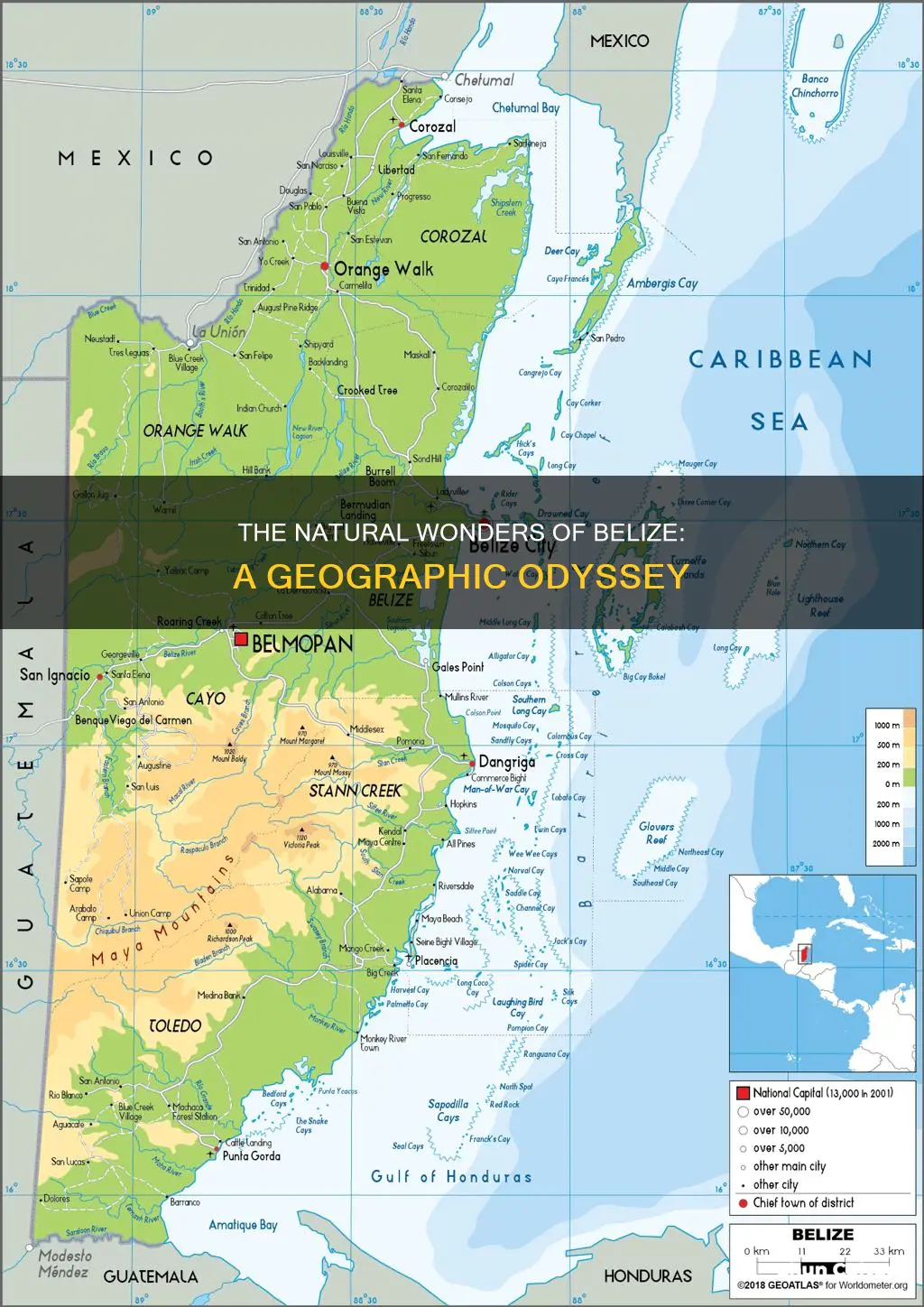
Belize is a Central American country with a diverse landscape of mountains, swamps, and tropical jungle. The country is bordered by Mexico to the north, Guatemala to the west and south, and the Caribbean Sea to the east. With a total area of 22,966 square kilometres, Belize is slightly larger than El Salvador or Massachusetts. The country's landscape can be divided into two main regions: the visually striking Maya Mountains and the associated basins and plateaus in the southern half of the country, and the northern lowlands and southern coastal plain. The Maya Mountains rise to heights of about 1,100 metres, with the highest point being Doyle's Delight at 1,124 metres. The northern lowlands and coastal plain are flat and swampy, with many lagoons and mangrove swamps. The country's largest river is the Belize River, which drains more than a quarter of the country and was a vital trade route for the Maya empire.
What You'll Learn

Belize's location and borders
Belize is located on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, Guatemala to the west and south, and the Caribbean Sea to the east. The country has a total land border length of 542 km, with 272 km shared with Mexico and 266 km with Guatemala.
Belize is situated at 17°15' north of the equator and 88°45' west of the Prime Meridian on the Yucatán Peninsula. The country has a rectangular shape, extending approximately 280 km north-south and 100 km east-west. The northern border with Mexico is defined by the Hondo River, while the Sarstoon River marks the southern boundary with Guatemala. The western border with Guatemala does not follow any natural features, running through lowland forest and highland plateau.
Belize has a total area of 22,966 km2 (8,867 sq mi), including 386 km of coastline along the Caribbean Sea. The country's territory includes many coral reefs, cays, and islands in the Caribbean Sea, forming the Belize Barrier Reef, the second-longest in the world.
Belize is the only Central American country without a coastline on the North Pacific Ocean. Its eastern border is defined by the Caribbean Sea and its network of rivers, creeks, and lagoons, which have played a significant role in the country's historical geography.
Punta Gorda's Tropical Climate
You may want to see also

The country's landscape and topography
The landscape and topography of Belize are characterised by mountains, swamps, and tropical jungle. The country can be divided into two main physiographic regions.
The first region is distinguished by the Maya Mountains and the associated basins and plateaus that dominate all but the narrow coastal plain in the southern half of the country. The mountains rise to heights of about 1,100 metres, with the highest point being either Doyle's Delight (1,124 m) in the Cockscomb Range, or Victoria Peak (1,120 m). These heavily forested highlands are very sparsely inhabited and are covered with shallow, highly erodible soils of low fertility. The southern highland plateaus, such as the Mountain Pine Ridge, are noticeably cooler year-round than the rest of the country. The hilly regions surrounding the Maya Mountains are formed from Cretaceous limestone and are characterised by a karst topography, which includes numerous sinkholes, caverns, and underground streams. In contrast to the Mountain Pine Ridge, some of the soils in these regions are quite fertile and have been cultivated for at least the past 4,000 years.
The second region comprises the northern lowlands, along with the southern coastal plain. Eighteen major rivers and many perennial streams drain these low-lying areas. The coastline is flat and swampy, with many lagoons, especially in the northern and central parts of the country. The savannas of northern Belize are flat and dry compared to the rest of the country, receiving only 50 inches of rain per year. The primary source of income for the predominantly Mestizo population in this region is sugarcane. The terrain in the northern coastal areas changes from mangrove swamp to tropical pine savanna and hardwood forest. Westward, the country gives way to the Yucatan Platform, a tectonically stable region. Although mostly level, this part of the country also has occasional areas of hilly, karst terrain, such as the Yalbac Hills along the border with Guatemala.
Belizean: Central America's Hidden Gem
You may want to see also

Belize's geology
Belizean geology consists largely of limestone, which is the primary stone found in coastal areas, reefs, and atolls. The notable exception to this is the Maya Mountains, a large block of intrusive Paleozoic granite and other sediments, which run from the northeast to the southwest across the south-central part of the country. The Maya Mountains are the high, rugged core of Belize, composed of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that are between 125 and 320 million years old. The surrounding flat plains are underlain by Cretaceous and Tertiary rocks (1.6-65 million years old), which indicate that Belize was once covered by a warm, shallow sea.
The hilly regions surrounding the Maya Mountains are formed from Cretaceous limestone and are characterised by a karst topography, which includes numerous sinkholes, caverns, and underground streams. The soils in these regions are often more fertile than those of the Mountain Pine Ridge and have been cultivated for at least 4,000 years.
Much of the northern half of Belize lies on the Yucatán Platform, a tectonically stable region. Although mostly level, this part of the country also has occasional hilly, karst terrain, such as the Yalbac Hills along the border with Guatemala and the Manatee Hills between Belize City and Dangriga. The landscapes of the coastal plains are relatively flat and covered by alluvial deposits of varying fertility.
Belize is located near the junction of the North American and Caribbean tectonic plates, which have moved past each other over the last 80 million years. The eastward drift of the Caribbean plate resulted in the major features of Belize, including the Maya Mountains, offshore atolls, and the location of the coral barrier reef. The entire area of Belize was covered by a shallow sea during the Cretaceous period, and the oldest land surface in Central America, the Mountain Pine Ridge plateau, was created when what is now the western part of the Maya Mountains stood above sea level.
The modern barrier reef sits atop a prominent fault that separates the shallow platform to the west from the deeper Caribbean to the east. The major NE-trending faults are "normal faults" that include portions that have dropped down on their eastern sides. The nearly EW-trending fault on the south is the boundary of the North American and Caribbean plates.
Belize Real Estate: A Smart Investment Move?
You may want to see also

Climate and weather
Belize has a tropical climate with an average annual temperature of 84°F (29°C). The coastal sea breezes, large areas of jungle, and rainforests provide cooling relief in the hottest months, and while it can get cool in winter, temperatures rarely fall below 60°F (16°C). The climate is mild enough to allow for outdoor activities all year round.
Belize has two seasons: the wet and the dry. The dry season falls between February and May, with significantly less rainfall than the rest of the year, and when rain does come, it is usually in short bursts. The wet season runs from June to December, when parts of the country receive up to 150 inches of rain. The wet season is also hurricane season, and while Belize does not attract many major direct hits, it does experience severe tropical weather with high winds and rain. The wettest month is October, with an average of 11.9 days of rain.
The transitional period between the seasons is from November to February, with the coolest temperatures of the year and limited rainfall. The true dry season is very short, lasting from February to April. There is a large difference in rainfall between the north and the south of the country, with the north receiving around 1500mm or 60 inches of rain per year, and the south receiving about 4000mm or 160 inches. In the north and centre of the country, there is a dip in rainfall in August, between peaks in July and September.
The uplands (Mountain Pine Ridge and the Maya Mountains) are cooler than the rest of the country, with temperatures falling by about 3°C for every 1000ft rise in altitude. The mean annual temperature in the mountains is a comfortable 72°F.
The mean annual humidity is 83%, but this is often dispersed by cooling sea breezes. The Belize coastal area is exposed to southeast trade winds averaging 10-13 knots, which are particularly consistent during July.
Belize City After Dark: Is It Worth Staying the Night?
You may want to see also

Natural resources and environmental issues
Belize is a small Central American country with a diverse ecology and a wide range of natural resources. The country's landscape is divided into two main regions: the northern lowlands and the southern region, which is dominated by the Maya Mountains and associated basins and plateaus. The northern region consists mostly of flat plains covered in indigenous forests, while the southern region is home to mountain ranges.
Belize's natural resources include its indigenous forests, fertile land, maritime territory, beaches, limestone, sand, clay, gravel, and Bagasse. The country's forests provide a natural habitat for a variety of animals and have been a major source of income for the government through the forestry industry. Belize also has a large agricultural sector, with an estimated 38% of its land used for farming. The country's sub-tropical climate is ideal for agriculture, and the sector contributes significantly to national income through exports.
Belize is also rich in water resources, with the Caribbean Sea to the east and a 386-kilometer coastline. The country's water resources support a thriving fishing industry, and the world's second-largest barrier reef provides a habitat and food for diverse marine life. The fishing industry has become a major contributor to the country's economy, with exports to the United States, the Caribbean, and Europe.
However, Belize faces several environmental issues and challenges. Deforestation, coastal development, and crude oil exploitation have taken a toll on the country's natural environment. Illegal logging, particularly along the Guatemalan border, has resulted in the loss of precious forest cover and contributed to environmental problems. The country has also struggled with inadequate waste management systems, especially with the increase in tourism, which has led to air and water pollution.
Climate change is another pressing issue for Belize, with rising sea temperatures causing coral bleaching and reduced fish catch, impacting local livelihoods. The government has implemented projects such as the Marine Conservation and Climate Adaptation Project (MCCAP) to strengthen the climate resilience of the Belize barrier reef and promote sustainable practices. Additionally, Belize is vulnerable to natural disasters such as hurricanes and coastal flooding, which have caused significant damage and loss of life in the past.
Belize's natural resources are vital to its economy, with the tourism and agriculture industries relying heavily on them. However, the country faces challenges in managing these resources sustainably and protecting its fragile environment.
Toledo: Belize's Southernmost District
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Belize is a small Central American nation with a diverse geography that includes flat, swampy coastal plains, low mountains in the south, and hundreds of offshore islands. The landscape is divided into two main regions: the visually striking Maya Mountains and the associated basins and plateaus in the south, and the northern lowlands.
The highest point in Belize is Doyle's Delight, at 1,124 m (3,688 ft) above sea level.
Belize has a tropical climate with a rainy season from May or June to November and a dry season from February to May. The average daily temperature in Belize City is 85°F, but the daytime high is often in the 90s between May and October.
Belize is vulnerable to hurricanes and tropical storms from June to November and experiences frequent coastal flooding, especially in the south.







