Belize is considered an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank. With a population of about 359,000–405,000, it has a per capita income of US$4,906–6,049. Belize has the second or third highest per capita income in Central America. However, the country faces high poverty rates, with 43% of its population living below the national poverty line and 16% facing extreme poverty.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Income level | Upper-middle income country |
| Population | 359,000-405,000 |
| Per capita income | $4,906 (2016) |
| Per capita GDP | $6,049 (2022) |
| GDP | $2.5 billion (2022) |
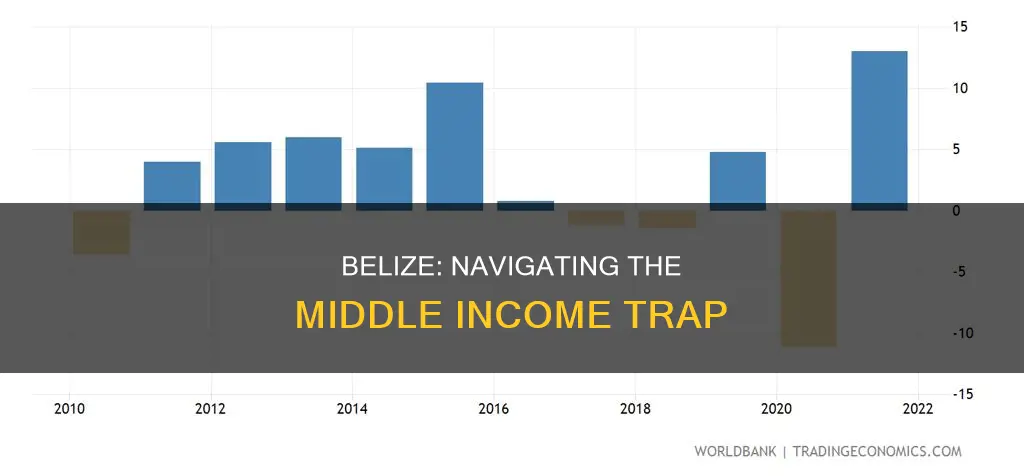
| GDP growth rate | 15.2% (2021) |
| GDP growth rate estimate | 9.6% (2023) |
| Unemployment rate | 5% |
| Poverty rate | 43% |
| Extreme poverty rate | 16% |
| Main sources of income | Tourism, agriculture |
| Top trade partners (2021) | United States, China, Mexico |
| Top exported goods (2021) | Sugar, confectionery, fruit, nuts, seafood |
What You'll Learn

Belize's economic transformation
Belize is an upper-middle-income country in Central America with a unique cultural heritage and a developing free-market economy. It is the only English-speaking country in Central America and has close sociopolitical and economic ties to the Caribbean as a CARICOM member.
Belize's economy is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and services, with a focus on exports. The country has a small domestic market and limited domestic industry due to high-cost labour and energy. However, it has the second-highest per capita income in Central America and is considered a tax haven.
Historically, Belize's economy relied heavily on forestry, with logwood and mahogany as its main exports. In the 20th century, the country shifted to new sectors, and cane sugar became its principal export. More recently, Belize has expanded its production of citrus fruits, bananas, seafood, and apparel. The country's agricultural sector employs about one-fifth of the population, and its arable land covers around 8,090 square kilometres, only a fraction of which is under cultivation.
Tourism is the most important source of foreign exchange for Belize, driven by its diverse ecology, including the largest coral reef in the Americas, pristine tropical forests, and numerous Mayan ruins. The travel and tourism industry directly contributed 350.6 million BZD (176 million USD) to Belize's GDP in 2011, and this figure is expected to grow.
Belize has a growing trade deficit, largely due to low export prices for sugar and bananas. The country's economic performance is susceptible to external market changes, and it relies heavily on foreign trade, particularly with the United States, its number one trading partner.
To stimulate economic growth, Belize has implemented various measures, such as joining preferential trade agreements and benefiting from initiatives like the Caribbean Basin Initiative (CBI). The discovery of oil in Spanish Lookout presents new prospects and challenges for the country's economic transformation.
Belize vs Roatan: Beach Paradise?
You may want to see also

Income disparity
Belize is considered an upper-middle-income country in Central America, with the second-highest per capita income in the region. However, despite its status, Belize faces high rates of poverty, with about 43% of its population living below the national poverty line and 16% facing extreme poverty. This disparity can be attributed to various factors, including the country's economic structure, income distribution, and social inequalities.
Belize's economy relies heavily on agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism, which are all susceptible to fluctuations in global markets and weather conditions. While tourism is the most significant source of foreign exchange, contributing 25% of the GDP, it is closely followed by agricultural exports, which include citrus, sugar, bananas, and fisheries. The manufacturing sector, which includes petroleum, is also subject to volatile world commodity prices. This reliance on a few key sectors leaves the country vulnerable to economic shocks and contributes to income disparity.
The income disparity in Belize is further exacerbated by differences in income levels between urban and rural areas. Urban centres, such as Belize City, tend to offer higher salaries due to a greater concentration of businesses and higher costs of living. In contrast, rural areas, where agricultural jobs predominate, often have lower wages. Additionally, expatriates working in Belize may earn higher incomes due to their specific skill sets and experience, further contributing to the income disparity.
The gender wage gap is another critical issue in Belize, with women earning less than men for similar roles across various sectors. While Belizean women often achieve similar or higher levels of education, this has not translated into equal pay. Societal and cultural biases, as well as discriminatory practices during hiring, promotion, and pay-setting, contribute to this disparity.
Belize also faces challenges in addressing income disparity due to high debt repayments. In 2014, the country's debt-to-GDP ratio was 78.6%social services and human capital development, which are crucial for reducing poverty and income inequality.
To address these disparities, Belize has received aid from Official Development Assistance (ODA) and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). Additionally, the country has sought assistance from international organisations and other countries, including Cuba, Venezuela, the United States, and the Organisation of American States. While these efforts have put Belize on the right track, more work is needed to achieve sustainable economic growth and reduce income inequality.
Belize's Best Snorkel Spots
You may want to see also

The role of tourism
Belize is an upper-middle-income country in Central America with a population of 405,000 and a diverse ecological landscape. The country has the second-highest per capita income in Central America, and tourism is its most important source of foreign exchange, contributing 15% of its total GDP in 2017.
Tourism in Belize has grown significantly in recent years, and it is now the second-largest industry in the nation. The Belizean Prime Minister, Dean Barrow, has expressed his intention to use tourism to combat poverty throughout the country. The tourism industry has positively impacted the agricultural, commercial, and financial industries, as well as the construction industry.
Belize has a lot to offer tourists, from its natural attractions to its historical sites. The Belize Barrier Reef, the second-largest in the world, is a significant draw for tourists, along with over 450 offshore islands, excellent fishing spots, and safe waters for a range of water sports. The country also boasts numerous rivers for rafting and kayaking, as well as jungle and wildlife reserves for hiking, birdwatching, and helicopter tours.
In addition, Belize has a rich history dating back to the Pre-Columbian Maya civilisation, with many well-preserved ruins that attract tourists interested in archaeology and history. The archaeological sites are managed by the Institute of Archaeology, a branch of the National Institute of Culture and History (NICH).
The growth in tourism has led to an increase in the number of hotels and available rooms in the country, with the hospitality industry recognising the potential of the tourism sector. The travel sector, which includes transport, storage, and telecommunications services, is the most important service export in the tourism industry, accounting for approximately 70% of Belize's total service exports since the 1990s.
The United States is the largest consumer of the Belizean travel industry, accounting for approximately 62% of stopover arrivals in 2006. However, the number of cruise ship passengers has also been increasing, with a significant rise from 14,183 passengers in 1998 to 705,219 in 2009.
The development of the tourism industry in Belize has had a positive impact on the economy, creating jobs and contributing to the growth of other industries. It has also provided opportunities for marginalised communities, such as the Maya and Garifuna people, to engage in alternative markets, preserve their culture, and diversify their income.
Overall, tourism plays a crucial role in Belize's economy, and the country's diverse attractions continue to draw visitors from around the world, contributing to its status as an upper-middle-income country.
Belize's Democratic Paradox
You may want to see also

The impact of agriculture
Belize is an upper-middle-income country in Central America with the second-highest per capita income in the region. The country has a unique cultural heritage and is the only English-speaking nation in Central America. Belize's economy is export-oriented, with agricultural exports being the second-most important source of foreign exchange after tourism.
Agriculture and agribusiness are integral parts of Belize's economy, supporting a large number of workers and contributing to the country's overall food security. The sector benefits from significant rainfall and a relatively stable year-round subtropical climate. Sugar, bananas, and shellfish production are the main sources of revenue, while corn, rice, beans, and sorghum are the largest agricultural products by volume, mainly consumed domestically. Belize's agricultural sector faces challenges such as a lack of modern equipment and irrigation systems, as well as disease and natural disasters, which impact citrus and shrimp farming.
Economic Impact
The agriculture sector in Belize contributes approximately BZE$500 million to the economy. Sugar, bananas, and citrus fruits are the main economic drivers within the sector, with sugar being the most significant export product. In 2019, Belize exported sugar worth $136.36 million, accounting for 48% of the country's total exports. The country also exports bananas, papayas, and other agricultural products.
Employment
Agriculture employs 9.687% of Belize's total workforce, providing income and livelihood for a significant portion of the population.
Food Security
Belize's agricultural sector plays a crucial role in ensuring food security for the country. Locally grown fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes are consumed domestically, reducing the country's reliance on food imports.
Trade Opportunities
Belize's agricultural products have access to international markets, including the United States, the European Union, CARICOM, and Latin America. These trade opportunities contribute to foreign exchange earnings and promote economic growth.
Rural Development
Agriculture in Belize supports the development of rural communities, especially in underprivileged areas. Various projects and initiatives aim to empower women, rural youth, and vulnerable communities by providing training, fostering entrepreneurship, and improving access to services and markets.
Environmental Impact
Belize's agricultural practices have an impact on the environment. While the country boasts extensive natural capital, including the largest coral reef in the Americas and a vast mangrove ecosystem, sustainable agricultural practices are crucial to preserving these ecosystems and maintaining the country's ecological diversity.
In summary, agriculture in Belize has a significant impact on the country's economy, employment, food security, and rural development. It offers opportunities for trade and investment while also presenting challenges related to modernisation, disease prevention, and environmental sustainability.
Punta Gorda's Tropical Climate
You may want to see also

Belize's foreign debt
Belize is an upper-middle-income country in Central America with a population of 405,000 and a gross domestic product (GDP) of $2.5 billion as of 2022. The country has strong ecological, sociopolitical, and economic ties to the Caribbean.
Belize has actively sought to manage its debt and has requested consideration for debt reduction from the United States government under the Enterprise for the Americas Initiative. The country has also benefited from foreign aid and concessional loans from international organisations and other countries, including the United States and Britain.
The World Bank has been actively involved in supporting Belize's economic development and sustainability initiatives. As of FY2023, the World Bank's portfolio in Belize includes three active projects with a total commitment of US$39.2 million. These projects focus on building climate resilience, promoting financial inclusion, and responding to crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Belize's economic prospects are expected to improve, with a projected economic growth rate of 2-3% in the medium term. However, the country continues to face challenges, including a high unemployment rate and the need to address the impacts of climate change.
Belize's Nurse Sharks: A Feeding Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, Belize is an upper-middle-income country with a per capita income of US$4,906 in 2016.
Belize has a huge income disparity between rich and poor, with 43% of its population living below the national poverty line and 16% facing extreme poverty.
Tourism is the main source of income and foreign exchange in Belize, followed by agriculture and exports.
Belize's economy is facing challenges such as high debt repayments, a growing trade imbalance, and a slow growth rate, which restrict the government's budget for development programming and social services.







