Belize is a small country in Central America with a population of around 400,000 people. It has a developing free-market economy, with a focus on private enterprise, agriculture, tourism, and services. While it has a social security safety net, maternity leave, and some social programs, Belize's economy is largely driven by private enterprise. Its economic system has been described as a hybrid of capitalism and a free market, with some government regulation. In this paragraph, we will explore the extent to which Belize can be considered a capitalistic country and examine the characteristics of its economic system.
What You'll Learn

Belize's economy is a hybrid of capitalism and free market
Belize's economy is a hybrid of capitalism and a free market. It is a developing, small, and private enterprise economy, based primarily on agriculture, tourism, and services. Belize's economic system is similar to that of the US, with a free market and capitalistic economic system.
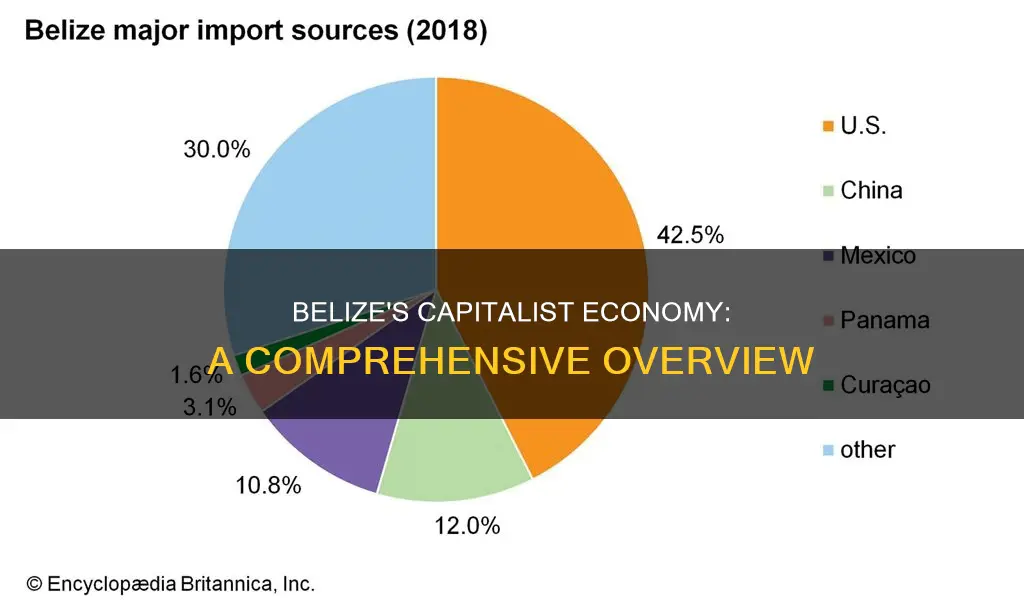
Belize's economy is driven mainly by private enterprise, with a social security safety net for the unemployed, maternity leave, and a few social programs. The government regulates business and gets involved in economic planning. The economy is also import-driven, relying heavily on foreign trade, particularly with the US, which is its biggest trading partner.
Belize's economy is susceptible to external market changes and vulnerable to fluctuations in world commodity prices. The country has a trade deficit, largely due to low export prices for sugar and bananas, its primary exports.
Belize's economic activities include agriculture, forestry, fishing, manufacturing, and services. The service sector, including tourism, has been the largest contributor to the country's GNP since the 1980s.
Belize's agricultural sector employs about one-fifth of the population and includes crops such as sugarcane, citrus fruits, bananas, corn, beans, and vegetables. The country also has a small manufacturing sector, producing food products, fertilizers, textiles, footwear, rum, beer, and cigarettes.
The government has attempted to expand the economy, but heavy borrowing led to debt restructuring in the mid-2000s. The discovery of oil presents new prospects and challenges for the economy.
Golfing in Corozal, Belize: A Tropical Paradise for Golf Enthusiasts
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is driven by private enterprise
Belize's private sector is largely driven by exports, including petroleum, crude oil, sugar, bananas, citrus fruits, seafood, apparel, and agro-based industry. The country's primary exports are citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas, with sugar accounting for nearly half of exports, and the banana industry being the largest employer. Belize's economy is also heavily dependent on sugarcane, with other agricultural products including orange, maize, papaya, rice, and soy.
Tourism is another key driver of Belize's economy, with the country's natural attractions, including the Belize Barrier Reef, offshore islands, jungle flora and fauna, and Mayan ruins, supporting a thriving tourism and ecotourism industry. In 2011, tourist arrivals totaled 888,191, with tourist receipts amounting to $260 million. The travel and tourism industry directly contributed 350.6 million BZD (176 million USD) to Belize's GDP, accounting for 12.0% of GDP. When including indirect and induced effects, the industry contributed 971.9 million BZD (486 million USD) to GDP, or 33.2%.
Belize also has a strong financial services sector, with a community of accounting and law firms, as well as international banks catering to international clients. The country is considered a tax haven, with favourable legislation for offshore companies and investments.
The Belize Chamber of Commerce and Industry (BCCI) is the largest private-sector membership-based organisation in the country, with over 300 Belizean businesses across various sectors as members. The BCCI aims to foster the economic growth and social well-being of the nation through the free enterprise system.
Belize Jungle: Survival Tips for the Wild Adventure
You may want to see also

Belize is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
Belize joined CARICOM on 1 May 1974, three years before it gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1977. As a member of CARICOM, Belize is part of a regional single market (Caricom Single Market) and benefits from the coordination of economic policies and development planning. CARICOM also devises and implements special projects for the less-developed countries within its jurisdiction. Belize is designated as a Less Developed Country (LDC) within CARICOM.
Belize's economy is small and primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and services. As a member of CARICOM, Belize has access to preferential trade agreements with other member states, such as the Caribbean Basin Initiative (CBI) with the United States, which provides duty-free access to the U.S. market for most Caribbean products. Belize also benefits from significant foreign investment in the tourism, energy, telecommunications, and agricultural sectors through its membership in CARICOM.
In addition to economic integration, CARICOM also promotes cultural exchange among its members. The Caribbean Festival of Arts (CARIFESTA), a roving multidisciplinary art festival, has been held in various CARICOM countries since its establishment in 1972. It provides a platform for artists, performers, and cultural practitioners to meet and exchange ideas, fostering a sense of Caribbean unity.
Belizean Treasures: Authentic Souvenirs to Seek Out
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is susceptible to external market changes
Belize's economy is heavily dependent on foreign trade, with the US as its top trading partner, followed by the European Union, Canada, Mexico, and other Caribbean Community (CARICOM) member states. The country's primary exports are citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas, which are susceptible to changes in global demand and pricing. For instance, the trade deficit has been growing due to low export prices for sugar and bananas. Additionally, Belize's economy is influenced by its history of dependence on forestry and the mahogany industry, which experienced ups and downs that significantly impacted the economy.
The country's economic stability is also tied to tourism, which attracts the most foreign direct investment. A decrease in tourism, such as during the COVID-19 pandemic, can have a significant impact on Belize's economy. The service sector, including tourism, has been the largest contributor to the country's gross national product since the early 1980s.
Belize's economy is also influenced by its energy sector, with high-cost labour and energy constraints impacting domestic industry. The discovery and cultivation of oil present new opportunities, but also challenges, for the country's economic development.
Overall, Belize's small and diverse economy makes it susceptible to external market changes, and its economic performance is closely tied to global commodity prices, trading agreements, and the stability of its key industries, such as agriculture and tourism.
Belize's Gas Sources: Origins and Impact
You may want to see also

Belize's economy is developing
Belize's economy is primarily driven by agriculture, tourism, and services, with the country's natural resources providing a key foundation. The country has a diverse range of ecosystems, including extensive coral reefs, terrestrial and marine plants and animals, and various types of forests. Belize's economic activities are closely tied to these natural resources, with agriculture and agro-based industries playing a significant role.
Belize's agricultural sector includes the cultivation of crops such as sugarcane, citrus fruits, bananas, corn, beans, and vegetables. The country also has a history of logging and timber production, although this has declined due to deforestation and price fluctuations. Belize's agricultural exports include citrus fruits, sugar, and bananas, which have traditionally been the country's primary exports. However, the country has been diversifying its agricultural products, with non-traditional crops like papaya and habanero peppers gaining importance.
In addition to agriculture, tourism is a significant contributor to Belize's economy and a major source of foreign income. The country's natural attractions, such as its reefs, islands, diverse flora and fauna, and Mayan ruins, draw visitors from around the world. Ecotourism, in particular, has been growing in popularity.
Belize's economy also includes manufacturing, which accounts for about one-eighth of the gross national product (GNP). The manufacturing sector focuses on food products, fertilizers, and textiles, with import substitution playing a role in its development.
While Belize's economy has faced challenges, such as a trade deficit and fluctuations in export prices, the country has been working to expand and diversify its economic activities. The discovery of oil in Spanish Lookout has presented new opportunities and challenges for this developing nation. Overall, Belize's economy is in a state of development, with a mix of traditional and non-traditional industries, a growing focus on tourism, and ongoing efforts to attract foreign investment.
Belize's Currency: The Belize Dollar
You may want to see also







