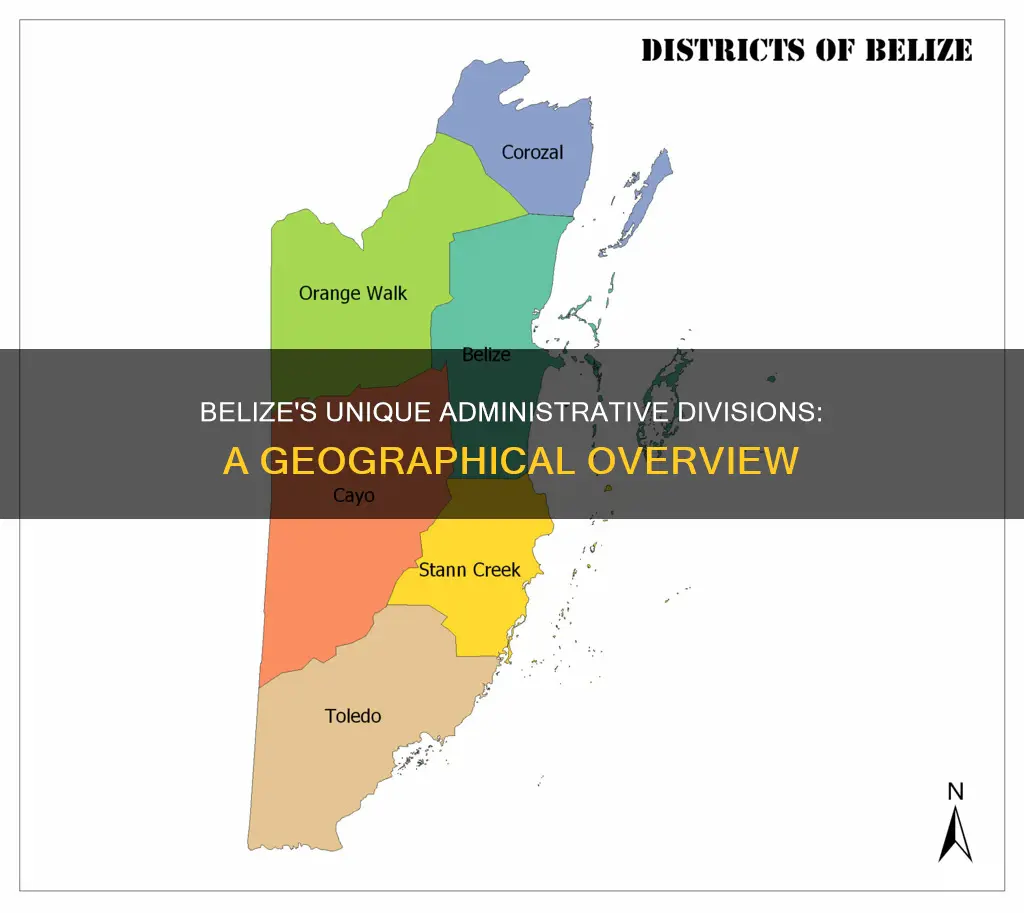
Belize is divided into six districts: Corozal, Orange Walk, Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo. The country is further divided into 31 constituencies.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Country | Belize |
| Continent | Central America |
| Population | 397,483 (2022) |
| Area | 22,970 sq km (8,867 sq mi) |
| Capital | Belmopan |
| Largest City | Belize City |
| Official Language | English |
| Other Languages | Belizean Creole, Spanish, Mayan languages, German dialects, and Garifuna |
| Religion | Roman Catholic (40.1%) |
| Government | Parliamentary Democracy |
| Monetary Unit | Belize Dollar (BZD) |
| Exchange Rate | $2 BZD to $1 USD |
| Districts | Corozal, Orange Walk, Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo |
What You'll Learn
- Belize is divided into six districts: Corozal, Orange Walk, Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo
- Belize is split into two physiographic regions: the Maya Mountains and the northern lowlands
- Belize's population is made up of several ethnic groups, including Maya, Mestizo, Creole, Garinagu, Mennonites, East Indians, and Chinese
- Belize is divided into ten constituencies, including Freetown, Caribbean Shores, Pickstock, and Lake Independence
- Belize City is split into two areas: Northside and Southside

Belize is divided into six districts: Corozal, Orange Walk, Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo
Corozal
Corozal is the northernmost district of Belize, bordering Mexico. It is primarily populated by Mestizo—a cultural blend of Spanish and Maya. Corozal is popular with US expats, who enjoy a laid-back lifestyle in small coastal villages and towns, with easy access to nearby Chetumal in Mexico.
Orange Walk
Referred to as "Sugah City", Orange Walk is home to Belize's sugarcane industry. Much like Corozal, Orange Walk is home to many Mestizo—descendants of Spanish and Yucatec Maya who fled Mexico during the Caste War. The main tourist attraction is Lamanai, one of the top ancient Maya sites in Belize.
Belize
The Belize district is located in Eastern Belize and has Belize City and the popular northern islands of Caye Caulker and Ambergris Caye. Belize City is the largest city in Belize and was once the capital of the country. It is not a popular tourist destination, but it serves as the main gateway to Belize as it is home to the country's only international airport.
Cayo
Cayo is the largest district in Belize and borders Guatemala. It serves as the main destination for ecotourism in Belize, with San Ignacio being the most popular stop for travellers. San Ignacio provides easy access to many of Belize's top jungle attractions, while also having a restaurant and nightlife scene that is not seen elsewhere on the mainland.
Stann Creek
Stann Creek, in Southern Belize, offers a blend of culture and adventure. The villages of Hopkins and Placencia are the most popular destinations. Hopkins is a seaside village that is a hotspot for outdoor adventures and learning about the Garifuna culture of Belize. Placencia is a charming seaside village located on an 18-mile peninsula. With a beautiful coast and some of the best beachfront resorts, the peninsula primarily attracts beach lovers.
Toledo
Toledo is the southernmost district of Belize and is not heavily visited due to its rural and remote location. Its main settlement is Punta Gorda, which has a large East Indian population. Toledo serves as a base for adventure and cultural activities such as off-shore fishing, river trips, caving, bird watching, and visiting ancient Maya sites and present-day Maya villages.
Positive in Paradise: Navigating COVID-19 Protocols in Belize
You may want to see also

Belize is split into two physiographic regions: the Maya Mountains and the northern lowlands
The northern lowlands, along with the southern coastal plain, are drained by eighteen major rivers and many perennial streams. The coastline is flat and swampy, with many lagoons, especially in the northern and central parts of the country. Westward from the northern coastal areas, the terrain changes from mangrove swamp to tropical pine savanna and hardwood forest. The country's largest lake is the approximately 13.5 km2 (5.2 sq mi) New River Lagoon.
Best Lodging Options in Hopkins, Belize
You may want to see also

Belize's population is made up of several ethnic groups, including Maya, Mestizo, Creole, Garinagu, Mennonites, East Indians, and Chinese
Belize is the most sparsely populated nation in Central America, with just under 441,500 people as of 2022. The population is made up of several ethnic groups, including Maya, Mestizo, Creole, Garinagu, Mennonites, East Indians, and Chinese.
Belize is ethnically diverse, with most Belizeans being of multiracial descent. About 52.9% of the population is of mixed Indigenous (mainly Maya) and European ancestry (Mestizo). The Maya people, who constitute about 10.6% of the population, consist of three main language groups: Yucatec, Q'eqchi', and Mopan. The Yucatec Maya fled to Belize in the late 1840s to escape the Caste War in Yucatán, Mexico, and now primarily work in the sugar cane industry. The Q'eqchi' Maya migrated to Belize in the 1870s and 1880s due to the seizure of their communal land in Guatemala, and they mainly work in agriculture and tourism. The Mopan Maya originated in Belize but were driven out to Guatemala by the British in the 18th century; they returned in 1886 and now reside in the Cayo and Toledo districts.
Approximately 24.9% of Belize's population is Creole, also known as Kriols. They are primarily the mixed-race descendants of enslaved West and Central Africans and the European colonisers who trafficked them. Over time, the Creole community has intermarried with other ethnic groups, including Miskito from Nicaragua, Jamaicans, other Caribbean peoples, Mestizos, Europeans, Garinagu, Maya, Chinese, and East Indians. The Creole language, or Kriol, is an English-based creole that serves as the first language for about 37% of Belizeans and is understood by all Kriol speakers.
The Garinagu, or Garifuna, make up about 6.1% of the population. They are the descendants of an Afro-indigenous population from the Caribbean island of St. Vincent, who were exiled to the Honduran coast in the 18th century and later migrated to Belize. The Garinagu have traditionally faced discrimination and stereotyping due to their cultural differences and rural lifestyle. However, in recent years, they have become more closely allied with the dominant Creole population because of their shared African ancestry.
The remaining population of Belize includes smaller groups such as Europeans (mostly descendants of Spanish and British colonial settlers), East Indians (brought as indentured labourers), Chinese, Middle Easterners, and North Americans. Additionally, there is a significant population of Mennonites, who began settling in Belize in 1958, primarily in isolated rural areas.
The Coastal Commute: Cancun to Corozal, Belize - A Journey of Discovery
You may want to see also

Belize is divided into ten constituencies, including Freetown, Caribbean Shores, Pickstock, and Lake Independence
Belize is divided into six districts: Corozal, Orange Walk, Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo. Each district is further divided into constituencies, with 31 in total. Belize City, the country's largest city and former capital, is divided into ten constituencies: Freetown, Caribbean Shores, Pickstock, Lake Independence, Collet, Port Loyola, Mesopotamia, Queen's Square, Albert, and Fort George.
Freetown is the westernmost constituency in Belize City, home to the suburbs of Belama, Coral Grove, Buttonwood Bay, and Vista Del Mar. The constituency includes areas up to the former Belize Technical College.
Caribbean Shores includes Kings' Park, West Landivar, and residential University Heights. The University of Belize has two of its three city campuses in this constituency.
Pickstock is situated on the banks of the Haulover Creek, extending to Barrack Road.
Lake Independence, Collet, and Port Loyola are home to some of the city's poorest residents.
On the east side of Central American Boulevard are Mesopotamia, Queen's Square, and Albert. Albert contains the downtown streets of Albert and Regent.
Fort George is perhaps the most colonial area in Belize City, containing Memorial Park, the Baron Bliss Grave, Baron Bliss Lighthouse, and the Museum of Belize.
Hurricane's Path: Will Belize Take a Direct Hit?
You may want to see also

Belize City is split into two areas: Northside and Southside
Belize City is divided into two areas: Northside and Southside. The city is split by the Haulover Creek, which is a distributary of the Belize River. The Belize River empties into the Caribbean Sea, eight kilometres from Belize City.
The Northside of Belize City is considered the safest and most prosperous area of the city centre. Good hotels, casinos, and the Museum of Belize are located in this zone, as are the cruise ship and marine terminals. The Northside is also home to the Fort George neighbourhood, which is perhaps the most colonial area in the city. It contains Memorial Park, the Baron Bliss Grave and Baron Bliss Lighthouse, and the Museum of Belize.
The Southside of Belize City has a couple of tourist attractions, namely the historic St. John's Cathedral and the House of Culture. Lake Independence, Collet, and Port Loyola are home to some of the city's poorest residents.
Four bridges connect the Northside and Southside of Belize City: the new Chetumal Street Bridge (unofficially called the Dean Barrow Bridge), the BelCan (Belize-Canada), BelChina (Belize-China), and the original Belize City Swing Bridge.
Belize's Pristine Snorkeling Paradise: Discovering the Clearest Waters at Glover's Reef
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Belize is divided into six districts: Corozal, Orange Walk, Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo.
Belize is divided into two main physiographic regions. The first is distinguished by the Maya Mountains and the associated basins and plateaus that dominate the southern half of the country. The second region comprises the northern lowlands, along with the southern coastal plain.
Belize is made up of various ethnic groups that co-exist together, including people of Maya, Mestizo, Garinagu, Creole, Mennonite, East Indian, and Chinese descent.
While English is the national language of Belize, other commonly spoken languages include Spanish, Belizean Creole, Maya, and Garifuna.







