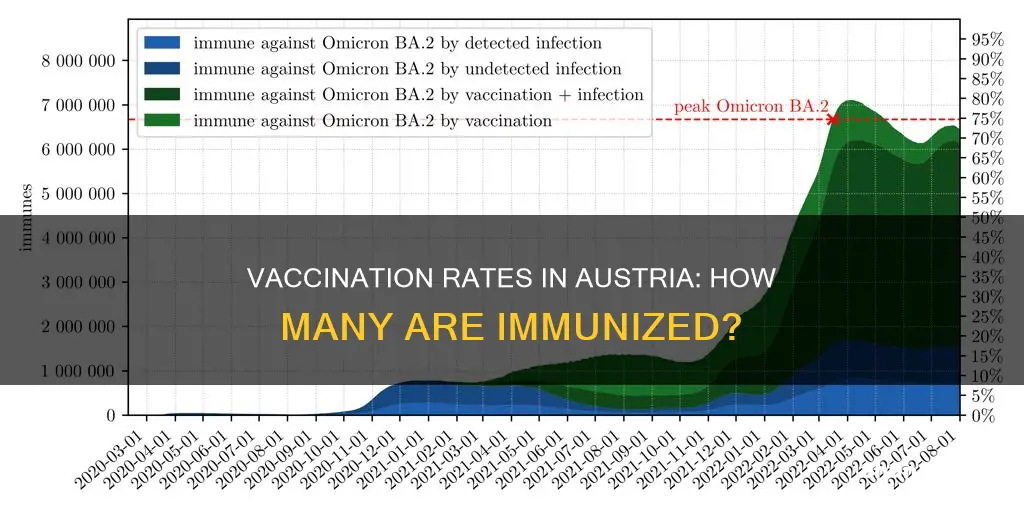
Austria has had a mass vaccination programme in place since the 1980s, with vaccination coverage of over 80%. However, measles cases are on the rise in Austria, with 542 cases reported between 1 February 2024 and 31 January 2025. The vast majority of infected people (86%) were unvaccinated. Austria has a free child vaccination programme, which provides free vaccinations for children and young people up to their 15th birthday.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Vaccination coverage | Over 80% |
What You'll Learn

Measles cases in Austria are rising
Austria has had a mass vaccination programme since the 1980s, and its vaccination coverage is over 80 per cent. The Austrian child vaccination programme provides free-of-charge vaccinations for children and young people up to their 15th birthday. The free-of-charge vaccination programme guarantees free-of-charge vaccination against measles, mumps and rubella for all age groups.
Despite this, measles cases are rising in Austria. This is part of a wider trend across Europe, with a steep rise in cases reported during 2024. After a period of unusually low measles activity during the COVID-19 pandemic, an uptick was initially noted in 2023, with 3,973 reported cases in the EU/EEA.
Health authorities are warning that measles cases are expected to grow in the coming months. Adults and parents are encouraged to check their vaccination history and, if in doubt, consult a healthcare professional.
The Coal Age: Austria's Historical Fuel Source
You may want to see also

Austria's vaccination coverage is over 80%
Austria's high vaccination coverage can be attributed to its comprehensive child vaccination programme, which provides free-of-charge vaccinations for children and young people up to their 15th birthday. The costs of this programme are covered by the Federal Ministry of Social Affairs, Health, Care and Consumer Protection, the federal provinces, and the social insurance system. This ensures that all children have access to essential vaccinations, such as measles, mumps and rubella, regardless of their family's financial situation.
The country's commitment to vaccination is further demonstrated by its response to the COVID-19 pandemic. During the pandemic, there was an unusually low measles activity, with only 3,973 reported cases in the EU/EEA in 2024. However, this was followed by an uptick in cases in 2025, with Austria reporting 542 cases. Despite this increase, Austria's high vaccination coverage has likely contributed to a lower overall incidence of measles compared to other countries.
While Austria's vaccination coverage is impressive, there is still room for improvement. The country's last study on vaccination coverage was conducted in 2018, and there may be pockets of the population that are underserved or hesitant about vaccinations. Additionally, as new variants of diseases emerge and vaccination technology advances, it is important to continuously promote vaccination and ensure that all Austrians have access to the latest vaccines.
Winter Tyre Rules in Austria: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Austria offers free child vaccinations
Austria has a high vaccination coverage, with over 80% of the population vaccinated. Mass vaccination was initiated in the country in the 1980s, and since then, the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases has been much lower than in other European countries.
Despite this, Austria is not immune to vaccine-preventable diseases. Between February 2024 and January 2025, 542 cases of measles were reported in the country, with the vast majority of infected people being unvaccinated.
To address this issue, Austria offers free child vaccinations to ensure that all children and young people up to their 15th birthday are protected against vaccine-preventable diseases. The costs of these vaccinations are covered by the Federal Ministry of Social Affairs, Health, Care and Consumer Protection, the federal provinces, and the social insurance system. This programme guarantees free measles, mumps, and rubella vaccinations for all age groups.
By offering free child vaccinations, Austria is taking proactive measures to protect its young population from vaccine-preventable diseases. It is important for parents to ensure that their children are up to date with their vaccinations and to consult a healthcare professional if they have any concerns.
Student Life in Austria: Affordable or a Splurge?
You may want to see also

Measles cases in Austria are mostly in unvaccinated people
Austria has a mass vaccination programme, which was initiated in the 1980s. Their vaccination coverage is now over 80%, and the incidence of measles is much lower than in Switzerland. The Austrian child vaccination programme provides free-of-charge vaccinations for children and young people up to their 15th birthday. The free-of-charge vaccination programme guarantees free-of-charge vaccination against measles, mumps and rubella for all age groups.
Despite this, measles cases are on the rise again in Europe, and health authorities are warning that cases are expected to grow in the coming months. The ECDC has said that the ongoing transmission indicates gaps in vaccination coverage against this preventable illness among children, adolescents and adults. Adults and parents are encouraged to check their vaccination history and, if in doubt, consult a healthcare professional.
Exploring Austria: Transportation and Travel Options
You may want to see also

Measles cases in Austria are highest in children under 4
Austria has had a mass vaccination programme since the 1980s, and its vaccination coverage is over 80%. The Austrian child vaccination programme provides free-of-charge vaccinations for children and young people up to their 15th birthday. The free-of-charge vaccination programme guarantees free-of-charge vaccination against measles, mumps and rubella for all age groups.
Despite this, measles cases in Austria are highest in children under 4. This indicates gaps in vaccination coverage against this preventable illness among children, adolescents and adults alike. It is important for adults and parents to check their vaccination history and, if in doubt, consult a healthcare professional.
Hitler's Austrian Roots: How Did He Rule Germany?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Over 80%.
The 1980s.
Austria's vaccination coverage is higher than Switzerland's.
542 cases were reported between 1 February 2024 and 31 January 2025.