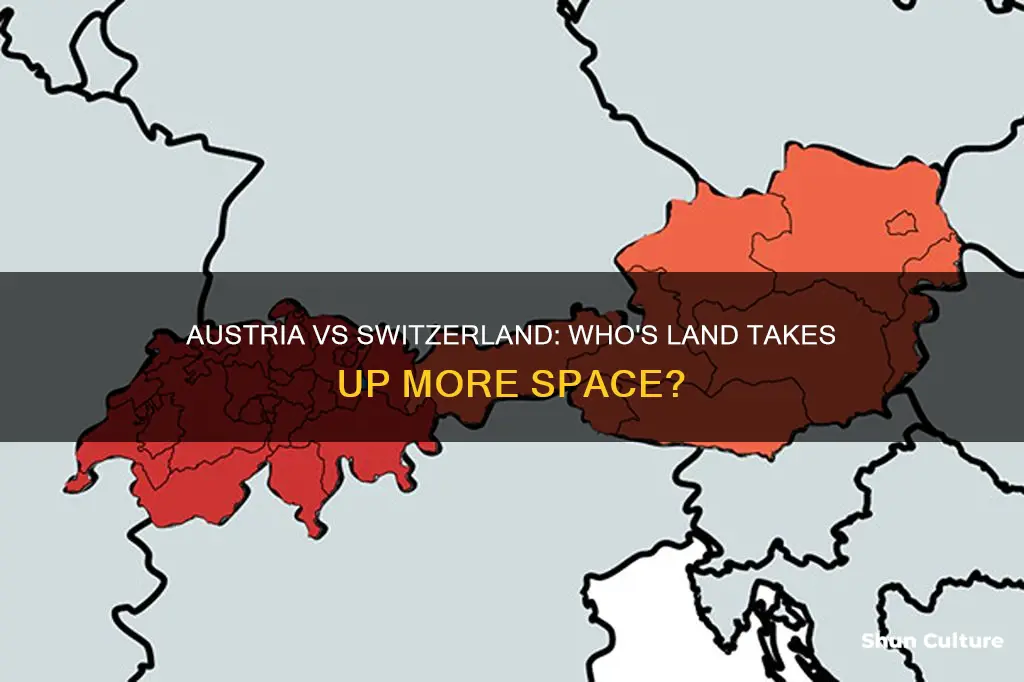
Austria and Switzerland are neighbouring countries with a lot in common, including similar populations of around 8.5 million people. However, Austria is significantly larger than Switzerland in terms of land mass. Austria measures approximately 83,871 sq km, while Switzerland is 41,277 sq km, making Austria about twice the size of Switzerland.
What You'll Learn

Population
Switzerland has a population of around 8.5 million people, while Austria's population is approximately 404,390 higher, at 8.9 million.
In 2020, the population distribution in Switzerland was as follows:
- 0-14 years: 15.34% (male 664,255/female 625,252)
- 15-24 years: 10.39% (male 446,196/female 426,708)
- 25-54 years: 42.05% (male 1,768,245/female 1,765,941)
- 55-64 years: 13.48% (male 569,717/female 563,482)
- 65 years and over: 18.73% (male 699,750/female 874,448)
In the same year, the population distribution in Austria was:
- 0-14 years: 14.01% (male 635,803/female 605,065)
- 15-24 years: 10.36% (male 466,921/female 451,248)
- 25-54 years: 41.35% (male 1,831,704/female 1,831,669)
- 55-64 years: 14.41% (male 635,342/female 641,389)
- 65 years and over: 19.87% (male 768,687/female 991,621)
The population growth rate in Switzerland is 10.41 births/1,000 population, while in Austria, it is slightly lower at 9.48 births/1,000 population. The death rate in Switzerland is 8.44/1,000 population, and in Austria, it is 9.85/1,000 population.
In terms of life expectancy, Switzerland has a higher life expectancy than Austria. As of 2021, the average life expectancy at birth in Switzerland is 83.03 years, while in Austria, it is 82.07 years. Breaking this down by gender, Swiss males have a life expectancy of 80.71 years, compared to 79.42 years for Austrian males. For females, the life expectancy is 85.49 years in Switzerland and 84.85 years in Austria.
The total fertility rate, or the number of children born per woman, is slightly higher in Switzerland, at 1.58 children born/woman, compared to 1.5 children born/woman in Austria.
Both countries have a similar urban population, with Switzerland's at 59% and Austria's at 66%.
In terms of major cities, Zurich is the most populous Swiss city, with 1.408 million people, while the capital, Bern, has a population of 434,000. Vienna, Austria's capital, has a population of 1.945 million people.
Austria's Royal Family: A Historical Overview
You may want to see also

Cost of living
Switzerland is approximately 41,277 sq km, while Austria is approximately 83,871 sq km, making Austria around twice the size of Switzerland. In addition to being physically larger, Austria also has a higher population, with around 404,390 more people living there than in Switzerland.
The cost of living in Switzerland is significantly higher than in Austria. Switzerland is 93.2% more expensive overall, with the average cost of living for one person being $2978 in Switzerland compared to $1840 in Austria.
- Restaurants: Switzerland is 65.4% more expensive.
- Groceries: Switzerland is 42.3% more expensive.
- Transportation: Switzerland is 75.8% more expensive.
- Housing: Switzerland is 52.1% more expensive.
- Childcare: Switzerland is 400% more expensive.
- Entertainment and sports: Switzerland is 66.5% more expensive.
- Clothing: Switzerland is 46.6% more expensive.
The average after-tax salary in Switzerland is enough to cover living expenses for 2.2 months, while in Austria, it is enough for 1.5 months. However, it is worth noting that Austria has a lower unemployment rate than Switzerland, by 2.3%.
Other Differences
There are several other notable differences between the two countries:
- Switzerland has a higher GDP per capita than Austria, with $71,000 compared to $51,936.
- Switzerland has 46.82% less public debt as a percentage of GDP, with 41.8% compared to Austria's 78.6%.
- Switzerland has a 67.06% lower inflation rate.
- Switzerland has a Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) score that is 10 points higher.
- Switzerland has a 40.67% higher real GDP growth rate.
- Switzerland spends 17.34% more on healthcare as a percentage of GDP, with 12.25% compared to Austria's 10.44%.
- Switzerland has 2.9 more hospital beds per 1,000 inhabitants.
- Switzerland has 21.23% more physicians per 1,000 people.
- Switzerland has a 5.5% higher percentage of GDP spent on education, with 5.5% compared to 5.1% in Austria.
- Switzerland has a 48.79% lower population density, with 106 people/km² compared to 207 people/km² in Austria.
- Switzerland has 54.55% fewer people living below the poverty line.
- Switzerland has a 2.9 lower Gini Index, indicating more equitable income distribution.
Austrian Airlines: Do They Serve Peanuts?
You may want to see also

Healthcare
Austria has a two-tier healthcare system, with publicly funded care available to all and the option to purchase supplementary private health insurance. Healthcare in Austria is universal for residents of Austria and those from other EU countries. Enrollment in the public healthcare system is generally automatic and linked to employment, but insurance is also guaranteed for spouses and dependents, pensioners, students, the disabled, and those receiving unemployment benefits. Enrollment is compulsory, and employers are responsible for registering their employees and deducting the health insurance tax from their salaries.
Austria has a relatively high density of hospitals and physicians. In 2011, there were 4.7 physicians per 1,000 people, which is slightly greater than the average for Europe. In-patient care is emphasized within the Austrian healthcare system, and the average hospital stay is 6.6 days, compared with an EU average of 6. The Austrian healthcare system is decentralized, with each of the nine states and the federal government having legal limitations and roles.
Switzerland also has universal healthcare, regulated by the Swiss Federal Law on Health Insurance. Private health insurance is compulsory for all persons residing in Switzerland, and all residents are required by federal law to purchase basic health insurance. The Swiss healthcare system is a combination of public, subsidized private, and totally private systems. Switzerland's healthcare costs are the second-highest in the world, and the country has the highest density of nurses among 27 countries measured by the OECD. Switzerland also has the highest rate of psychiatrists per population in the OECD.
Austria's Defiance: Resisting Nazi Germany's Annexation
You may want to see also

Language
Austria is about twice the size of Switzerland, with an area of 83,871 sq km compared to Switzerland's 41,277 sq km.
Austria and Switzerland share German as an official language, but the variety of German spoken in each country differs. Austrian German is influenced by the Austro-Bavarian dialect, which is the main dialect outside of Vorarlberg, a state in western Austria. In Vorarlberg, the main dialect is Alemannic, which is also the dialect group spoken in northern Switzerland and parts of southern Alsace, France. Swiss German is a collection of Alemannic dialects no longer spoken in Germany or Austria, and it is very difficult for speakers of standard German to understand.
In Switzerland, multilingualism is the norm, with four recognised national languages: German, French, Italian, and Romansh. German is the most widely spoken language, with 62.3% of the population speaking Swiss German at home. French is the second most common language, spoken by 22.8% of the population, mostly in the western part of the country. Italian is the third most common language, spoken by around 8% of the population in the south of Switzerland along the border with Italy. The smallest national language, Romansh, gained official recognition in 1996 and is spoken by only 37,000 people in the southeastern canton of Grisons.
In Austria, German is the official language and the lingua franca, with approximately 97-98% of the population speaking it and over 93% calling it their mother tongue. However, there are several other minority languages spoken in the country, some of which have official status in certain regions. These include Hungarian, Slovenian, Burgenland-Croatian, Czech, Slovak, Romani, and sign language. Serbo-Croatian is the largest minority language in Austria, spoken by more than 4% of the population, followed by Turkish, spoken by 2.3%.
Lufthansa and Austrian Airlines: Partners in Flight?
You may want to see also

Retirement
Austria is approximately twice the size of Switzerland, with an area of 83,871 sq km compared to Switzerland's 41,277 sq km. Both countries offer a high quality of life and are popular destinations for retirement. Here is a guide to retiring in either country.
Austria does not have a specific retirement visa, but retired citizens from outside the country can obtain a residence title called a "settlement permit except gainful employment". This is a type of residence permit issued to financially independent individuals. The permit is usually issued for a period of 12 months and there is a limited number available each year.
To be eligible, you must meet the general requirements for a residence permit, demonstrate a regular monthly income (from a pension, income from assets, savings, etc.), have health insurance coverage, and have customary accommodation according to local standards.
Austria has a two-tier healthcare system, with free access for low-income citizens and small contributions from others. Foreign retirees can choose between public or private health insurance, or both.
Austria is known for its high quality of life, excellent healthcare, safety, and natural attractions. Popular places to retire include Vienna, Innsbruck, Salzburg, Feldkirch, and Bregenz.
Switzerland has a relatively open policy for retirees, but foreign nationals must meet certain criteria to receive residency. The criteria vary depending on nationality and the canton (region) in which you wish to live. Switzerland is divided into 26 cantons, each with autonomy over immigration in their area.
If you are over 55 and not working, you can apply for a residency permit by demonstrating financial self-sufficiency, having valid health and accident insurance, and showing a tie to Switzerland through family, property, business, or financial investment.
After residing in Switzerland for 10 continuous years, retirees can apply for a permanent residence permit, and after 12 years, they can apply for citizenship. Switzerland is considered one of the most expensive countries in the world, so a considerable amount of money is needed to retire there comfortably.
Switzerland has world-class healthcare, but it is compulsory and comes at a cost. All residents must have accident and health insurance. Switzerland is known for its high quality of life, safety, and scenic beauty. Popular places to retire include Vaud, Zurich, Zug, Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Geneva, Winterthur, Bern, Lugano, and Zurich.
Driving in Austria: US License Validity and Regulations
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, Austria is about twice the size of Switzerland. Austria is approximately 83,871 sq km, while Switzerland is approximately 41,277 sq km.
Switzerland has a population of about 8.5 million people, while Austria's population is around 404,390 more people, at about 8.9 million.
According to the Economist Intelligence Unit's Global Liveability Index, Vienna, the capital of Austria, is ranked as the "world's most liveable city". Zurich, Switzerland's largest city, is ranked third.
US News and World Report rated Switzerland as the second-best place in the world (and first in Europe) for a comfortable retirement. Austria is ranked 15th.
Switzerland's healthcare system is ranked higher according to The Euro Health Consumer Index (EHCI). Switzerland's system is more expensive, but it offers more efficient and comprehensive coverage.