Belize has a developing free-market economy. It is a small, private enterprise economy, with a mixed economic system that includes a private-enterprise system, combined with centralised economic planning and government regulation. Belize's economy is based primarily on tourism, agriculture, energy and services.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Economic system | Developing free-market economy |
| GDP | US$2.5 billion in 2021, US$2.95 billion in 2022, US$3.1 billion in 2023 |
| Economic sectors | Tourism, agriculture, energy, services |
| Primary exports | Citrus, sugar, bananas |
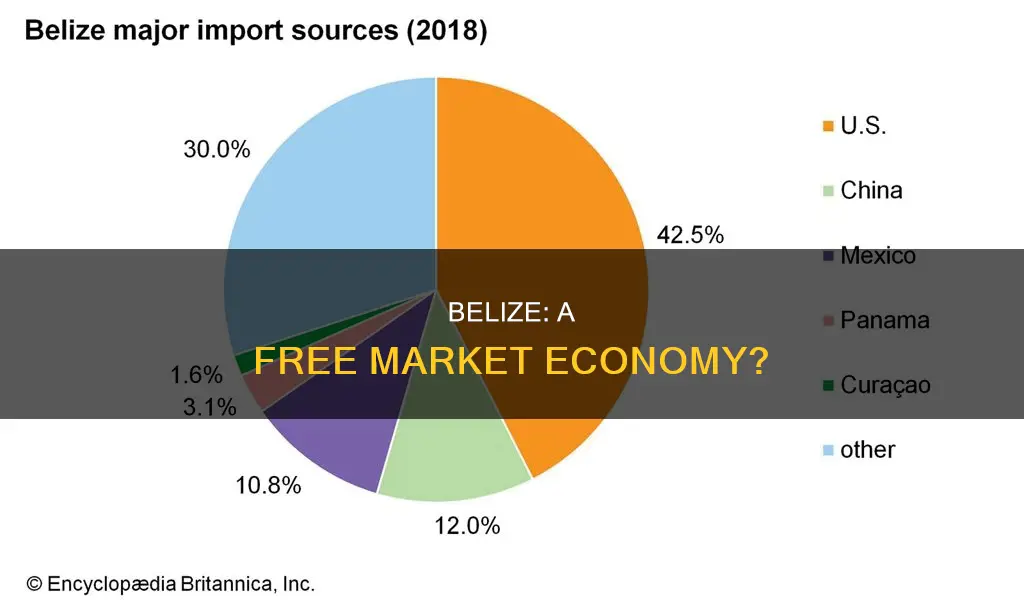
| Primary imports | Refined petroleum, rolled tobacco, recreational boats, passenger and cargo ships, ethers |
| Main import partners | United States, Mexico, China, Guatemala, Japan |
| Population | 397,483 (2022) |
| Land area | 22,970 sq km (8,867 sq mi) |
| Official language | English |
What You'll Learn
- Belize's economy is based on tourism, agriculture, energy and services
- Belize's economy is vulnerable to external shocks and climate-related disasters
- Belize's economy is susceptible to fluctuations in world commodity prices
- Belize's economy is characterised by progressive development strategies and a business-friendly environment
- Belize's economy is supported by foreign direct investment

Belize's economy is based on tourism, agriculture, energy and services
Belize has a developing free-market economy. The country's economy is largely based on tourism, agriculture, energy, and services.
Tourism
Tourism is a major source of foreign income for Belize, with the industry expanding rapidly in the 1990s. The number of visitors increased fivefold from the late 1990s to the mid-2000s. Popular tourist activities include fishing, boating, swimming, and diving along the Belize Barrier Reef, as well as exploring the country's Mayan ruins, such as Caracol, Xunantunich, El Pilar, and Cahal Pech. Ecotourism in the interior of the country has also grown in popularity.
Agriculture
Belize's agricultural sector employs about one-fifth of the population, although only a small proportion of the land is actively used for this purpose. Most farms are smaller than 100 acres (40 hectares) and practice traditional shifting cultivation due to the nutrient-poor soils of the lowlands. The main crops grown for export include sugarcane, citrus fruits, and bananas. Sugarcane is primarily grown around the towns of Corozal and Orange Walk, with some of it being converted into molasses for rum distillation. Citrus crops, such as oranges and grapefruit, and bananas are mainly grown in the Stann Creek and Cayo areas. Rice is cultivated on large mechanized farms in the Belize River valley, while corn, roots, tubers, red kidney beans, and vegetables are grown throughout the country on smaller plots. Large-scale chicken farming was introduced by the Mennonite community, and beef cattle and pigs are raised in many parts of the country.
Energy
Belize has invested in domestically produced energy over the last 20 years to strengthen and stabilize its energy sector. The country has focused on developing sustainable energy project policies, including expanding biomass power and solar-based distributed power systems. The government is eager to enhance its energy sustainability and become a net exporter of energy to neighbouring countries. Belize has invested in hydropower, biomass, solar, and liquified petroleum gas (LPG). However, Belize remains a net importer of electricity from Mexico, which makes energy imports expensive and unpredictable. The government has also launched initiatives to promote the use of electric vehicles and is working to upgrade electrical productivity and operational efficiency.
Services
The service sector of the economy has accounted for the largest share of the gross national product (GNP) since the early 1980s. Nearly half of the labour force and the GNP are sustained by services. The Central Bank of Belize oversees the country's banks and issues the country's currency, the Belize dollar.
Belize Border Closure: What's Happening?
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is vulnerable to external shocks and climate-related disasters
Belize has a developing free-market economy, with a focus on tourism, agriculture, and services. However, Belize's economy is vulnerable to external shocks and climate-related disasters. The country is highly susceptible to natural disasters and climate change, ranking 8th out of 167 countries for climate risk. It faces hurricanes, flooding, sea level rise, coastal erosion, coral bleaching, and droughts. These issues are expected to intensify due to increasing weather volatility and rising sea temperatures.
Belize's low-lying terrain exacerbates the impacts of flooding and sea level rise, and the country is also at risk of extreme temperature events. The effects of these climate-related disasters are far-reaching, impacting various sectors of the economy. For example, agriculture, which employs about one-fifth of Belize's population, is vulnerable to crop damage and decreased productivity. This, in turn, can lead to food shortages and increased prices, affecting both local populations and export revenues.
The country's infrastructure is also at risk, with ports, roads, and communication networks potentially being damaged or disrupted by extreme weather events. This can hinder transportation and trade, further affecting the economy. Additionally, the destruction of forests and natural resources can have long-term consequences for the environment and industries such as forestry and agriculture.
Belize has recognized the importance of building resilience and has been actively engaged in policymaking to address these challenges. The country submitted its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) to the Paris Accord in 2015, demonstrating its commitment to climate action. The Climate Change Policy Assessment (CCPA), a joint initiative by the IMF and World Bank, also assists Belize in understanding and managing the economic impact of climate change.
However, despite these efforts, Belize's economy remains vulnerable to external shocks. The country's small size and limited domestic industry make it susceptible to fluctuations in global markets. For example, the manufacturing industry has been declining due to increasing utility costs, and the country has a substantial trade deficit. Additionally, global inflationary trends and events such as Russia's invasion of Ukraine have further widened the current account deficit and impacted the country's economy.
In conclusion, while Belize has a developing free-market economy, it remains vulnerable to external shocks and climate-related disasters. The country is taking steps to build resilience and address the challenges posed by climate change, but the impacts on various economic sectors, infrastructure, and natural resources are significant. Continued efforts and international support are necessary to enhance Belize's resilience and mitigate the effects of these external shocks and disasters.
Belize City to Caracol: A Journey Through Time and Space
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is susceptible to fluctuations in world commodity prices
Belize has a developing free-market economy, which is highly susceptible to fluctuations in world commodity prices. The country's economy is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and services. Citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas are the primary exports, but low export prices for these commodities have contributed to the country's growing trade deficit.
Belize's economic performance is vulnerable to changes in external markets, particularly fluctuations in world commodity prices. The country's heavy reliance on foreign trade, especially with the United States as its main trading partner, makes it susceptible to global economic shifts. While tourism, agriculture, and services are the main drivers of the economy, fluctuations in commodity prices can impact the country's ability to maintain economic growth and stability.
Citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas are the primary agricultural exports of Belize. However, these commodities are susceptible to price fluctuations in the global market. For example, citrus crops, such as oranges and grapefruit, and bananas produced in Belize have experienced the impact of varying global prices. While these commodities remain important exports, the country has also started producing non-traditional agricultural products like papayas and habanero peppers to diversify its economic activities.
The country's economic achievements are vulnerable to changes in world commodity prices. For instance, the production and export of sugar and bananas are dependent on preferential trading agreements with the United States and the United Kingdom, respectively. Any fluctuations in global prices for these commodities can affect the profitability and viability of these industries in Belize.
Additionally, Belize's manufacturing industry, which includes food manufacturing, has been declining due to high utility costs. This decline further exposes the country's economy to the impact of world commodity price fluctuations. When global prices for commodities rise, it can increase production costs for manufacturers, making it challenging to maintain profitability, especially in industries with thin profit margins.
In summary, Belize's economy is susceptible to fluctuations in world commodity prices due to its reliance on a few primary exports, such as citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas, and its exposure to external market changes. The country's economic achievements and stability are closely tied to global commodity prices, highlighting the need for economic diversification and resilience to external factors.
Belize's Tour Guide Salary Secrets Unveiled
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is characterised by progressive development strategies and a business-friendly environment
Belize's business-friendly environment is reflected in its low tax rates, ease of registration, and confidentiality for foreign investors. The typical tax rate for a standard trading business is only 1.75%pure equity holding companies can enjoy a 0% tax rate. The country also offers stable democracy, peace, and a diversified national economy.
Belize's progressive development strategies are evident in its commitment to sustainable development and long-term planning. The country has adopted the "Growth and Sustainable Development Strategy (GSDS) 2016-2019", which aims to bring economic, social, and environmental policies into balance. This strategy builds on the "Horizon 2030: National Development Framework for Belize 2010-2030", which guides the country's long-term development planning. Belize is also committed to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, with a focus on gender equality and life below water.
The country's development strategies also include efforts to improve productivity and competitiveness, attract foreign investment, and support priority sectors such as agriculture, agro-processing, tourism, and energy. Additionally, Belize seeks to improve access to development financing and promote the use of green technologies and sustainable economy innovations.
In summary, Belize's economy is characterised by progressive development strategies that prioritise sustainability, social equity, and economic growth. The country also offers a business-friendly environment with low taxes and efficient registration processes, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment.
Belize's Import Economy: A Gateway to Central America
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is supported by foreign direct investment
Belize has a small, developing, free-market economy that is highly dependent on foreign trade, particularly with the United States, its number one trading partner. The country's economy is based primarily on tourism, agriculture, and services, with international tourism accounting for approximately 40% of the country's economic activity.
Belize has a history of stable democratic government and peaceful transitions of power, and its political parties are generally centre-left and centre-right, with similar views on trade, economics, and development. The government encourages foreign direct investment (FDI) to relieve fiscal pressure and diversify the economy, and sectors that have traditionally attracted investment include tourism, business processing outsourcing, agriculture, telecommunications, and renewable energy.
Belize's economy is susceptible to external market changes and vulnerable to exogenous shocks, such as the global health crisis and economic downturns in the US. The country's small population, high cost of doing business, high public debt, bureaucratic delays, insufficient infrastructure, and corruption pose challenges to investment. However, its regionally high per capita GDP, political and currency stability, bilingual population, and developing infrastructure provide some investment opportunities.
In recent years, Belize has experienced a surge in international tourism, with revenues surpassing pre-COVID levels and annual cruise and overnight arrivals nearing 1 million visitors in 2022. The country's agricultural and seafood exports have also increased, driven by the removal of trade barriers and regional partnerships, particularly with Mexico.
To promote economic growth and social programs, the government has implemented various strategies, such as the National Investment Policy and Strategy (NIPS) and the Micro, Small, Medium Enterprise (MSME) Strategy, and has passed a credit reporting act to increase the availability of financing for MSMEs. Additionally, the government is working on establishing a credit bureau and collateral registry, and several digitalization projects are underway as part of its e-governance agenda.
While Belize faces challenges such as a fragile banking system, high lending rates, and inflationary pressures, its economy is supported by foreign direct investment, particularly in the tourism, energy, telecommunications, and agricultural sectors. The country's stable political environment, qualified workforce, and preferential trade agreements make it an attractive market for foreign investment, and the government's commitment to economic development and transparency is expected to contribute to a positive investment climate.
Belize Border Entry and Exit Protocols: A Guide to Smoothly Navigating In and Out of the Country
You may want to see also







