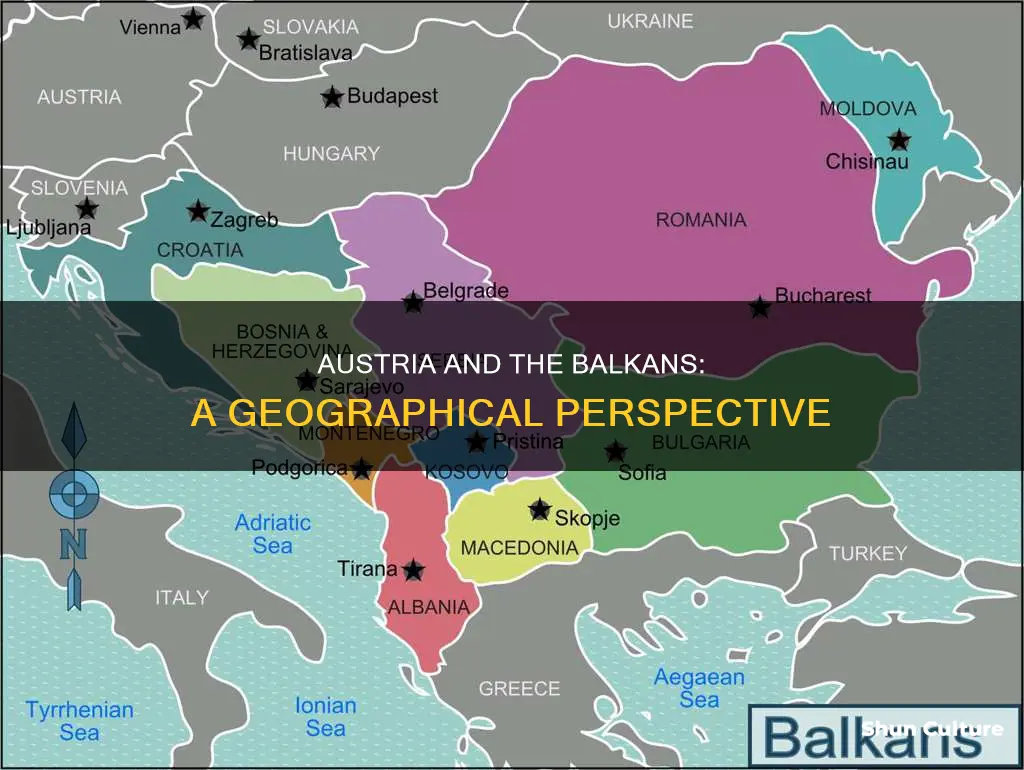
The Balkans is a diverse region in southeastern Europe with a rich and complicated history. While there is no universal agreement on what constitutes the Balkans, it generally includes the countries of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and Slovenia. Portions of Greece and Turkey are also within the Balkan Peninsula, and some definitions include all of these countries. Austria, while not in the Balkans, has strong historical, economic, and cultural ties to the region and is one of the biggest sources of foreign investment in Southeast Europe.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Is Austria in the Balkans? | No |
| Countries in the Balkans | Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Greece, and Turkey |
| Alternative names for the Balkans | Balkan Peninsula, Balkan States, South East Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe, South-East Europe, South-Eastern Europe |
What You'll Learn
- Austria is not in the Balkans but is closely linked to the region through historic, economic and cultural ties
- The Balkans is a diverse region with a complicated history and varying definitions
- The region is bordered by the Adriatic, Ionian, Aegean and Black Sea
- The term 'Balkans' was coined by German geographer August Zeune in 1808
- The Balkans is dominated by mountain ranges, including the Carpathian, Dinaric, Balkan and Pindus Mountains

Austria is not in the Balkans but is closely linked to the region through historic, economic and cultural ties
Austria is not in the Balkans, but it is closely linked to the region through historic, economic, and cultural ties. More than half a million Austrians have roots in Southeast Europe, and Austria is among the biggest sources of foreign investment in the region.
Austria's foremost foreign policy objective in Southeast Europe is to implement a clear EU accession perspective. The country actively supports the efforts of six countries in the region that are not yet members of the European Union: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and Serbia. These countries are often collectively referred to as the "Western Balkans." Austria participates in initiatives such as the Berlin Process and the Regional Cooperation Council to facilitate regional cooperation and encourage these countries' inclusion in the EU's comprehensive model of integration.
Austria also has strong historical and cultural ties with Romania, which lies north of the Danube River and is not part of the Balkan Peninsula but is often included in discussions of the Balkans due to its historical and cultural connections with the region.
Additionally, Austria has played a significant role in the stabilization and association agreements between the EU and several Balkan countries, including Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and Serbia. These agreements aim to strengthen the political, economic, and cultural ties between the EU and these Balkan nations.
In summary, while Austria is not geographically located in the Balkans, it has a close relationship with the region due to shared history, economic ties, and cultural connections. The country actively supports the integration of several Balkan countries into the European Union and has played a role in regional cooperation initiatives.
The Austria-Hungary Empire: Mapping a Complex Legacy
You may want to see also

The Balkans is a diverse region with a complicated history and varying definitions
The Balkans is a region in southeastern Europe with a complicated history and varying definitions. The term "The Balkans" is derived from the Balkan Mountains, which stretch throughout Bulgaria and were once thought to be the dominant mountain system in Southeast Europe. The region encompasses all or parts of several countries, including Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, and Turkey. The borders of the Balkans are disputed due to contrasting definitions, and there is no universal agreement on which countries are included.
Historically, the Balkans have been a diverse region with a rich and complex past. It has served as a crossroads of civilizations and cultures, including the Latin and Greek bodies of the Roman Empire, pagan Bulgars and Slavs, Orthodox and Catholic Christianity, and Islam and Christianity. The region has also been influenced by various empires, such as the Byzantine and Ottoman Empires, which have left their mark on the cultural, religious, and political landscape of the Balkans.
The Balkans have a long history of ethnic and religious diversity, with South Slavs forming the majority in several countries. However, the region has also been marked by conflict and division, with frequent wars and political upheaval. The term "Balkanization" has acquired a negative connotation, referring to the fragmentation and ethnic divisiveness associated with the region's history.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards using the term "Southeast Europe" or "South East Europe" to describe the region, as it is seen as less stigmatized and carries fewer negative connotations. Additionally, the term "Western Balkans" has been coined to refer specifically to Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Kosovo, North Macedonia, and Serbia.
Austria and Ukraine: How Close Are They Geographically?
You may want to see also

The region is bordered by the Adriatic, Ionian, Aegean and Black Sea
The region in question is the Balkan Peninsula, which is bordered by the Adriatic, Ionian, Aegean and Black Sea. The peninsula is geographically located in southeastern Europe and is partially synonymous with the Balkan Mountains, which stretch throughout Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is surrounded by the Adriatic Sea to the northwest, the Ionian Sea to the southwest, the Aegean Sea to the south, the Turkish Straits to the east, and the Black Sea to the northeast.
The Balkan Peninsula is a diverse region with a rich history and culture. It is home to various ethnic and religious groups, including Albanians, Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Greeks, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Romanians, Serbs, and Slovenes, among others. The region has been influenced by different civilizations, including the Ottoman Empire, Byzantine Empire, and various Slavic and Romance language groups.
The Balkan Peninsula has a complex history that has shaped its current borders and cultural identity. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was first introduced by German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly believed the Balkan Mountains were the dominant mountain range in Southeast Europe. The borders of the peninsula have been a subject of debate, with geographers and politicians dividing it in various ways due to its complicated history.
The Balkan Peninsula is known for its diverse landscapes, including mountain ranges such as the Carpathian Mountains, Dinaric Mountains, Balkan Mountains, and Pindus Mountains. The region's climate varies, with northern areas experiencing weather similar to central Europe, while southern and coastal areas have a more Mediterranean climate with hot, dry summers and rainy winters.
The Balkan Peninsula is rich in natural resources and has a diverse ecosystem. The area is home to various plant and animal species, including endemic flora and fauna found only in this region. The surrounding seas also support a variety of marine life, with common bottlenose dolphins, harbour porpoises, and monk seals being some of the marine mammals found in these waters.
The region's economy is diverse, with fisheries, tourism, maritime transport, and hydrocarbon exploration being significant contributors. The Balkan Peninsula has a complex and fascinating history, culture, and natural environment that makes it a unique and captivating part of Europe.
Austria and Germany: Two Nations, One History
You may want to see also

The term 'Balkans' was coined by German geographer August Zeune in 1808
Zeune mistakenly believed the Balkan Mountain range to be the dominant mountain system in Southeast Europe, spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. In reality, the Balkan Mountains are confined to Bulgaria.
The term 'Balkan Peninsula' was a synonym for Rumelia in the 19th century, referring to the provinces of the Ottoman Empire at the time. The term acquired geopolitical significance during the creation of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the early 20th century.
The term 'Balkans' has since acquired a stigmatized and pejorative meaning, often associated with the process of Balkanization. Due to its historical and political connotations, the term Southeast Europe is increasingly used in its place.
Skiing in Hallstatt: A Winter Adventure in Austria
You may want to see also

The Balkans is dominated by mountain ranges, including the Carpathian, Dinaric, Balkan and Pindus Mountains
The Balkans, a region in southeastern Europe, is dominated by mountain ranges, including the Carpathian Mountains, the Dinaric Alps, the Balkan Mountains, and the Pindus Mountains. These mountain ranges significantly influence the region's climate and biodiversity, making it a unique and vibrant destination.
The Carpathian Mountains, located in northern Romania, are part of the larger Alp-Himalayan chain that stretches across most of Eurasia. This mountain range is known for its diverse flora and fauna, including important species such as the brown bear, wolf, boar, chamois, and deer.
The Dinaric Alps, or Dinaric Mountains, extend along the Adriatic coastline, starting from the Julian Alps in the north and running in a southeasterly direction through Albania and Greece. This mountain range is known for its rugged terrain and provides a diverse landscape of crystal-clear lakes, rivers, and historical sites.
The Balkan Mountains, also known as Stara Planina in Bulgarian and Serbian, stretch across Bulgaria and form a natural barrier between the northern and southern halves of the country. These mountains are the source of the name "Balkans" and reach their highest point at Botev Peak, standing at 2,376 meters (7,795 feet).
The Pindus Mountains, located in Greece, are part of the larger Pindus range that spans southern Albania and central Greece. This mountain range is home to diverse wildlife and includes notable peaks such as Smolikas Mountain and Mount Parnassus.
Together, these mountain ranges not only shape the geography of the Balkans but also contribute to its rich history and cultural diversity. They have served as natural borders, fortresses, and trade routes throughout the region's complex past.
Texting Austria from Australia: A Guide to International Messaging
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Balkan region, also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region is bordered by the Adriatic Sea to the northwest, the Ionian Sea to the southwest, the Aegean Sea to the south, the Turkish Straits to the east, and the Black Sea to the northeast.
The term "Balkan" is derived from the Turkish word for "mountain", and the region is indeed dominated by mountain ranges such as the Carpathian Mountains, the Dinaric Mountains, the Balkan Mountains, and the Pindus Mountains.
There is no universal agreement on what constitutes the Balkans, but the following are usually included: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and Slovenia. Portions of Greece and Turkey are also within the Balkan Peninsula and are sometimes included in the definition.
The Balkans have been a crossroads of various civilizations and cultures, contributing to their rich and complicated history. The region has been influenced by ancient empires such as the Byzantine and Ottoman, and it was the first area in Europe to experience the arrival of farming cultures in the Neolithic era. The Balkans were also a key theatre during World War I, with the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, serving as a catalyst for the conflict.
The Balkan Mountains have a significant impact on the region's climate. The northern and central parts of the Balkans have cold winters, warm summers, and well-distributed rainfall. In contrast, the southern and coastal areas have a Mediterranean climate with hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters.







