caribbean coast, and the Caribbean islands
- The country's highest point is Doyle's Delight, at 1,124 m (3,688 ft)
- The Belize River is the country's largest and most historically important river
- The Maya Mountains are a large block of intrusive Paleozoic granite and sediments, with the highest point being Victoria Peak
- The northern lowlands are dominated by flat agricultural fields, small towns, and lowland rainforest

Belize's landscape is divided into four regions: mountains, rainforest, the Caribbean coast, and the Caribbean islands
Mountains
Belize is a land of mountains, swamps, and tropical jungle. The southern half of the country is dominated by the rugged Maya Mountains, a plateau of igneous rock cut by erosion into hills and valleys. The Cockscomb Range, a spur of the Maya Mountains, runs towards the sea and rises to Doyle's Delight, the country's highest peak at 1,124 m (3,688 ft). The Maya Mountains also contain numerous Mayan ruins. The northern half of the country consists of limestone lowlands and swamps less than 200 ft (60 m) above sea level.
Rainforest
Almost half of inland Belize is covered in rainforest. The country's northern lowlands are dominated by flat agricultural fields, small farming towns, and lowland rainforest. The southern coast boasts spectacular snorkelling and diving in the South Water Caye Marine Reserve. The southern coast is also home to the beautiful beaches of the Placencia peninsula, where whale sharks can usually be found between April and June.
Caribbean Coast
Belize has a 240-mile (386 km) coastline along the Caribbean Sea. The coastline is flat and swampy, with many lagoons, especially in the northern and central parts of the country. The Belize Barrier Reef, the second-longest in the world, flanks much of the coastline and is dotted with small cay islands. The reef is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a major draw for tourists.
Caribbean Islands
Belize has many islands off its coast, called cayes, with palm trees and mangrove forests. The water surrounding these islands is bright blue and studded with coral reefs and atolls. The islands are a playground for ocean lovers, offering opportunities to get up close to the reef and its marine life.
Jamaicans in Belize City: Why?
You may want to see also

The country's highest point is Doyle's Delight, at 1,124 m (3,688 ft)
Belize is a small Central American country, situated south of the Yucatán Peninsula. It is a land of mountains, swamps, and tropical jungle, with a coastline along the Caribbean Sea to the east. The country's physical landscape can be divided into two main regions: the southern half, dominated by the rugged Maya Mountains, and the northern half, consisting of limestone lowlands and swamps.
The Maya Mountains are a striking feature, rising to heights of about 1,100 meters. Within this range lies Doyle's Delight, the highest point in Belize, reaching an elevation of 1,124 meters (3,688 feet). Doyle's Delight is located in the Cockscomb Range, a spur of the Maya Mountains in western Belize. The peak was named by Sharon Matola, the founder of the Belize Zoo, in 1989. The name is derived from Arthur Conan Doyle's novel "The Lost World", reflecting the wild and wonderful nature of Belize.
Doyle's Delight stands out as a technicality, as it is not a true peak but a spur that is slightly higher than the surrounding mountain range. The peak is accessible through a relatively easy hike due to the shallow slope of that region. In contrast, reaching the nearby Victoria Peak requires more challenging hiking, and the trail is often impassable.
The Maya Mountains, including Doyle's Delight, are considered geologically old for Central America, dating back at least 65 million years. The high-elevation forests in this region are rare and unique to Belize. The first successful international expedition to summit Doyle's Delight occurred in 2008, after a seven-day hike and climb through the virgin jungle.
The southern half of Belize, where the Maya Mountains are located, is sparsely inhabited. The mountains are covered with shallow, highly erodible soils of low fertility, and the region is heavily forested. The northern lowlands and the southern coastal plain, on the other hand, are drained by numerous rivers and streams, including the Belize River, the country's largest and most historically important river.
Belize's Economy: A Focus on Service and its Impact on Job Creation
You may want to see also

The Belize River is the country's largest and most historically important river
Belize is a small Central American country with a diverse landscape of mountains, swamps, and tropical jungle. One of its most prominent physical features is the Belize River, which is the country's largest and most historically significant river.
The Belize River, also known as the Old River, runs for approximately 290 kilometres (180 miles) through the centre of Belize. It is formed by the confluence of the Mopan River and the Macal River, just east of San Ignacio in Belize. From there, it winds its way along the northern edge of the Maya Mountains, draining more than one-quarter of the country's land area. The river valley is characterised by tropical rainforests and is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna.
The Belize River has played a crucial role in the country's history and development. During the pre-Columbian era, it served as a major trade route for the Maya Indians. Well into the 20th century, it was the primary artery for commerce and communication between the interior and the coast. Loggers, for instance, used the river and came into conflict with the Maya and Spaniards in the early 19th century. By the late 19th century, over 130 small settlements had sprung up along the river, and it continued to be a hub for forestry and the transport of goods such as logwood, mahogany, and chicle.
Today, the Belize River remains vital for domestic and economic purposes. It provides drinking water for the local populations living along its banks, although water quality has deteriorated due to sediment, nutrient loading, pesticides, and other toxins from unsustainable agricultural practices and deforestation upstream. The river is also used to carry lumber and chicle to market areas, and it supports tourism with canoe and tubing tours that showcase the river's natural beauty, including deep ravines, waterfalls, and rock formations.
The Belize River's catchment area, which includes the Mopan and Macal rivers, is home to over 45% of Belize's population. Along with the Sibun and New rivers, it has been integral to the country's historical geography, shaping the patterns of communication, trade, and settlement over centuries.
Mahogany Bay: Adventure and Relaxation
You may want to see also

The Maya Mountains are a large block of intrusive Paleozoic granite and sediments, with the highest point being Victoria Peak
The Maya Mountains are a large block of intrusive Paleozoic granite and sediments. They are a mountain range located in Belize and eastern Guatemala in Central America. The range falls abruptly to the coastal plain in the east and north, but slopes more gently to the west, becoming the Vaca Plateau, which extends into eastern Guatemala. The Maya Mountains are the only source of igneous and metamorphic materials in Belize.
The highest point in the Maya Mountains is Victoria Peak, which reaches 3,680 feet (1,120 metres) in height. The second-highest peak is Doyle's Delight, which measures approximately 3,688 feet (1,124 metres) tall. Doyle's Delight is named after Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, the author of the Sherlock Holmes mysteries. Doyle wrote a book in 1912 called 'The Lost World', in which he refers to the Belize mountains as beautiful and wild places.
The Maya Mountains are a relatively short range of peaks. They rise to heights of about 1,100 metres. The mountains are mainly made of Paleozoic era granite and sediments. The range is extensively dissected and of uniform elevation throughout. The mountains are wedged between the easterly to northeasterly trending Corozal and Belize Basins, themselves sub-basins of the Peten-Corozal Basin, which fully encompasses the mountains.
The Maya Mountains and associated foothills contain a number of important Mayan ruins, including the sites of Lubaantun, Nim Li Punit, Cahal Pech and Chaa Creek. The mountains take their name from the Maya people, who retreated into the mountains before the Spaniards, leaving great centres, such as Lubaantun, deserted behind them.
Belize Red Cross: A Humanitarian Organization
You may want to see also

The northern lowlands are dominated by flat agricultural fields, small towns, and lowland rainforest
The northern lowlands of Belize are characterised by flat agricultural fields, small towns, and lowland rainforest. This region spans the area east and west of the Northern Highway up to the Mexican border and is one of the least travelled in Belize. While tourist attractions are limited, the region is home to the ancient Mayan ruins at Lamanai, as well as the towns of Orange Walk and Corozal.
The northern lowlands are part of a larger region that also includes the southern coastal plain. This region is drained by eighteen major rivers and many perennial streams. The coastline is flat and swampy, with many lagoons, especially in the northern and central parts of the country. The terrain changes from mangrove swamp to tropical pine savannah and hardwood forest as you move inland.
The northern lowlands are also home to a diverse range of wildlife. The Orange Walk, for example, has the oldest and most impressive Mayan sites and is home to over 200 species of birds, as well as Howler monkeys, crocodiles, and iguanas. The region's lowland rainforest covers almost half of inland Belize.
The northern lowlands are an important agricultural area, with sugar being a key crop. The New River, for instance, flows through the northern sugar-growing areas. The river valleys in this region possess fertile alluvial soils and have supported considerable cultivation and human settlement.
The northern lowlands are also significant from a historical perspective. The Belize River, also known as the Old River, was the main artery of commerce and communication between the interior and the coast until the 20th century. It remains an important source of drinking water and for other domestic uses for the locals living along it.
Belize Diving: Expert Opinions
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Belize is divided into two main physiographic regions, distinguished by the Maya Mountains and the northern lowlands. The Maya Mountains, located in the southern half of the country, are characterised by basins and plateaus. The highest point in Belize, Doyle's Delight, stands at 3,688 feet (1,124 meters) and can be found in this region. The northern lowlands are flat and marshy and are home to Belize's most productive agricultural lands.
The Belize River, also known as the Old River, is the largest and longest river in Belize, stretching about 180 miles (290 kilometers) through the country. It serves as an essential water source and a historic transportation route. Eighteen major rivers and many perennial streams drain the country's low-lying areas.
The climate in Belize is tropical, with a rainy season from May/June to November and a dry season from February to May. The average temperature in the coastal regions ranges from 24 °C (75 °F) in January to 27 °C (81 °F) in July. The seasons are marked more by differences in humidity and rainfall than in temperature.







