Transylvania is a historical region in central and northwestern Romania. It was under the rule of the Agathyrsi, part of the Dacian Kingdom, Roman Dacia, the Goths, the Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Gepids, the Avar Khaganate, the Slavs, and the 9th-century First Bulgarian Empire. In the late 9th century, Transylvania was part of the Hungarian conquest, and the family of Gyula II of the seven chieftains of the Hungarians ruled Transylvania in the 10th century.
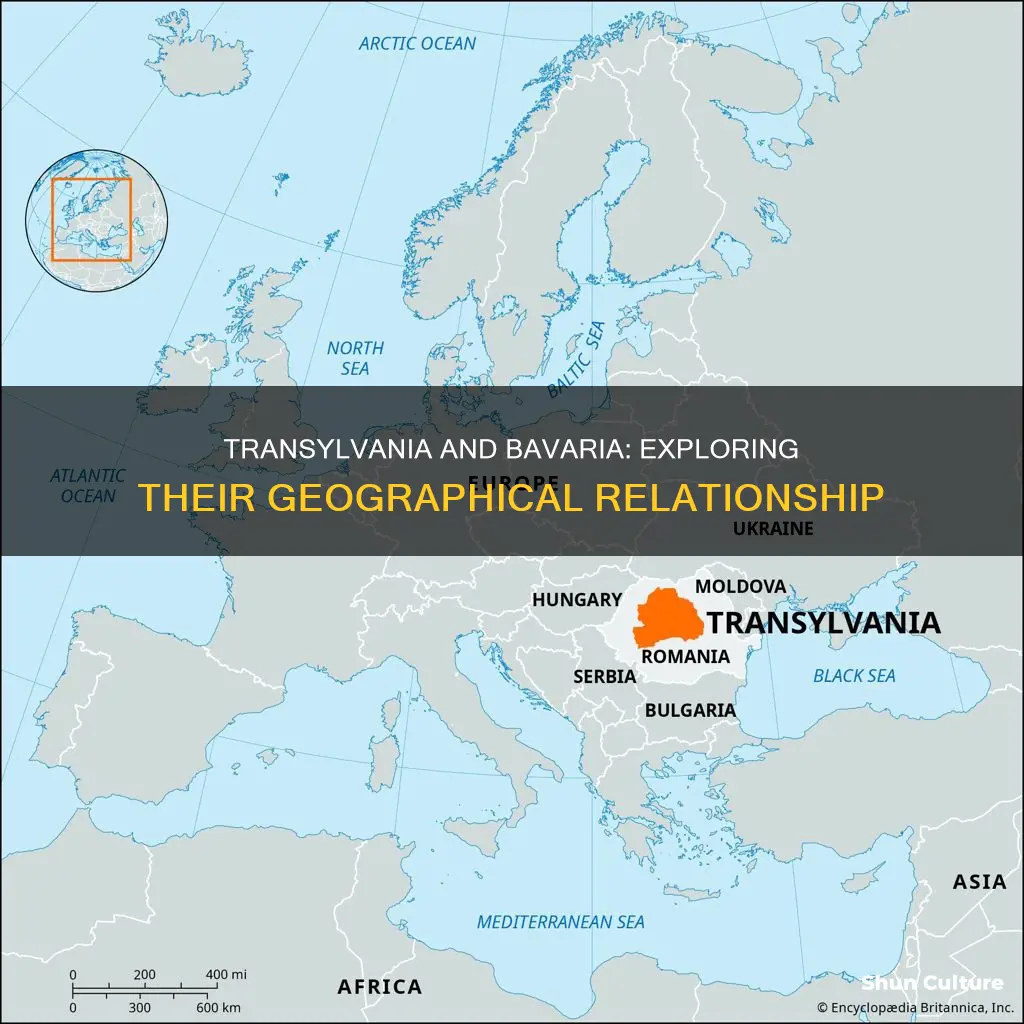
Transylvania is not in Bavaria. Bavaria is a state in the southeast of Germany.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Is Transylvania in Bavaria? | No |
| Is Transylvania a real place? | Yes |
| Where is Transylvania located? | Romania, Europe |
| What does Transylvania mean? | "Territory beyond the forest" |
| Is Transylvania in Hungary or Romania? | Romania |
| Is Transylvania safe for tourists? | Yes |
What You'll Learn
- Transylvania is a historical region in Romania, and was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for several years
- Transylvania is not in Bavaria, which is a state in the southeast of Germany
- Transylvania is in Europe, while Bavaria is in Germany
- Transylvania is a province in Romania, while Bavaria is a state in Germany
- Transylvania is home to the Romanian language, while Bavaria is home to the Austro-Bavarian dialect

Transylvania is a historical region in Romania, and was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for several years
Transylvania is a historical region in Romania. It was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for several years.
Transylvania is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. It was under the rule of the Agathyrsi, part of the Dacian Kingdom, Roman Dacia, the Goths, the Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Gepids, the Avar Khaganate, the Slavs, and the 9th-century First Bulgarian Empire. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and conquered by the Hungarian tribes, and Gyula's family from the seven chieftains of the Hungarians ruled it in the 10th century. King Stephen I of Hungary asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords. He personally led his army against his maternal uncle Gyula III, and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1002.
After the Battle of Mohács in 1526, Transylvania belonged to the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, from which the Principality of Transylvania emerged in 1570 by the Treaty of Speyer. During most of the 16th and 17th centuries, the principality was a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire; however, the principality had dual suzerainty (Ottoman and Habsburg).
In 1690, the Habsburg monarchy gained possession of Transylvania through the Hungarian crown. After the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence in 1711, Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian Transylvanian princes were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848. After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land entirely independent of Hungary. The separate status of Transylvania ended with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, and it was reincorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary (Transleithania) as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
During this period, Romanians experienced the awakening of self-consciousness as a nation, manifested in cultural and ideological movements such as the Transylvanian School, and drafted political petitions such as Supplex Libellus Valachorum. After World War I, the National Assembly of Romanians from Transylvania proclaimed the Union of Transylvania with Romania on 1 December 1918, and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Romania by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. In 1940, Northern Transylvania reverted to Hungary as a result of the Second Vienna Award, but it was returned to Romania after the end of World War II.
Transylvania is a real place, a province where people live their ordinary lives, without giving importance to the fame that surrounds this region. The name “Transylvania” is derived from medieval Latin. It was attested in 1075. Transylvania is a word composed of the terms “trans” (“over”, “beyond”) and “silva” (“forest”) and means “(territory) beyond of the forest “.
Transylvania is in Romania, being a historical province of Romania. It was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for several years. After the First World War, it was united with Romania.
The Bavarian Illuminati: A Secret Society's Enduring Legacy
You may want to see also

Transylvania is not in Bavaria, which is a state in the southeast of Germany
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the areas in the south and northeast were settled by German colonists known as Saxons. Tradition holds that Siebenbürgen, the German name for Transylvania, derives from the seven principal fortified towns founded by these Transylvanian Saxons.
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of 70,550.19 km2 (27,239.58 sq mi), it is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia.
Exploring Amsterdam to Bavaria: How Far is the Journey?
You may want to see also

Transylvania is in Europe, while Bavaria is in Germany
Transylvania is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. It is known for its scenery, rich history, and multi-cultural character. It is also home to some of Romania's UNESCO World Heritage Sites, such as the Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains, and the Roșia Montană Mining Cultural Landscape.
Transylvania has had a tumultuous history, having been ruled by the Agathyrsi, the Dacian Kingdom, Roman Dacia, the Goths, the Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Gepids, the Avar Khaganate, the Slavs, and the First Bulgarian Empire. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was conquered by the Hungarian tribes and became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1002. After the Battle of Mohács in 1526, it became part of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, from which the Principality of Transylvania emerged in 1570. During most of the 16th and 17th centuries, the principality was a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. In 1690, the Habsburg monarchy gained possession of Transylvania through the Hungarian crown. After the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence in 1711, Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian Transylvanian princes were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848. After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land entirely independent of Hungary. The separate status of Transylvania ended with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, and it was reincorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. After World War I, the National Assembly of Romanians from Transylvania proclaimed the Union of Transylvania with Romania on December 1, 1918, and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Romania by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. In 1940, Northern Transylvania reverted to Hungary as a result of the Second Vienna Award, but it was returned to Romania after the end of World War II.
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a state in the southeast of Germany. It is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia. Bavaria has a distinct culture, largely because of its Catholic heritage and conservative traditions, which includes a language, cuisine, architecture, festivals, and elements of Alpine symbolism. It also has the second-largest economy among the German states by GDP figures, giving it the status of a wealthy German region.
Bavaria has had a long and tumultuous history, having been inhabited by Iron Age Celtic tribes, conquered by the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, and incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became the independent Kingdom of Bavaria in 1806, joined the Prussian-led German Empire in 1871, and finally became a state of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.
Bavaria's Beer: Taste and Tradition
You may want to see also

Transylvania is a province in Romania, while Bavaria is a state in Germany
Transylvania is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. It is known for its scenery, rich history, and multi-cultural character. It is also home to some of Romania's UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The region was under the rule of the Agathyrsi, part of the Dacian Kingdom, Roman Dacia, the Goths, the Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Gepids, the Avar Khaganate, the Slavs, and the 9th-century First Bulgarian Empire. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was conquered by Hungarian tribes and became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1002. After the Battle of Mohács in 1526, it belonged to the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, from which the Principality of Transylvania emerged in 1570. During most of the 16th and 17th centuries, the principality was a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. In 1690, the Habsburg monarchy gained possession of Transylvania through the Hungarian crown. After the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence in 1711, Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian Transylvanian princes were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848. After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land, entirely independent of Hungary. The separate status of Transylvania ended with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, and it was reincorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. After World War I, the National Assembly of Romanians from Transylvania proclaimed the Union of Transylvania with Romania on December 1, 1918, and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Romania by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. In 1940, Northern Transylvania reverted to Hungary as a result of the Second Vienna Award, but it was returned to Romania after the end of World War II.
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of 70,550.19 square kilometres, it is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. Bavaria has a distinct culture, largely because of its Catholic heritage and conservative traditions, which includes a language, cuisine, architecture, festivals, and elements of Alpine symbolism. It also has the second-largest economy among the German states by GDP figures, giving it the status of a wealthy German region. Bavaria has a population of approximately 13.1 million inhabitants and is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia. Munich is its capital and largest city, which is also the third-largest city in Germany.
Bavarian Inn's Dog-Friendly Policy: All You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Transylvania is home to the Romanian language, while Bavaria is home to the Austro-Bavarian dialect
Transylvania and Bavaria are two distinct regions in Europe with their own unique languages and dialects. Transylvania, a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, is predominantly home to the Romanian language, while Bavaria, a state in Germany, is known for the Austro-Bavarian dialect or the Bavarian language.
Transylvania, located in central and northwestern Romania, has a rich history and is known for its multicultural character. Romanian, the official language of Romania, is spoken by approximately 89% of the country's population. In Transylvania, Romanian is the majority language, with around 24-26 million speakers, and it is considered an Eastern Romance language descending from Vulgar Latin. The region also has a significant Hungarian-speaking population, mainly in Transylvania, accounting for about 7% of the total population. Additionally, there is a small percentage of German speakers, including the Transylvanian Saxons, who make up around 1.5% of the national population.
On the other hand, Bavaria is home to the Austro-Bavarian dialect, also known as Bavarian (Bairisch). It is a major group of Upper German varieties spoken in the southeast of the German language area, including the state of Bavaria, most of Austria, southern Czechia, western Hungary, and even parts of Italy, such as Tyrol. Bavarian is considered a dialect of German by some, while others classify it as a separate language due to its distinct features. Approximately 12 million people speak Bavarian, making it the largest of all German dialects.
The Transylvanian Saxon dialect, spoken by the Transylvanian Saxons, is a unique dialect that has evolved relatively isolated from other German dialects. It is closely related to Luxembourgish and sounds similar to medieval German. This dialect has influenced the region's literature, with works written in Latin, the Transylvanian Saxon dialect, and Standard German by writers such as Josef/Joseph Haltrich and Gustav Schuster-Dutz.
While Transylvania is known for its Romanian language and Hungarian and German influences, Bavaria is characterized by its Austro-Bavarian dialect, which has a strong presence in southern Germany and beyond. Both regions showcase the linguistic diversity and complexity of Europe, with Transylvania embracing multiple languages and Bavaria boasting a robust dialectal variation of German.
James & Muller: A Dynamic Duo for Bayern?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, Transylvania is not in Bavaria. Transylvania is located in Romania, in Central Europe. It is a historical and cultural region that encompasses central Romania. Transylvania was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for several years, but after the First World War, it was united with Romania.
No, Transylvania is not in Hungary. Transylvania is in Romania, being a historical province of Romania. It was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for several years. After the First World War, it was united with Romania.
The name “Transylvania” is derived from medieval Latin. It was attested in 1075. Transylvania is a word composed of the terms “trans” (“over”, “beyond”) and “silva” (“forest”) and means “(territory) beyond of the forest “.
You can get to Transylvania if you land in one of the large airports outside the region, Bucharest or Budapest. Both of them have great connections with the major cities around the world, so it is easier to find a flight to Bucharest or Budapest than directly to Transylvania.







