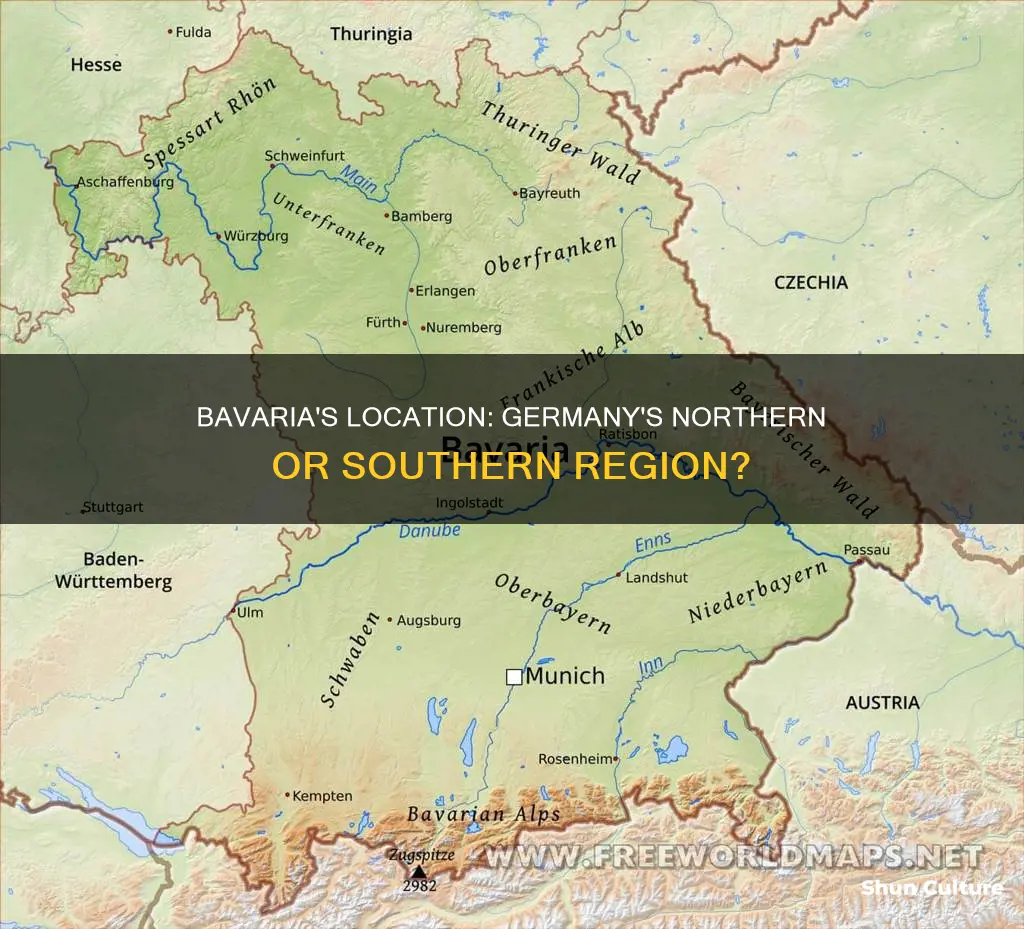
Bavaria, or Bayern in German, is the largest state in Germany, located in the southeast of the country. It borders the Czech Republic to the east, Austria to the south, and Switzerland to the west. It is known for its distinct culture, largely due to its Catholic heritage and conservative traditions, including its language, cuisine, architecture, and festivals.
Bavaria is divided into several regions, including Franconia in the north, Bavarian-Swabia in the southwest, and Upper Bavaria, home to the state's capital, Munich. The state is known for its natural beauty, including the Bavarian Alps, the Bavarian Forest, and the Danube River.
Bavaria has a rich history, having been settled by Iron Age Celtic tribes and later conquered by the Roman Empire. It became the independent Kingdom of Bavaria in 1806 and joined the Prussian-led German Empire in 1871. Today, it is a federal state within the Federal Republic of Germany, with a strong economy and a unique cultural identity.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast of Germany |
| Population | 12,397,614 (2011); 12,843,514 (2015); 13.1 million (2020) |
| Area | 70,550 km²; 27,240 sq mi |
| Capital | Munich |
| Other Cities | Nuremberg, Augsburg, Regensburg, Würzburg, Ingolstadt, Bamberg, Bayreuth, Erlangen, Fürth, Passau, and Rothenburg ob der Tauber |
| Religion | 46.9% Catholic; 17.2% Evangelical Lutheran; 3% Orthodox; 4% Muslim; 31.9% Irreligious or other |
| Economy | Car industry, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, foods, tourism |
| Agriculture | Dairy products, cheese, meat, sugar, beer, hops |
| Natural Resources | Sand, gravel, natural stone, clay, silica sand, kaolin |
| Landscape | Bavarian Alps, Bavarian Alpine Foreland, Eastern Bavarian central mountains, Swabia and Frankenalb plateaus |
| Borders | Austria, Czech Republic, Switzerland, Baden-Württemberg, Hesse, Thuringia, Saxony |
| Administrative Regions | Upper Palatinate, Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria, Upper Franconia, Middle Franconia, Lower Franconia, Bavarian Swabia |
| Rivers | Danube, Main |
| Lakes | Chiemsee, Ammersee |
What You'll Learn

Bavaria is the largest state in Germany by land area
Bavaria is located in the southeast of Germany, extending from the North German Plain to the Alps in the south. It borders the German states of Thuringia and Saxony to the north, Baden-Württemberg and Hesse to the west, and Saxony to the northeast. To the east, it shares borders with the Czech Republic and Austria to the south and southwest, and Switzerland to the south, along Lake Constance.
Bavaria is divided into seven administrative regions, or Regierungsbezirke: Upper Palatinate, Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria, Upper Franconia, Middle Franconia, Lower Franconia, and Swabia. The state is further divided into 71 rural districts, or Landkreise, and 25 independent cities, or Kreisfreie Städte.
The capital of Bavaria is Munich, which is also the state's largest city and the third-largest city in Germany. Other major cities in Bavaria include Nuremberg, Augsburg, Regensburg, and Würzburg.
Bavaria has a rich history, dating back to the 6th century AD when it became the Duchy of Bavaria. Over the centuries, it has been ruled by various dynasties, including the Welfs and the Wittelsbachs. After World War I, Bavaria became a free state and has since enjoyed a period of democracy, peace, and prosperity.
The state is known for its distinct culture, largely influenced by its Catholic heritage and conservative traditions. It is also known for its picturesque landscapes, including the Bavarian Alps, the Bavarian Forest, and numerous lakes and rivers.
Bavaria has a strong economy, with a GDP of €832.4 billion in 2019, making it one of the wealthiest regions in Europe. The state has a diverse range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and food and beverage.
Bavaria is also a popular tourist destination, attracting over 40 million visitors in 2019. Popular attractions include the Neuschwanstein Castle, the Oktoberfest beer festival in Munich, and the historic cities of Nuremberg and Regensburg.
Bavarian Pretzels: The Ultimate Recipe and Guide
You may want to see also

It is in the southeast of Germany
Bavaria is in the southeast of Germany. It is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the country. It borders the German states of Thuringia, Saxony, Baden-Württemberg, and Hesse, and shares international borders with Austria, the Czech Republic, and Switzerland.
The landscape of Bavaria is divided into four major regions: the Bavarian Alps, the Bavarian Alpine Foreland, the Eastern Bavarian central mountains, and the plateaus of Swabia and Frankenalb (Jura). The Bavarian Alps include Germany's highest mountain, the Zugspitze, which rises to 2,962 metres (9,718 feet). The Alpine Foreland is known for its numerous lakes, while the Eastern Bavarian central mountains are a wooded low-mountain region home to Germany's first national park, the Bavarian Forest National Park. The western plateaus of Swabia and Frankenalb include the Allgäu, Germany's leading cheese and butter-producing region.
Bavaria is divided into seven administrative regions: Upper Franconia, Middle Franconia, Lower Franconia, Bavarian Swabia, Upper Palatinate, Upper Bavaria, and Lower Bavaria. Munich, Bavaria's capital and Germany's third-largest city, is located in Upper Bavaria. Other major cities in Bavaria include Nuremberg, Augsburg, Regensburg, and Würzburg.
Bavaria has a distinct culture, largely due to its Catholic heritage and conservative traditions. The state also has a booming economy and is home to several internationally recognised companies, including BMW, Adidas, Siemens, and Audi.
Bavaria has a rich history, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Paleolithic era. The region was settled by Iron Age Celtic tribes and later conquered by the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC. It became the Duchy of Bavaria in the 6th century AD and was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire. Bavaria became an independent kingdom in 1806, joined the Prussian-led German Empire in 1871, and finally became a state of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949.
Today, Bavaria is a popular tourist destination, known for its stunning natural scenery, picturesque villages, and vibrant cities. It offers a range of attractions, from the famous Neuschwanstein Castle to the lively Oktoberfest celebration in Munich.
Bavarian Inn Waterpark: Opening Dates and Attractions
You may want to see also

It borders Austria, Switzerland, the Czech Republic, Baden-Württemberg, Hesse, Thuringia, and Saxony
Bavaria shares borders with several neighbouring countries and German states.
Bavaria's international borders include Austria to the south and southeast, Switzerland to the south, and the Czech Republic to the east. It also shares borders with several German states: Baden-Württemberg and Hesse to the west, Thuringia to the north, and Saxony to the northeast.
Bavaria is Germany's largest state by land area, and it comprises roughly a fifth of the country's total land area. It is located in the southeast of the country and extends from the North German Plain to the Alps in the south.
The landscape of Bavaria varies from high plateaus and medium-sized mountains in the south to basalt knolls and high plateaus in the north. The northwest of the state is drained by the Main River, which flows into the Rhine. The Danube, another major river, divides Bavaria north and south.
Bavaria's capital, Munich, is Germany's third-largest city and is located in the south of the state, beyond a plateau in the Bavarian Alps.
Bavarian Cream King Cake: A Step-by-Step Guide to Making It
You may want to see also

The capital is Munich, which is Germany's third-largest city
Munich is the capital of Bavaria, Germany, and the state's most populous city. With a population of 1,594,632 as of May 2024, it is Germany's third-largest city, after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that does not constitute its own state.
Munich is the capital of the Free State of Bavaria and the seat of the Bavarian administrative region of Upper Bavaria. It is the second-largest city in the Bavarian dialect area, after the Austrian capital of Vienna. Munich straddles the banks of the river Isar, north of the Alps, and is the most densely populated municipality in Germany, with 4,500 people per square kilometre.
Munich was first mentioned in 1158. In 1175, it received city status and fortification. In 1255, when the Duchy of Bavaria was split in two, Munich became the ducal residence of Upper Bavaria. In 1314, Duke Louis IV, a native of Munich, was elected German king. He was later crowned Holy Roman Emperor in 1328.
Munich is a global centre of science, technology, finance, innovation, business, and tourism. It enjoys a very high standard and quality of living and is consistently ranked as one of the most expensive cities in Germany in terms of real estate prices and rental costs. Munich has one of the strongest economies of any German city and the lowest unemployment rate of all cities in Germany with more than one million inhabitants.
Munich is home to many multinational companies, including BMW, Siemens, Allianz, and Munich Re. It also has two research universities and a multitude of scientific institutions.
Munich is famous for its annual Oktoberfest, the world's largest Volksfest, which attracts considerable tourism.
How to Prepare Bavarian Kraut: To Rinse or Not?
You may want to see also

It is divided into seven administrative regions
Bavaria is divided into seven administrative regions called Regierungsbezirke (singular Regierungsbezirk). Each of these regions has a state agency called the Bezirksregierung (district government). The seven administrative districts in Bavaria are:
- Upper Palatinate (German: Oberpfalz), with its seat of district government in Regensburg
- Upper Bavaria (Oberbayern), with its seat of district government in Munich, the capital of Bavaria
- Lower Bavaria (Niederbayern), with its seat of district government in Landshut
- Upper Franconia (Oberfranken), with its seat of district government in Bayreuth
- Middle Franconia (Mittelfranken), with its seat of district government in Ansbach
- Lower Franconia (Unterfranken), with its seat of district government in Würzburg
- Swabia (Schwaben), with its seat of district government in Augsburg
Bavarian Mountains: How Close to Switzerland?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Bavaria is in the south-east of Germany.
Munich (München) is the capital of Bavaria.
Some major cities in Bavaria include Nuremberg, Augsburg, and Regensburg.
Some attractions in Bavaria include the Neuschwanstein Castle, the Oktoberfest beer festival, and the Bavarian Alps.
Bavaria has a rich cultural heritage, including traditional costumes such as Lederhosen, and a variety of food and drinks such as sausages and beer. Bavarians also value their natural surroundings and have a slower pace of life, with many shops and businesses closed on Sundays.







