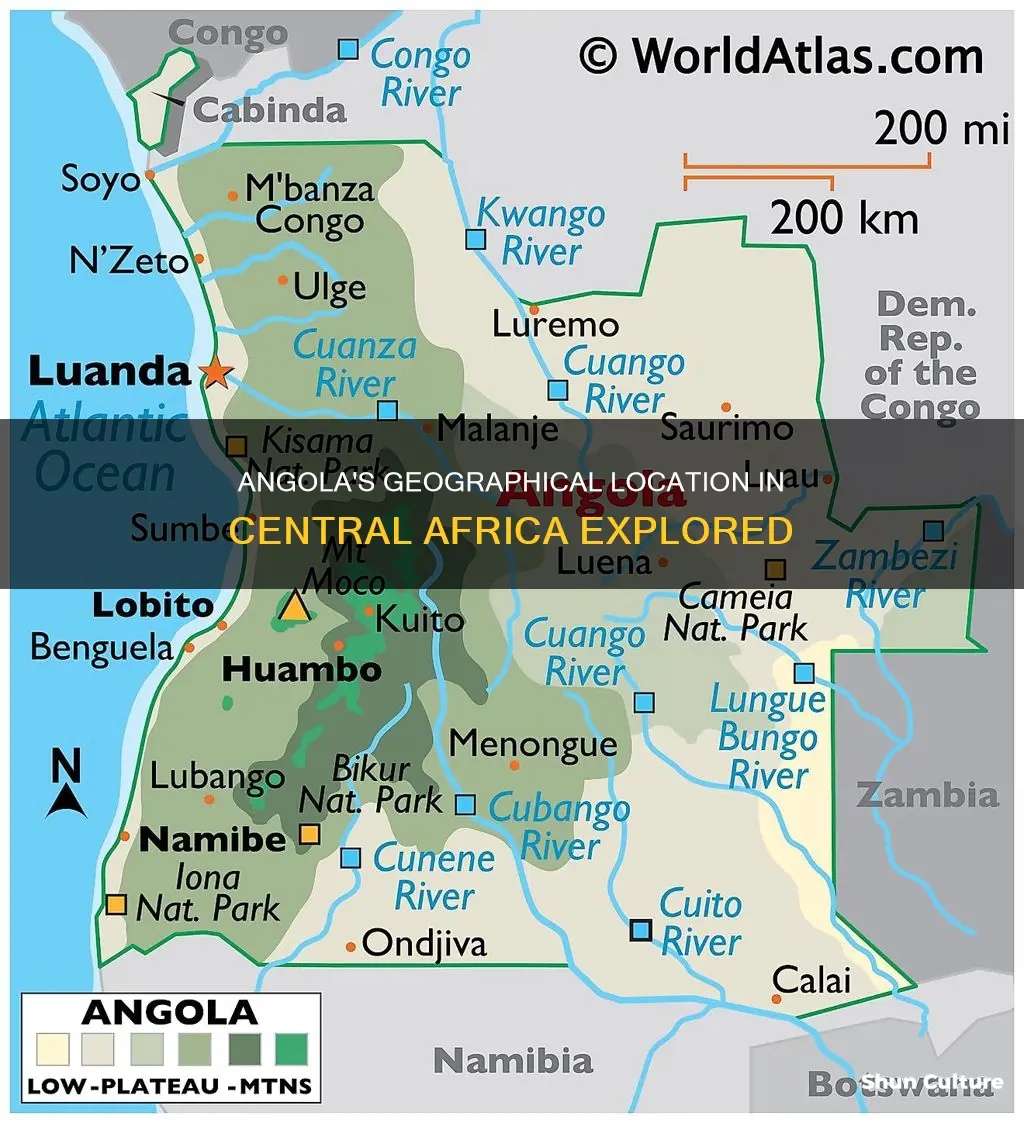
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is bordered by Namibia to the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Zambia to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Angola is a member of the African Union (AU), the Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPL), the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), and the United Nations (UN). Angola is also considered a part of Central Africa, a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa, for instance, includes Angola in its definition of Middle Africa.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Is Angola in Central Africa? | Yes |
| Continent | Africa |
| Subregion | Central Africa |
| UN geoscheme | Middle Africa |
| African Development Bank definition | No |
| Area | 1,246,700 km² |
| Population | 24.4 million (2014) |
| Capital | Luanda |
| Official language | Portuguese |
| Other languages | Kikongo, Kimbundu, Tchokwe, Umbundo and others |
| Ethnic groups | Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, mixed racial 2% |
| Religion | Christians 88%, indigenous beliefs |
What You'll Learn

Angola is bordered by Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Atlantic Ocean
The Republic of Angola has a diverse landscape, ranging from a semidesert Atlantic littoral bordering Namibia's "Skeleton Coast" to the densely populated towns and cities of the northern coast. The country's capital, Luanda, is a large port city on the northern coast that blends Portuguese-style colonial landmarks with traditional African housing styles and modern industrial complexes.
Angola's border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo is formed of two non-contiguous sections. The first runs along the border with Angola's province of Cabinda, a coastal exclave separated from the rest of the country by a strip of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This section of the border runs from the Atlantic Ocean to the tripoint with the Republic of Congo. The second section runs from the Atlantic to the tripoint with Zambia.
Angola's border with Namibia is located in the south of the country, while its border with Zambia is in the southeast.
Quality Inn: Angola Prison's Closest Comfort
You may want to see also

Angola's capital is Luanda
Luanda was founded in January 1576 by Portuguese explorer Paulo Dias de Novais, who named it "São Paulo da Assunção de Loanda". It served as the centre of the slave trade to Brazil before the institution was prohibited.
Luanda is the largest Portuguese-speaking capital city in the world and the most populous Lusophone city outside of Brazil. In 2020, its population reached more than 8.3 million inhabitants, about a third of Angola's population.
Luanda has been ranked as one of the most expensive cities in the world for expatriates. The city has a hot semi-desert climate and is divided into six urban districts: Ingombota, Quiluanje, Maianga, Rangel, Samba, and Sambizanga.
Angola's Safety: A Secure Place to Work?
You may want to see also

Angola's official language is Portuguese
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is officially known as the Republic of Angola and is the seventh-largest country in Africa. Portuguese is the official language of Angola, and it is the second-largest Lusophone (Portuguese-speaking) country in terms of both total area and population.
The history of Portuguese in Angola dates back to the 15th century when Portuguese explorers established relations with the Kingdom of Kongo, which encompassed parts of modern-day Angola, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo. The Portuguese established settlements, trading posts, and forts along the Angolan coast, with São Paulo de Loanda (Luanda) founded in 1575.
Today, Portuguese is the sole official language of Angola, while 46 other languages are spoken throughout the country, mostly Bantu languages. A 2014 census found that about 71% of the nearly 25.8 million inhabitants of Angola speak Portuguese at home. In urban areas, 85% of the population declared to speak Portuguese at home, compared to 49% in rural areas.
Angolan Portuguese (Portuguese: português de Angola) has distinct dialects and accents, with some variations approximating Standard European Portuguese pronunciation and others influenced by Brazilian Portuguese. The standard phonology in Angola is based on the European standard, as in the rest of Lusophone Africa. The variant of Portuguese used in Angola, known as Angolan Portuguese, is phonetically similar to the Mozambican variant, with some exceptions.
The influence of Bantu languages, such as Kimbundu, is evident in Angolan Portuguese. For example, the word "kota," meaning "old person" in Kimbundu, is used in Angolan Portuguese. Additionally, certain aspects of Brazilian culture, such as samba and capoeira, have left linguistic traces in Angolan Portuguese.
Angolan Portuguese has had a significant impact on the vernacular of younger generations in Portugal, with words like "bazar" ("to go away/home") and "bué" ("many" or "a lot") becoming part of the Portuguese lexicon.
Check Your Angola Visa Status: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Angola is a member of the African Union and the United Nations
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the African continent. It was founded on 26 May 2001 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and launched on 9 July 2002 in Durban, South Africa. The AU's secretariat, the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa. The AU has more than 1.3 billion people and an area of around 30 million km2. The primary working languages are Arabic, English, French, Portuguese, Spanish, and Swahili.
The objectives of the AU include achieving greater unity, cohesion, and solidarity among African countries; defending the sovereignty, territorial integrity, and independence of its member states; and promoting peace, security, and stability on the continent. The AU also aims to accelerate the political and socio-economic integration of the continent and promote democratic principles and institutions, popular participation, and good governance.
United Nations
Angola is also a member of the United Nations, having been elected for a second time as a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council in 2014. The United Nations Angola Verification Mission II (UNAVEM II) was established in May 1991 and lasted until February 1995. It was the second of four United Nations peacekeeping missions deployed to Angola during the Angolan Civil War, the longest war in modern African history. The mission consisted of military observers, civilian police, electoral observers, paramedics, and both local and international staff from 25 countries across five continents.
Louisiana's Prison Problem: A Deep Dive into the Numbers
You may want to see also

Angola's economy is largely driven by oil production
Angola is a country on the west-central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Lusophone (Portuguese-speaking) country in both total area and population and is the seventh-largest country in Africa. Angola's economy is largely driven by oil production.
Angola has vast mineral and petroleum reserves. Its economy is among the fastest-growing in the world, especially since the end of the civil war. Angola's high growth rate in recent years was driven by high international prices for its oil. Oil production and its supporting activities contribute about 85% of GDP and diamond exports contribute an additional 5%. Angola became a member of OPEC in late 2006.
Angola holds abundant untapped oil and gas resources estimated at 9 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves and 11 trillion cubic feet of proven natural gas reserves. The country currently produces approximately 1.16 million barrels of oil per day (bpd) but hit as high as 2 million barrels of oil per day (bpd) by 2010 during prosperous oil production years. The petroleum industry is key and accounts for almost 75% of the country's revenues. Angola is the second-largest oil-producing country in sub-Saharan Africa and an OPEC member with output of approximately 1.37 million barrels of oil per day (bpd) and an estimated 17,904.5 million cubic feet of natural gas production.
The oil-rich continental shelf off the Angolan coast is divided into 50 blocks but the number of blocks is expected to double with the auctioning of new blocks from 2019 to 2025. The first round of bids occurred in September 2019 and included 10 blocks: 9 from the Namibe basin and 1 from the Benguela basin. The blocks located in the Namibe basin hold post and pre-salt potentials, while block 10 in the Benguela basin is in shallow waters.
The refining of crude oil and distribution of its derivatives remain well below domestic demand. Angola is a leading producer in the continent – and has recently surpassed longtime leaders Nigeria and Algeria – yet is heavily dependent on imported refined petroleum. The country spends over $2 billion on petroleum imports annually. To address this imbalance, the Government of Angola is prioritizing refinery development, with upgrades to the country's only operating facility in Luanda as well as three new projects in the pipeline. The aim is to attain sufficiency in refined hydrocarbons through public-private partnerships (PPPs), with private companies financing investments in midstream projects.
The Government of Angola seeks to engage more U.S. firms to compete for multi-billion U.S. dollar projects including exploration and development of oil and gas fields, transportation and storage of petroleum products, refinery construction and associated infrastructure.
Transfer Money from Angola to India: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also