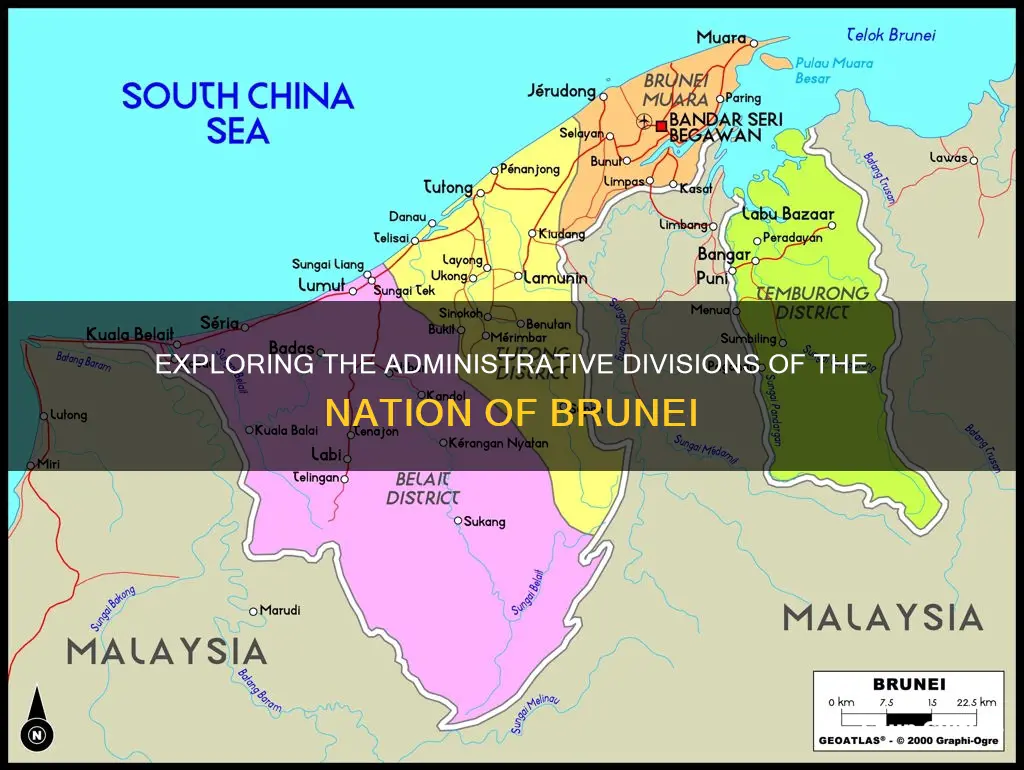
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia consisting of two unconnected parts with a total area of 5,765 square kilometres on the island of Borneo. It is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. Each district has a town as its administrative and main economic centre, except for Brunei-Muara, where the principal centre is Bandar Seri Begawan, the country's capital and largest city. So, to answer the question, there are four provinces in Brunei.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of Provinces | 4 |
| Names of Provinces | Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, Temburong |
| Capital | Bandar Seri Begawan |
| Population | 455,858 (2023) |
| Official Language | Malay |
| State Religion | Islam |
| Government | Constitutional absolute monarchy |
| Head of State and Government | Sultan and Prime Minister: Sir Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Muʿizzaddin Waddaulah |
| Area | 5,765 sq. km |
| GDP per Capita | 9th in the world |
What You'll Learn
- Brunei is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong and Temburong
- Brunei's capital, Bandar Seri Begawan, is in the Brunei-Muara district
- Brunei's official language is Malay, with English as a second language
- The country's official religion is Islam, with the Sultan as head of the Islamic faith
- Brunei is a member of the Commonwealth and ASEAN

Brunei is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong and Temburong
Brunei is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. Each district is further divided into several mukims, and each mukim consists of several villages (kampung or kampong). Bandar Seri Begawan, the capital of Brunei, is also the capital of the Brunei-Muara district. It is the country's principal centre, with a population of approximately 180,000 as of 2023. Brunei-Muara is the smallest district by area but has the largest population.
Belait is the birthplace and centre of the country's oil and gas industry. Seria and Kuala Belait are towns in the Belait district. Seria is the seat of the oil and gas industry, while Kuala Belait is known for its role in the discovery of oil in 1929.
Temburong is an exclave, separated from the other three districts by the Brunei Bay and the Malaysian state of Sarawak. Bangar is the focal town of Temburong, but it has not yet achieved municipal status.
Tutong is home to Tasek Merimbun, the country's largest natural lake. Pekan Tutong is the administrative centre of the Tutong district.
The Sultan of Brunei's Skiing Adventures
You may want to see also

Brunei's capital, Bandar Seri Begawan, is in the Brunei-Muara district
Brunei is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. The capital, Bandar Seri Begawan, is located in the Brunei-Muara district, which is the smallest yet most populous district. It is home to over 70% of the country's population.
Bandar Seri Begawan, often abbreviated to BSB, is the largest city in Brunei and is located on the northern bank of the Brunei River. The city has an estimated population of 100,700 as of 2007, with around 300,000 people living in the Brunei-Muara district. The district itself is located in the northeastern corner of the country and is considered the metropolitan area of Brunei City.
Bandar Seri Begawan is the country's largest urban centre and is home to Brunei's seat of government, as well as a commercial and cultural hub. The city has a rich history, dating back to the establishment of a Malay stilt settlement on the waters of the Brunei River. It became the capital of the Bruneian Sultanate in the 16th century and remained so during the 19th century when it became a British protectorate. The city was formerly known as Brunei Town until it was renamed in 1970 to honour Omar Ali Saifuddien III, the 28th Sultan of Brunei.
The Brunei-Muara district offers a range of attractions, including historical and religious sites, museums, and natural landmarks. Notable mosques in the area include the Ash-Shaliheen Mosque, Jame' Asr Hassanil Bolkiah Mosque, and Omar Ali Saifuddien Mosque, considered one of the most beautiful mosques in Southeast Asia. The Istana Nurul Iman, the royal palace and official residence of the Sultan of Brunei, is also located in the district.
The district is easily accessible by road, with a well-developed highway system connecting it to other parts of the country. Bandar Seri Begawan also has an international airport, making it a convenient gateway to Brunei for visitors from around the world.
Explore Brunei's Fashion: A Guide to Dressing in the Country
You may want to see also

Brunei's official language is Malay, with English as a second language
Brunei is divided into four districts: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. The country has a rich history and cultural heritage, with influences from various periods, including animist, Hindu, Islamic, and Western cultures.
The official language of Brunei is Malay, with English as a second language. Malay was designated as the official language in the 1959 Constitution of Brunei, and it is used in courts and as a medium of instruction in schools. The Latin alphabet (Rumi) and the Arabic alphabet (Jawi) are both used to write Malay, although the language transitioned to the Latin alphabet around 1941. Standard Malay is the variety that is widely accepted as the national language and is used for most official purposes. However, the local dialect, Brunei Malay or Melayu Brunei, is the most widely spoken language in the country, with about 266,000 speakers. It is quite distinct from Standard Malay, sharing only about 84% of cognate words. Brunei Malay is also used as a lingua franca in some parts of East Malaysia.
English is widely used in business and official dealings in Brunei, and it is spoken by a majority of the population. It is the primary language of instruction in schools, with the bilingual education system being introduced in 1985. Since 2008, with the implementation of the SPN21 education system, maths and science have been taught in English from the start of primary school. Additionally, all official documents are reproduced in English, and the Borneo Bulletin, an English-language daily newspaper, circulates in the country. The language of the courts is mainly English, although code-switching between English and Malay is a common occurrence.
The promotion of both English and Malay as important languages in Brunei has had an impact on minority languages in the country, such as Tutong and Dusun, which are now less commonly spoken.
Exploring Brunei: A Guide to the Must-Do Activities
You may want to see also

The country's official religion is Islam, with the Sultan as head of the Islamic faith
Brunei is an Islamic country, with the official state religion being Islam. The country is ruled by Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah, who is also the head of the Islamic faith in the country. The Sultan is the Supreme Executive Authority and holds several ministerial positions, including Prime Minister, Defence Minister, Finance Minister, and Foreign Affairs Minister.
The Sultan's role as the head of the Islamic faith in Brunei is significant, as it gives him religious authority in addition to his political power. This combination of religious and political leadership is unique to Brunei and reflects the country's history and culture. The Sultan's authority is further strengthened by the absence of elections and the tight control of the media, with Brunei ranking low on the annual press freedom index.
The Sultan has introduced Sharia law in Brunei, which has been controversial and attracted international criticism due to its harsh punishments. However, the Sultan has also been credited with providing a welfare state for his citizens, with significant subsidies in areas such as housing, healthcare, and education.
The Sultan's role as the head of the Islamic faith is not just symbolic but is actively practised and promoted. For example, during a rare public address to the nation, the Sultan emphasised his desire to see "Islamic teachings in this country grow stronger and more visible". This statement highlights his commitment to ensuring that Islam plays a prominent role in the country's present and future.
The Sultan's leadership, both religious and political, has had a significant impact on the country's laws, culture, and international relations. Brunei's legal system is based on English common law but is influenced by Islamic jurisprudence, including Sharia law. The country's national tradition, the Malay Islamic Monarchy (MIB), also reflects the Sultan's role, encompassing Malay culture, the Islamic religion, and the political framework under the monarchy.
The Sultan's commitment to Islam is evident in his personal life as well. For example, the Sultan has visited Islamic sites during his travels and has made the Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca. Additionally, the Sultan has been known to incorporate Islamic principles into his governance, such as promoting modesty and prohibiting the sale and public consumption of alcohol in the country.
The Sultan's role as the head of the Islamic faith extends beyond Brunei's borders, as the country is a member of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and maintains relations with other Islamic countries. The Sultan has also been known to use his religious authority to further his diplomatic goals, such as when he hosted an Islamic summit in 2000 to promote regional stability and cooperation.
In conclusion, the Sultan's role as the head of the Islamic faith in Brunei is integral to understanding the country's political, social, and religious landscape. His leadership has shaped the country's laws, culture, and international relations, and his commitment to Islam is evident in both his personal life and his governance of the nation.
Coronavirus in Brunei: What's the Situation?
You may want to see also

Brunei is a member of the Commonwealth and ASEAN
Brunei, officially known as Brunei Darussalam, is a small equatorial country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. It is bordered by the South China Sea to the north and by the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the east, west, and south, which divides the country into two segments.
Brunei is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). It became a member of the Commonwealth immediately upon gaining independence from British rule on 1 January 1984. Brunei joined ASEAN on 7 January 1984, just one week after becoming fully independent, and gives its ASEAN membership the highest priority in its foreign relations.
As a member of the Commonwealth, Brunei has benefited from various initiatives and programmes offered by the Commonwealth Secretariat. The Secretariat has provided information and training to Bruneian youth leaders on how to combat violent extremism, using dialogue and social media to promote peace and foster unity among communities. The Secretariat has also provided training to senior officials on policies that support young people in starting and managing businesses. Additionally, Brunei has received guidelines, tools, model laws, and regulations from the Secretariat to strengthen its legislation and methods for tackling corruption and controlling the illegal trade of weapons. The Secretariat has further assisted Brunei in improving its skills to negotiate multilateral and regional trade agreements.
Brunei's membership in ASEAN has facilitated close relations with other member states in the region, particularly the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia. As one of its first initiatives toward improved regional relations, Brunei hosted the ASEAN summit in 2013, during its tenure as the chair of ASEAN for that year.
Both the Commonwealth and ASEAN have played significant roles in shaping Brunei's international relations and enhancing its cooperation with other nations.
Celebrating Chinese New Year: Brunei's Cultural Diversity
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are four districts in Brunei: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong.
The four districts of Brunei are: Brunei-Muara, Belait, Tutong, and Temburong. Brunei-Muara is the smallest district by area but has the largest population.
Belait is the largest district in Brunei by area.
Brunei-Muara is the smallest district in Brunei by area.







