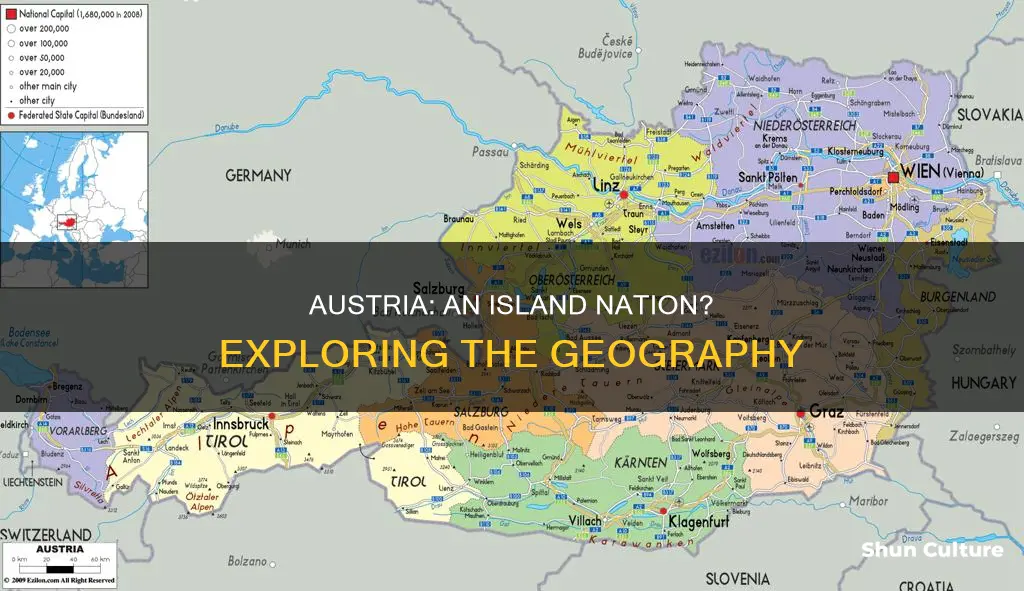
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, with a federation of nine states and a population of around 9 million. It is bordered by Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland and Liechtenstein. So, is Austria an island?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Is Austria an island? | No |
| Geography | Landlocked country in Central Europe |
| Area | 83,879 km² |
| Population | 8.942 million (as of Jan 1st, 2022) |
| Bordering Countries | Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein |
| Capital City | Vienna |
| Language | German (official), Croatian, Hungarian, Slovene (official regional languages) |
| Currency | Euro |
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Head of State | Alexander Van der Bellen |
| Chancellor | Karl Nehammer |
What You'll Learn

Austria's islands and lakes
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, and it is not an island. However, it does have several islands and lakes.
Austria's Islands
Austria has many islands, including the Danube Island, the largest in the country, which was built between 1972 and 1988 to protect Vienna from flooding. The island is 21 kilometres long and up to 250 metres wide, with an area of almost four square kilometres. Every June, the island hosts the Danube Island Festival, considered the largest open-air festival in Europe and the largest free music festival globally.
Other notable islands in Austria include the Gänsehäufel in the Old Danube in Vienna, which is home to a popular outdoor swimming pool; the Perner Island in Hallein, Salzburg, a natural island in the river Salzach; the island in Lake Faak in Carinthia, home to Austria's only island hotel; and the Mur Island in Graz, Styria, a floating platform in the shape of a shell designed by New York artist Vito Acconci.
Austria's Lakes
Austria is known for its beautiful lakes, which offer a range of activities such as swimming, boating, surfing, sailing, paddling, diving, sunbathing, and hiking. The country has approximately 400 bathing lakes and is considered one of the most water-rich countries in the world.
Some of the most popular lakes in Austria include:
- Lake Zell – known for its crystal-clear waters and majestic mountain backdrop
- Lake Achensee in Tirol – dubbed the "Tirol's ocean", this lake offers countless water sports activities
- Lake Attersee in Upper Austria – located in the heart of Austria's lake region, this lake has a laid-back vibe and stunning mountain views
- Lake Neusiedl in Burgenland – one of Austria's largest bodies of water in terms of surface area, this lake is known for its shallow depth and diverse bird species.
- Lake Mondsee in Upper Austria – a surfer's and sailor's paradise thanks to its shifting winds
- Lake Constance in Vorarlberg – shared by Austria, Germany, and Switzerland, this lake offers endless possibilities for water lovers and nature enthusiasts.
Graz, Austria: Time and the City
You may want to see also

Austria's land borders
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It shares land borders with eight countries: Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, and Italy.
Austria's border with Switzerland, a non-European Union member state, is 158 km (98 mi) long. Its border with the principality of Liechtenstein, also a non-EU member state, is 34 km (21 mi) long. Austria's border with Germany is 801 km (497 mi) long, while its border with the Czech Republic is 402 km (249 mi) long, and its border with Slovakia is 105 km (65 mi) long. Austria's eastern border with Hungary is 331 km (205 mi) long, and its southern border with Slovenia is 330 km (185 mi) long. Finally, Austria's border with Italy is 404 km (251 mi) long. In total, Austria's land borders extend over 2,534 km (1,574 mi).
The westernmost third of Austria is a narrow corridor between Germany and Italy, with a width of 32 to 60 km (20 to 37 mi). The rest of the country lies to the east and has a maximum north-south width of 280 km (170 mi). The country measures about 600 km (370 mi) in length, from Lake Constance on the Austrian-Swiss-German border in the west to the Neusiedler See on the Austrian-Hungarian border in the east.
Trapp Family's Austrian Home: What Remains Now?
You may want to see also

Austria's climate
The eastern part of Austria has a continental Pannonian climate, with hot summers and cold winters. The central Alpine region has a typical Alpine climate, with high precipitation, short summers, and long winters. The remaining western part of the country has a transitional central European climate, which is temperate and wet.
The lowland regions in the north and east of the country are more influenced by continental climate, with colder winters and hotter summers. The southeastern areas have longer, warmer summers, almost Mediterranean-like. In the west, the influence of the temperate Atlantic climate is stronger, with milder winters and warm summers. This part of the country also has high precipitation.
Austria's highest mountain, the Grossglockner, is 3,797 m (12,457 ft) above sea level. The altitude significantly impacts the weather, with temperatures decreasing by around 5°C for each additional 300 m of elevation. The coldest month is usually January, with snow cover lasting from late December through March in the valleys. Temperatures start to rise again in February, and by March, they can reach 12°C. Summers can be hot, with temperatures sometimes exceeding 30°C in July. Summer evenings are typically cool.
Precipitation is evenly distributed throughout the year, although the months of May, September, and the first half of October tend to be drier, while April and November are usually wetter. Altitude also determines precipitation patterns, with high-level areas in the Alps receiving over 2000 mm of rainfall annually, while some flatland regions only get 600 mm. From June to August, rain often comes in the form of heavy thunderstorms, and hail and snowfall can occur in the Alps even during summer.
The climate of Austria can be classified as Cfb in the Köppen-Geiger climate classification system: a warm, temperate, humid climate with the warmest month lower than 22°C and four or more months above 10°C. The mountainous regions have a Dfb climate classification: a humid snow climate with the warmest month between 10°C and 22°C, the coldest month below -3°C, and at least four months above 10°C.
Plug Types in Austria: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Austria's ecology and pollution
Austria is a landlocked country in Central Europe, with a diverse range of habitats and species. It is one of the most species-rich countries in Europe, with around 67,000 species, including about 45,000 animal species and 3,000 ferns and flowering plants. However, the diversity of species and habitats in Austria is under pressure from various factors, such as soil sealing, habitat destruction, climate change, and light emissions.
In terms of pollution, Austria has made significant progress in recent years. According to a preliminary assessment by the Umweltbundesamt (Environment Agency Austria), particulate matter concentrations (PM10) in 2020 dropped to their second-lowest level since records began in 2000, and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and ozone (O3) levels reached their lowest point since 1990. These improvements can be attributed to measures taken to combat the spread of COVID-19, particularly travel restrictions and an increase in remote work, which led to a significant decrease in transport volumes. Additionally, warm weather conditions in 2020 contributed to lower levels of NO2 and PM10 by reducing the demand for domestic heating.
Austria has also taken steps to address other environmental issues. For instance, the country generates more than half of its electricity from hydropower, and renewable energy sources account for 62.89% of its electricity supply. Austria's biodiversity efforts include the National Biodiversity Strategy, which outlines objectives and measures for preserving and promoting biodiversity across various policy areas. The country is also home to the Austrian Long-Term Ecosystem Research Network (LTER-Austria), which contributes to international long-term ecological research.
Overall, Austria ranks 8th in the Environmental Performance Index for 2024 and is known for its well-preserved natural landscapes and commitment to sustainability.
Exploring Munich to Vienna: How Far is the Journey?
You may want to see also

Austria's economy
Austria has a highly developed social market economy and is one of the fourteen richest countries in the world in terms of GDP per capita. The service sector generates the vast majority of Austria's GDP, with tourism being a particularly important contributor to the economy. Vienna has become a finance and consulting hub and is known as the gateway to the East.
Agriculture is a much smaller contributor to the economy, with Austrian farms being small and fragmented, and production relatively expensive. The agricultural sector has been undergoing substantial reform under the EU's Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), and now accounts for less than 3% of GDP.
Austrian Airlines: Safe or Not?
You may want to see also